Unit 1 Notes
advertisement

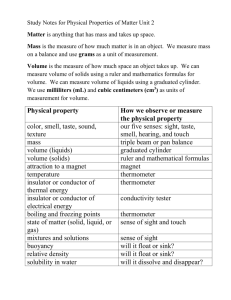
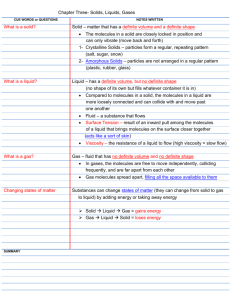
Unit One – What is Chemistry 16.1- Chemistry: The Central Science Write the definition of chemistry as given in class: 16.2-The Submicroscopic World Atom – the smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element Molecules – Examples: Macroscopic – can be seen without ______________________-. It can be measured and handled Microscope – need an instrument to been seen States of matter – solids, liquids, gases and plasma 1. Solids a. have a definite _______________ b. have a definite _______________ c. the particles are packed _______________ together d. types of solids 1) _______________ solids - have a regular, repeating _______________ of particles - examples: 2) _______________ solids - particles do not _______________ in a pattern - these solids do not retain their solid shape ____________ - examples: 2. Liquids a. has no definite _______________ b. has a definite _______________ c. have _______________: the resistance of a liquid to flow - higher viscosity- _______________ flow, lower viscosity – _______________ flow 3. Gas a. has no definite _______________ b. has no definite _______________ c. the particles tend to spread out more than in __________, _______________ d. _______________ Law – if the _______________ of a gas is decreased, the amount of _______________ the gas exerts increases (and vice versa) e. _______________ Law – as the _______________ of a gas increases, the volume of the gas increases (and vice versa) 4. Plasma - rare on earth, but very common in _______________ - very high _______________ phase of matter - present in ______________________________ when they are on and _______________ Draw the particles in a solid, liquid, and gas in the boxes below. Make sure to label which box corresponds to which phase. *****In your own words paraphrase what Ms. D said about the difference the molecular view in solids liquids and gases. Pay particular attention to solids and liquids. 16.3 – Change of Phase _______________ – change from solid to liquid _______________ _______________ – temperature & pressure at which a solid changes to a liquid - most substances have a characteristic melting point - example: _______________ – removing heat energy to change a liquid into a solid _______________ _______________ – temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid _______________ – the change of a substance from a liquid to a gas _______________ – a type of vaporization in which the particles of the liquid change into a gas at the surface of the liquid _______________ – a type of vaporization in which the particles of the liquid change into a gas inside the liquid and then travel to the liquid’s surface and into the air _______________ _______________ – the temp. & pressure at which a liquid boils - most substances have a characteristic boiling point - - example: water -> water vapor at if air pressure is _______________, boiling point is reduced (boiling point of water lowers below 100 degrees C) - if air pressure _______________, boiling point is increased (boiling point of water raises above 100 degrees C) _______________ – gas changes to a liquid as it loses heat energy - example: dew _______________ – surface particles of a solid change into a gas without passing through a liquid phase example: carbon dioxide, drying wet clothes outside in winter Phase Changes – Matter changes its state due to changes in its _______________ (heat) content - All phase changes are __________________ changes (the material is not changed) Energy and Phase Change -Energy is measured in ____________________ -Heat of Fusion: -each substance has their own particular heat of fusion value -water = _____________________ -Heat of vaporization: the amount of energy required to change any substance from_________________ to ________________ (and vice versa) - each substance has their own particular heat of fusion value - water = _____________________ Why is heat of vaporization higher than heat of fusion? Can you add heat to ice without melting it? temperature GASES LIQUIDS SOLIDS time 16.4 Physical and Chemical Properties Physical property – Two types a. Extensive – depends upon the amount of ___________________________ present Ex. b. Intensive – does not depend on the amount of matter present. Ex. Physical change – a change that affects any _____________________properties Chemical property – Chemical properties characterize the ability of a stance to react with other substances or to transform from one substance to another Example: Chemical change – a change that produces one or more new_______________________ ***During a chemical change, there is a change in the way the atoms are chemically bonded to one another. Chemical Bond – Chemical change means the same thing as ___________________________________ Chemical reaction (rxn) – new materials are formed by a change in the way atoms are bonded together. 16.5 – Determining Physical and Chemical Changes **After a physical change, the molecules are the __________________ as the ones you started with. After a chemical change, the original molecules have been ______________________ and new ones are in their place. Indications of a chemical change 1. (HCl and Mg) 2. (AgNO3 and HCl) 3. (HCl and Mg, NH4NO3) 4. (Mg and O2) 5. (acid and base)