Model Building - Digestive System Organs
advertisement

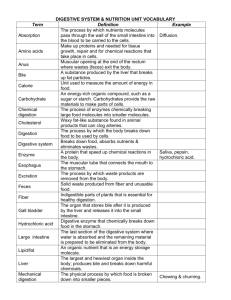
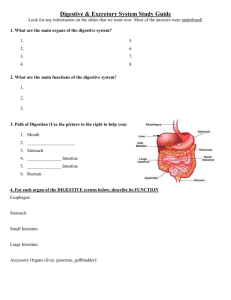
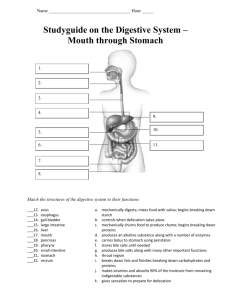
The Digestive System 1. Our only digestive decisions are: a.Whether to eat b.What to eat 2. What are the 2 main groups of organs and their functions? Use the diagram & text & list the organs involved. a. b. 3. Turn to pages 445-446 - Describe/define the 6 essential activities. a. The process of taking food into the digestive tract is known as ____________________________________. b. __________________________________ constitutes the processes that move food through the alimentary canal. The major means of propelling food through the digestive tract is known as ______________________________________. This process involves alternate waves of __________________________________ & ____________________________________ of muscles in the organ walls. i. Also see fig 14.12: In the process of segmentation, _______________________________segments of the intestine alternately contract and relax. This results in the _____________________________ of food since the food is moved forward and then backward. ii. Explain how peristalsis is different from segmentation: c. __________________________ digestion physically prepares food for chemical digestion. Examples of these physical processes include: 1. 2. 3. d. Chemical digestion is a _______________(term that means breakdown) process in which large food molecules are broken down by enzymes in reactions called _____________________________________________. e. Absorption is the transport of digested end products from the lumen of the ____________________________________ to the ______________________. The major absorptive site is the _____________________________. f. Defecation: _______________________________________________________ Structures of the Digestive System I. Mouth A. Why is the epithelium on the gums, hard palate, and dorsal surface of tongue keratinized? B. Lips and cheeks 1. keep food between teeth when we chew 2. play a role in speech C. Palate 1. hard palate & soft palate 2. What happens during swallowing so that we do not aspirate food into the lungs? II. Tongue A. Functions 1. speech movements 2. mixes food with saliva 3. forms food bolus B. What are the functions of the intrinsic & extrinsic muscles of the tongue C. Lingual Frenulum 1. secures tongue to floor of mouth 2. limits _________________________ movements 3. tongue tied: _________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________ D. Papillae 1. filiform: ____________________________________________________________ 2. fungiform: __________________________________________________________ 3. circumvallate: _______________________________________________________ III. Salivary Glands A. 4 functions of saliva 1. 2. 3. 4. B. Salivary Glands 1. parotid – Mumps ___________________________________________ 2. submandibular 3. sublingual 4. Types of cells i. serous cells produce salivary ________________________ to breakdown starch ii. mucous cells produce mucus for ______________________________ iii. different glands produce different types of secretions based on function needed IV. Pharynx A. 2 muscular layers (circular & longitudinal) cause ________________ waves to move food B. Oropharynx and laryngopharynx are common passageways for _________________________________________________________________ C. Nasopharynx has no digestive role (unless you laugh so hard that you blow your soda through your nose!!!) V. Esophagus A. ________________ inches long B. epiglottis routes food into it C. goes through the diaphragm to join stomach at ___________________________ sphincter D. Hiatal hernia: E. GERD & Heartburn: F. Esophageal Ulcers: Quiz #1 – Includes diagram VI. Stomach A. Function: site of mechanical & chemical breakdown B. define chyme: ___________________________________________________________ C. What is the position of the stomach in a. short, obese people: b. tall, thin people: D. ~ 10 inches long on ____________________ side of abdomen E. can hold _______________________ L of food F. _____________________ – large longitudinal folds that help mix food in stomach H. __________________ sphincter: controls stomach emptying into small intestine I. What important substance is produced by the parietal cells of the stomach & what does it do? What blood disorder can absence of this substance lead to? J. Mucosal Barrier – important 3 factors 1. 2. 3. K. Gastric Ulcers a. Erosion of ___________________________ b. Causes: c. Danger: VII. Small Intestine: Body’s major digestive organ A. 6 meters long (~21 feet) but only ______ inch in diameter B. suspended by mesentery (connective tissue) in the abdominal cavity C. List & define the 3 sections of the small intestine a. b. c. D. Function : all nutrient absorption – huge surface area due to length and modifications E. List & define the 3 structural modifications in the SI that increase SA a. b. c. VIII. Liver A. many metabolic & regulatory functions B. digestive function: produce _____________ for export to duodenum. Bile is used to ____________ fats – distributes fat in solution to be accessible to digestive enzymes. C. _____ lobes - Largest gland ~3 lbs - Very vascular because it also ______________________________________________________ D. Major cell types 1. Hepatocytes: 4 major functions a. b. c. d. F. What is the function of Kupffer cells? G. Define & differentiate: 1. hepatitis 2. cirrhosis IX. Gallbladder A. 4 inches long B. thin walled, greenish sac C. store & concentrate bile D. Sphincter of __________________ regulates release of bile into small intestine X. Pancreas A. principal enzyme producing organ of digestive system B. What are the 2 types of cells in the pancreas & what do they produce 1. 2. C. bile and pancreatic juice enter SI together through Sphincter of Oddi XI. Large Intestine A. ~ 5 feet long B. What is the major function of the large intestine? C. List the subdivisions of the LI. D. Why is the appendix a trouble spot? E. What is the difference in the 2 anal sphincters? Quiz #2 – including diagrams Physiology of Digestion 1. What 3 sensors are involved in controlling the GI tract and what stimuli does each respond to?(list name of sensor and stimulus) a. b. c. 2. Salivary amylase is an ______________________ found in saliva that begins the chemical digestion of _____________________________. 3. What are 4 helpful substances found in saliva that help protect/heal? a. b. c d. 4. The average output of saliva per day is _________________. 5. Why does fear/excitement cause dry mouth? 6. Define halitosis. 7. What structures are involved in swallowing? a. b. c. d. e. 8. What is the seriousness of a cleft palate? 9. What 3 things does your body do to cause food to be routed into the digestive tract only? a. b. c. 10. How long does it take food and fluids to reach the stomach? 11. What is the only stomach function essential to life? (HINT: we discussed it already) 12. What can be done in reference to the above function if a gastrectomy has been performed? 13. Give a detailed description of plasticity & its importance 14. It takes the stomach approx. ____________ to empty completely after a meal. 15. The rate of gastric emptying depends on: a. b. 16. What is the difference in digestion rates & why between a high carbohydrate meal & a high fat meal? 17. Vomiting: 18. The enzyme only produced by infants is ______________, it helps by _______________________________________ 19. The 2 commonly ingested substances that can be absorbed through the stomach mucosa are ____________________ and _____________________. 20. The nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine during their ___________ hour journey. 21. What is the role of bile salts? 22. What gives feces their brown color? 23. What causes lactose intolerance and what are some of the signs? 24. What can cause many food allergies in infants? 25. What is the purpose of fiber? 26. What are the 5 main byproducts of the bacteria in the LI? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 27. What are feces and what do they contain?