PATHOGENS and DISEASE STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

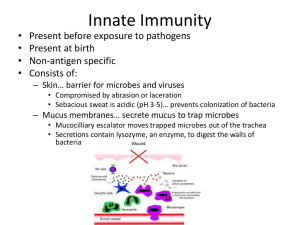
MICROBES, PATHOGENS and DISEASE STUDY GUIDE Name ____________ Class 2 3 4 Do the following exercises to prepare for the test. 1. Read chapter 19. Answer these review questions. Staple answers to the back of this packet. Review Questions 1-4, 6-9, 11-14, 17, 18-21, 23-28 2. Review all homework that has been passed back. This includes: 1. What is a Microbe? worksheet 2. Microbes: The World Within questions 3. Bacteria Concept Map 4. Ch. 6, sec. 3 Outline BACTERIA (know answers to chapter review questions) 5. Ch. 6, sec. 4 Outline VIRUSES (know answers to chapter review questions) 6. Review “The Body’s Defenses” worksheet and The Body’s Response to Infection. Write a definition in your own words. Reword definitions found in your book or in a dictionary. Protozoan Ameba Paramecium Bacterium Flagellum Binary fission Asexual reproduction 1 Sexual reproduction Conjugation Endospore Decomposer Infectious disease Toxin Antibiotic Toxin Virus Host Parasite Bacteriophage 2 Vaccine Epidemic Pathogen Pasteuriz(ation) Phagocyte Immune response Lymphocyte T-cell B-cell Antigen Antibody antibiotic 3 AIDS Immunity Active immunity Vaccination Vaccine Passive immunity ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- What are the four types of pathogens? What are four ways humans can become infected? 1. 3. 2. 4. Know the human body’s three lines of defense. 1. 2. a. 3. b. c. d. How does HIV relate to AIDS, and how does it attack the human body? 4 What is the difference between active immunity and passive immunity? Explain. Explain how microbes have helped the earth’s atmosphere. Are viruses living organisms? Explain. List five ways microbes are helpful to humans. How do viruses infect cells and multiply? Why are viruses considered non-living? How does a vaccination work? How did Edward Jenner discover the process of vaccination? How did Alexander Fleming discover antibiotics? List three ways disease might be avoided. 5 Why can bacteria become resistant to antibiotics over time? How would bacterial reproduction from conjugation help a colony of bacteria to become resistant to antibiotics more than if the bacteria reproduce by binary fission? How does the immune response work? Use the words lymphocyte, T-cell, B-cell, antigens, and antibodies, pathogen, phagocyte in a CONCEPT MAP to show your understanding. 6