Study Sheet for Chapter 13
advertisement
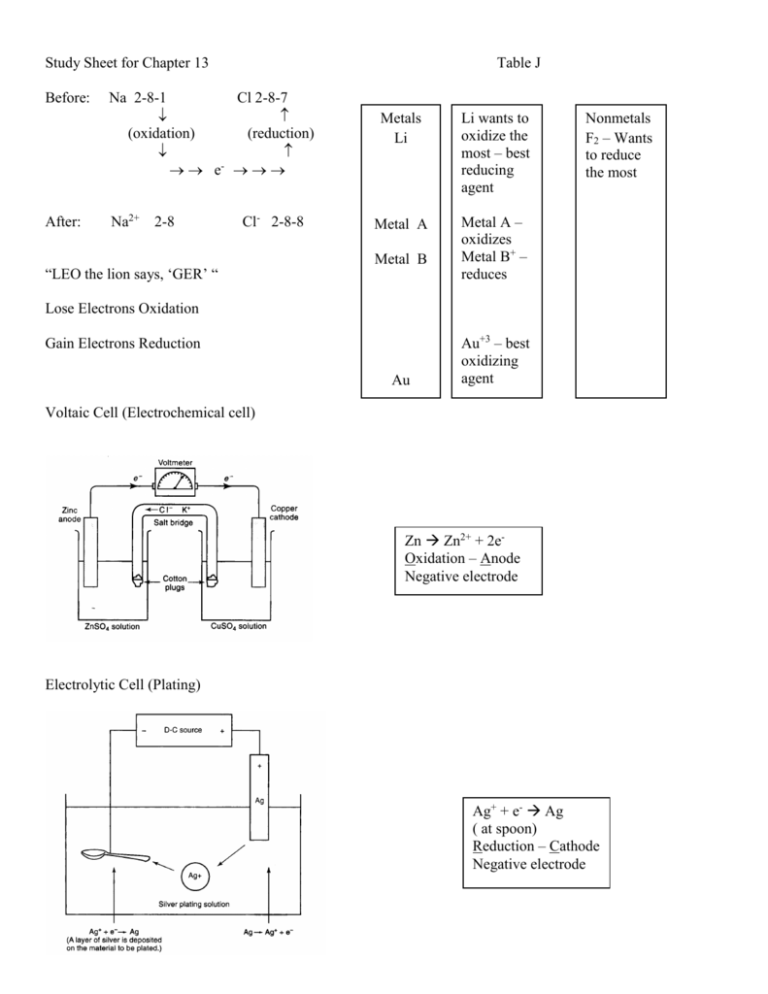
Study Sheet for Chapter 13 Table J Before: Na 2-8-1 Cl 2-8-7 (oxidation) (reduction) e- After: Na2+ 2-8 Cl- 2-8-8 “LEO the lion says, ‘GER’ “ Metals Li Li wants to oxidize the most – best reducing agent Metal A Metal A – oxidizes Metal B+ – reduces Metal B Nonmetals F2 – Wants to reduce the most Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain Electrons Reduction Au Au+3 – best oxidizing agent Voltaic Cell (Electrochemical cell) Zn Zn2+ + 2eOxidation – Anode Negative electrode Electrolytic Cell (Plating) Ag+ + e- Ag ( at spoon) Reduction – Cathode Negative electrode What is oxidation? What is reduction? If you lose an electron what is the resulting charge on the ion? How are redox reactions identified? How do you find the oxidation number for elements in a compound? Which metal oxidizes? Which type of cell creates electricity? Where does oxidation take place? Where does reduction take place? What does the salt bridge do? Which direction do electrons flow? In an electrochemical cell, what happens to the mass of the anode? In an electrochemical cell, what happens to the mass of the cathode? Which type of cell requires electricity? How do you balance an equation using redox? Lose electrons oxidation (LEO). Gain electron reduction (GER). +1 Oxidation numbers on an element will change from the left to the right side of the equation. They can be taken off the periodic table. If there is more than one oxidation number you chose the oxidation state that causes the charge on the compound to add to zero. The one higher on table J. Electrochemical (or Voltaic) cell. Anode (vowels). Cathode (consonants). Allows ions to move. From the more active metal through the wire to the less active metal. It gets smaller because atoms are being converted to ions. It gets greater because ions are being converted to atoms. Electrolytic cell. Write half reactions and then balance the electrons to find the coefficients. Oxidation __________________________________________________________________ Corrode/Corrosion __________________________________________________________________ Reduction __________________________________________________________________ Redox or Oxidation-reduction reactions__________________________________________________________ Oxidation number __________________________________________________________________ Half-reaction __________________________________________________________________ Species __________________________________________________________________ Electrochemical cell __________________________________________________________________ Voltaic cell __________________________________________________________________ Electrode __________________________________________________________________ Salt bridge __________________________________________________________________ Anode __________________________________________________________________ Cathode __________________________________________________________________ Spontaneous __________________________________________________________________ Electrolytic cell __________________________________________________________________ Electrolysis __________________________________________________________________ Conservation of charge __________________________________________________________________ Oxidizing agent __________________________________________________________________ Reducing agent __________________________________________________________________