Notes- Periodic Table 2011
advertisement
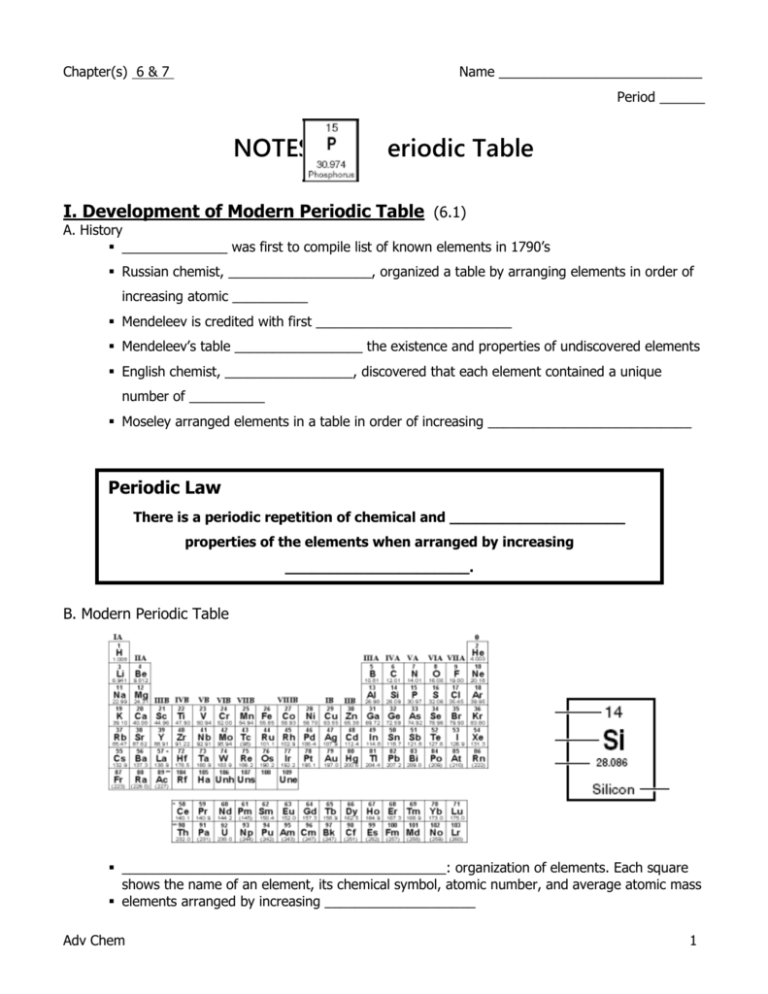
Chapter(s) 6 & 7 Name ___________________________ Period ______ NOTES: eriodic Table I. Development of Modern Periodic Table (6.1) A. History ______________ was first to compile list of known elements in 1790’s Russian chemist, ___________________, organized a table by arranging elements in order of increasing atomic __________ Mendeleev is credited with first __________________________ Mendeleev’s table _________________ the existence and properties of undiscovered elements English chemist, _________________, discovered that each element contained a unique number of __________ Moseley arranged elements in a table in order of increasing ___________________________ Periodic Law There is a periodic repetition of chemical and ____________________ properties of the elements when arranged by increasing _____________________. B. Modern Periodic Table ___________________________________________: organization of elements. Each square shows the name of an element, its chemical symbol, atomic number, and average atomic mass elements arranged by increasing ____________________ Adv Chem 1 Groups: vertical columns also called ____________________________ or just families Groups 1,2 through 13-18 are called __________ group elements (____ groups) Groups 3-12 are called ______________________ elements (_____ groups) contains elements with similar _______________________________ EX: Periods: horizontal rows physical and chemical properties change somewhat regularly _____________ a period elements close to each other in _____________ period are more similar than those further apart EX: The Staircase: The two sides of the periodic table can be divided into ___________________ and ______________________ by the ____________________ line __________________ are found to the right of the staircase all elements to the left of the staircase are considered _______________ (except ___________________) elements that border the staircase are called _______________________ Ex. Metals at the ________ of the staircase and bottom two rows (not including Hydrogen) conduct ____________ and ____________________ easily most are _____________ at room temperature (Hg is a liquid at RT) exhibit _________________________ (can be hammered or rolled into thin sheets) high tensile strength (ability to resist breaking when ______________) range from soft (sodium) to extremely hard (platinum) Physical properties of metals include: malleable, ductile, lustrous, and conductivity of heat and electricity Adv Chem 2 Non-Metals Can be solids, liquids, or gases toward _____________ of periodic table most are _____________ at RT examples of gases: examples of solids: solids are typically ________________ poor conductors of ________________ and _________________ Metalloids along the stair step line that separates _____________ and __________________ have some characteristics of _______________ and some of _____________________ all are __________________ at room temperature less _____________________ than metals not as ________________ as nonmetals ___________________________ of electricity used in ______________________ II. Electrons and the Periodic Table A. Valence electrons Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer-most energy level in an atom atoms in same group have similar __________________ properties because they have the same number of _________________________ the ____________ (row) can indicate the _____________ level of the element’s valence electrons the Roman numeral for the main group (A group) elements indicates the number of ________ ________________________________ for that group (exception: ____________________) B. Electron blocks s-block consists of groups _______ and ________ and the _________ orbitals are being filled p-block consists of groups _______ through _______ and the _______ orbitals are being filled the d-block consists of groups _______ through _______ and the _______ orbitals are being filled the f-block includes the __________________ series and ________________ series and the _______ orbitals are being filled Adv Chem 3 III. Properties of Elements (7.1, 7.2) A. Hydrogen Group ___________________ and has ______ valence electrons Only non-metal in group 1 has ______ naturally-occurring isotopes can act like a nonmetal and ________ an e- or act like a metal and _______ an e very ______________ B. Alkali Metals Group ___________________ and all have _____ valence electrons forms ions with a _______________ charge (cations) most _________________ metals only found ___________________ with other elements in nature C. Alkaline Earth Metals Group ___________________ and all have _____ valence electrons forms ions with a __________________ charge (cations) less _________________ than alkali metals, but still pretty ___________________ D. Halogens Group ___________________ and have ______ valence e most ________________ nonmetals only found ___________________ with other elements in nature forms ions with _____________________ charge (anions) E. Noble Gases (Inert Gases) Group ___________________ _____ valence electrons; except He that has ___ valence e rarely ____________ most are _________ at RT (room temperature) F. Transition Metals Groups ___________________through ___________________ Fills the _____ block G. Inner Transition Metals Also referred to as rare earth metals The two rows on the bottom of the periodic table Include Lanthanide and Actinide Series Fills the _____ block Adv Chem 4 IV. Periodic Trends Keep these 3 factors in mind when considering periodic trends: 1. Nuclear charge Whenever a __________ is added to the nucleus, it creates a stronger “_________________________” pulling in the ____________ even more. Electrons added to the same _________________________ (___________) will be pulled in tighter toward the ____________. Ex: Li 3p+ F 9p+ 2. Nuclear Shielding When an _________________________ is added to the atom (each new ________________), you are adding “______________” between the nucleus and the ______________ electrons. As energy levels are added, the atom becomes _______________ and you dilute the pull of the _____________ for the _______________ electrons because not only are there more “____________” , but the valence electrons are also now ________________ from the nucleus. (It is easier to ______________ a valence electron as energy levels are added.) Ex: Li 3p+ K 19p+ 3. Octet Rule _______________ will lose, gain or share _________________ so they can achieve the electron configuration of the closest _____________________. As elements get ______________ to the noble gases on the periodic table (further __________), the greater the attraction for electrons. Elements on the __________ side of the periodic table want to lose electrons, so they will not have a great _______________________ for electrons. Ex: Na 11p+ Adv Chem Cl 17p+ 5 Periodic Trends A. Atomic Radius Atomic radius is defined as one-half the distance between _______________ of two like atoms in a ________________ molecule and it indicates relative ___________ of the atom. It is measured in picometers (pm), 10-12 m or Angstroms (A), 10-10 m. EX: 1. Group trends. Atomic radius generally _________________ as you move down a group. This is mainly due to succeeding _____________________ being filled. 2. Period trends Atomic radius generally ________________ as you move across a period from left to right. This is mainly due to _________________________. Smallest Atomic Radius ___; Largest Atomic Radius ___ B. Ionic Radius Ionic radius is the measurement of an ion in a crystal lattice The units of measurements is picometers (pm) or Angstrom (Å) 1. Group trends for ionic radii Ionic radius ____________ as you move down a group. This is because of the added “___________” of electrons. 2. Period Trends for ionic radii Ionic radius generally _____________ as you move left to right across a period. Cations: Ion is ______________ than atom because fewer electrons and 1 less energy level. Anions: Ion is ______ than atom because more electron repulsion, but same nuclear charge. Cations 3p+ Atom Adv Chem Anions 3p+ Ion 9p+ Atom 9p+ Ion 6 Adv Chem 7 C. Ionization Energy (IE) Ionization energy is defined as the amount of energy required to remove an _____________ from an atom. EX: Na 11p+ Cl 17p+ If it is easy to remove an e- = _______IE If it is hard to remove an e- = _______IE 1. Group Trends Ionization energy ______________ as you move down a group. This is mainly due to the _________________. 2. Period trends Ionization energy _____________ as you move left to right across a period. This is mainly due to _________________________. Smallest IE __ ; Largest IE ___ D. Electronegativity (EN) Electronegativity is defined as the tendency for atoms of the element to attract ______________ when they are chemically combined with atoms of another element. EX: 1. Group trends Electronegativity ________________ as you move down a group. This is because the ________________ from the nucleus is ______________. 2. Period Trends Electronegativity ______________ as you move left to right across a period. This is mainly due to the ____________________. Note: Noble gases have no electronegativity because they don’t attract electrons at all. Again, think of the octet rule Most EN ___; Least EN (non-noble gas) ___ Adv Chem 8 E. Boiling Points (BP) The boiling point of an element is the temperature at which the element changes from the liquid phase to the gas phase EX: 1. Group trends Electronegativity ________________ as you move down a group. This is because the ________________ from the nucleus is ______________. 2. Period Trends Electronegativity ______________ as you move left to right across a period. This is mainly due to the ____________________. Note: Noble gases have no electronegativity because they don’t attract electrons at all. Again, think of the octet rule Shielding Nuclear Charge Electronegativity Ionizing Energy Ionic Radius V. Summary of Periodic Trends Atomic Radius Most EN ___; Least EN (non-noble gas) ___ Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Ionizing Energy Adv Chem Electronegativity Nuclear Charge 9