Exam 2 - Mansfield University of Pennsylvania
advertisement

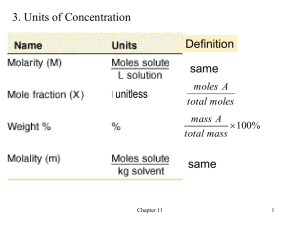
Chemistry 1111 Exam 2 Name _______________________________________ Aqueous solution Avogadro’s number Boyle’s law Charles’ law Chemical equation Coefficients Concentrated solution Concentration Dalton’s law Dilute solution Henry’s law Mass number Molar mass Molarity Mole Mole fraction Molecular mass Osmosis Partial pressure Precipitate Saturated solution Solubility Solute Solution Solvent Standard molar volume Stanislov’s law STP Supersaturated solution Universal (Ideal) gas law For each definition, select the BEST term from the above list. No term is used more than once (2 pts each) 1. ______________________________________ Moles of solute per liter of solution. 2. ______________________________________ Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3 + … 3. ______________________________________ The pressure contributed to the total pressure by an individual gas in a mixture of gases. 4. ______________________________________ 273 K and 1atm. 5. ______________________________________ The substance that dissolves when making a uniform mixture. 6. ______________________________________ A uniform mixture of particles. 7. ______________________________________ PV = nRT 8. ______________________________________ A solid that forms when two solutions are mixed together. 9. ______________________________________ In a uniform mixture, the substance that does the dissolving. 10. ______________________________________ Expresses the maximum grams of solute in 100 grams of solvent. 11. ______________________________________ A uniform mixture where the solute to solvent ratio is small. 12. ______________________________________ The ratio of the quantity of solute to some given unit of the solution. When applicable, show ALL work for the following problems. Answers arrived at with NO work shown will receive no credit. 13. A gas with a volume of 5.28 L, a pressure of 745 mm Hg and a temperature of 25.0 ºC is expanded to a volume of 7.75 L with a pressure of 645 mm Hg. What is the final temperature of the gas? 14. A solution is made by placing 49.3 g of KBr in water to a final volume of 215 mL of water. a. Express this volume in liters. b. KBr has a molecular weight of 119 g/mol. How many moles is 49.3 g KBr? c. Calculate the molarity of the solution. d. How many moles of KBr are present in 50.0 mL of this solution? e. 15.0 mL of this solution is taken and water is added to a final volume of 75.0 mL. Calculate the molarity of this diluted solution. 15. The following questions deal with the following reaction: 2NaBH4(s) + 2HCl(aq) B2H6(g) + 2NaCl(aq) + H2(g) a. We are reacting 0.0375 moles of NaBH4. How many moles of H2 would this amount of NaBH4 produce? b. What volume of H2 gas is this at 20oC and .90 atm? c. What volume of B2H6 would this produce under the same conditions? d. The HCl solution used in this reaction is 0.137 M. How many milliliters of HCl are needed to react with the 0.0375 mole of NaBH4? 16. Predict the product(s) for each of the following reactions. For each reaction circle AB (for acid-base), OR (for oxidation reduction), P (for precipitation), or NR (for no reaction). For precipitation reactions underline the insoluble product, for oxidation-reduction circle what is being oxidized. You do not have to balance the equations to receive credit. a. HNO3(aq) + KOH(aq) AB OR P NR P NR P NR b. MgCO3(aq) + HCl(aq) AB OR c. K(s) + HBr(aq) AB OR d. BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) AB OR P NR P NR P NR e. Ca(s) + NiCl2(aq) AB f. OR KF(s) + Cl2(g) AB OR 17. 42.5 L of O2 is trapped at -15oC and 720 Torr. What is the pressure, in Torr, if the volume is compressed to 38.5L and the temperature is 80oC? 18. For a gas, what happens to: i. the pressure, if temperature is decreased? ii. the volume, if pressure is increased? iii. the volume, if moles of gas are added? d) What is STP in gas laws? (Name it and define the conditions). The partial pressure of O2 required for some species to live is 130 Torr. What is the partial pressure of O2 in the a (fraction of O2 in dry air is 0.20) jungle atmosphere (PH20 = 95 Torr), pressure is 720 Torr.