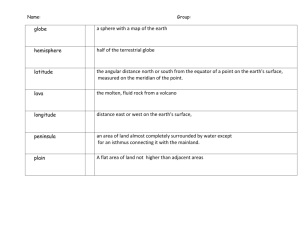
review your understanding
advertisement

CHAPTER 1 MARKETING: CONNECTING WITH CUSTOMERS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES: 1. Introduce the concept of marketing, including its definition, purpose, and role in creating exchanges. 2. Provide an overview of what is involved in making marketing decisions, including examples of product, price, promotion, and place decisions to create a marketing mix. 3. Contrast the periods of marketing evolution, from the early history through the eras of production, sales, and customer marketing, leading up to today. 4. Show the five key forces that are dramatically influencing how organizations will connect with customers in the 21st century. 5. Illustrate how marketing pertains to each individual. CHAPTER OUTLINE: Teaching Note: As discussed in the early part of this chapter, many people view marketing as promotion. Whether in the form of advertising, sales promotion, or even personal selling, these are the most visible and obvious elements of marketing to the typical consumer. As an instructor in this field we must be prepared to provide a detailed answer the question, “what is marketing?” In doing this, what we must initially accomplish is to show the student that much of marketing occurs “behind the scenes” and that marketing’s role in society has evolved over the years and continues to do so. In a way, marketing is just a complicated process of matching materials found in nature or fabricated from those materials with the needs of individuals. Matching of each individual need, of course, would be impossible if the consumer had to search out each item they required from the producer. As such, marketing plays an important role in the accumulation and allocation of goods. Marketing is also a study of considerations on the decision to trade or not to trade. Sellers may accept low prices if they are relived of certain requirements while buyers may pay a higher price if provide with extra services or some sort of additional value. Marketers also need some sort of general explanation for the behavior of individuals and organizations insofar as conscious choice is involved. As a result, marketing is often a function of psychology, sociology, and anthropology mixed with economics. Someday marketing may need to even look beyond the act of purchasing goods and service more to the study of why buyers consume products to begin with. 1 1) The Concept of Marketing: Connecting with Customers 2) The Definition of Marketing a) The Process of Planning and Executing b) Product, Price, Promotion, and Place c) Markets for Ideas, Goods, and Services i) Consumer Markets ii) Business-to-Business Markets iii) Nonprofit Markets iv) Internal Markets d) Creates Exchanges That Satisfy Individual and Organizational Objectives i) Form, Place, Time, and Ownership Utility ii) Organizational Objectives 3) The Marketing Concept: The Purpose of Marketing a) Understand the Needs and Wants of Customers b) Create Customer Value Through Satisfaction and Quality c) More Effectively and Efficiently Than Competitors 4) The Marketing Strategy Process a) Situation Analysis b) Targeting c) Positioning d) Marketing Mix Decisions i) Product Strategy ii) Place Strategy iii) Promotion Strategy iv) Price Strategy 5) The Evolution of Marketing a) The Production Era b) The Sales Era c) The Customer Marketing Era 6) Connecting With Customers in the 21st Century a) Connecting Through Relationships 2 b) Connecting Through Technology i) Process and Product Technology ii) The Internet iii) Marketplace and Marketspace c) Connecting Globally d) Connecting With Diversity e) Connecting Ethically i) Ethics ii) Social Responsibility 7) Marketing: Your Involvement CONNECTED: SURFING THE WEB Procter & Gamble 1. Find and read P&G’s history from 1945 to 1980 called “New Lands and Dynamic Growth.” Relate this information to its relevant period of marketing evolution. The information found in “New Lands and Dynamic Growth” relates to the production era of the marketing evolution. 2. Choose a recent news release that discusses one of the five key marketing forces. Describe how this might influence or affect P&G’s ability to connect with customers. A news release titled “Procter and Gamble Signs Record Contract with Minority Vendor, Specialized Package Group” shows P&G’s shows the use of one of the five key marketing forces. The contract with Specialized Package Group underlines the program’s unquestionable value in terms of building relationships with minority businesses and minority consumers. 3. Locate and read P&G’s pages on diversity. Why does P&G value a diverse organization? How might these values influence marketing decisions? P&G believes developing and managing a strong, diverse organization is essential to achieving their business purpose and objectives. They value the different perspectives that diverse people bring to the business. The workplace environment encourages collaboration, which brings different talents and experiences together to produce better ideas and superior services and products. General Mills 1. Find and read General Mills’ information on its international operations. Select a strategic alliance General Mills has formed with another organization. How do you think this alliance contributes to relationship marketing? 3 General Mills had formed a strategic alliance will Nestle to form Cereal Partners Worldwide. This joint venture will build a strong foundation for General Mills' future growth worldwide. 2. Read “What’s News” and select an example of General Mills using one or more elements of the marketing mix. Do you think this is an effective way to make a connection with customers? Why or why not? The news release titled "Betty's Baked Goods Coming to Knott's Camp Snoopy at Mall of America" shows that General Mills is effectively combining the four controllable variables of marketing- product, price, promotion, and place. This is an effective way to connect with consumers. The new store will be selling Betty Crocker products in a large, successful mall. This business decision is sure to become a money-maker. 3. In what types of markets foes General Mills operate? Give examples. General Mills operates in the market of consumer foods. With sales in excess of $5 billion, General Mills ranks among the largest consumer foods companies in the United States. REVIEW YOUR UNDERSTANDING 1. What is marketing? What are the key elements in its definition? Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives. (pp. 5-6) 2. What are the four basic areas (types of markets) where marketing is typically applied? Marketing is typically applied in consumer markets, business-to-business markets, nonprofit markets, and internal markets. (pp. 6-8) 3. What is a utility? What are the four types of utility involved in marketing exchanges? Utility is a term economists use to describe the want-satisfying potential of a good or service. There are four fundamental types of utility- form, place, time, and ownership. (pp. 8-9) 4. What is the difference between a need and a want? Give examples of each. Needs are fundamental requirements the meeting of which is the ultimate goal of behavior. Wants are a specific form of consumption desired to satisfy needs. For example, Boeing addresses the need of United Airlines for aircraft by designing planes the airline will want. (p. 10) 5. What is the marketing concept? What are its three key aspects? The marketing concept recognizes the long-run nature of successful marketing. It’s three key aspects are: to understand the needs and wants of customers, to create 4 customer value through satisfaction and quality, and to operate more effectively and efficiently than competitors. (pp. 9-10) 6. What is a marketing strategy? Describe each of its four steps. The marketing concept is implemented through the marketing strategy process, the series of steps the organization takes to interface with the rest of the world. The four steps are: situation analysis, targeting, positioning, and development of the marketing mix. (p. 12) 7. How do product, place, promotion, and price decisions form the marketing mix? Give examples of each decision. Product strategy includes decisions about which products to develop, how to manage current products, and which products to phase out. The object of place strategy is to serve customers by providing products where and when they are needed. The promotion strategy includes determining the objectives to be attained, as well as creating messages and the forms they will take. The objective of price strategy is to set prices to reflect the value received by customers and to achieve the volume and profit required by the organization. (pp. 14-16) 8. What the stages in marketing evolution? Describe each of the three marketing eras. The stages in marketing evolution are the production era, sales era, and customer marketing era. During the production era, companies focused on ways to make products in mass quantities. The sales era focused on ways to sell more efficiently. The customer marketing era emphasizes customer satisfaction and value. (pp. 16-17) 9. What are the five key forces shaping marketing as we enter the 21st century? Describe each. The future will center around better ways of connecting with customers. The five key forces are: connecting through relationships, connecting through technology, connecting with diversity, connecting globally, and connecting ethically. (p. 18) 10. How does marketing relate to you? List four ways. Marketing affects everybody in many ways. It comes from many angles- the prospective marketer, member of a target market, as a customer, and as a citizen. (p. 29) DISCUSSION OF CONCEPTS 1. Describe marketing, highlighting examples from your daily life that illustrate each of its four aspects. Marketing, as defined by the American Marketing Association (AMA), is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives. Marketing, is thus actions, decisions, and relationships that firms execute with respect to all customers in an attempt to satisfy their needs and 5 wants. Examples should look to exploring how the product, price, place, and promotion elements of marketing impact customers each and every day. Teaching Note: It is important to stress that marketing must adjust to the ever changing needs of customers and society. Some marketers will argue that selling to consumers is easier in some senses and more difficult in others. There are many new way to reach customers through direct marketing and yet the customer is often overwhelmed by communication and distribution tactics of today. Five different marketers can arrive at five different solutions to the same problem. All may be right; all may be wrong. In marketing we really don’t know the right decision from the wrong decision until after it has happened. Further, all the marketing science in the world will never eliminate the gut instinct that sometimes works in spite of all of the evidence to the contrary. Nevertheless, there is a logic and a system to marketing that greatly increases the probability of success. These are what must be learned. (See slides 1-1 and 1-2) 2. Identify one company with which you are familiar and describe four ways in which it provides utility. The local tire stores offers form utility selling rubber, nylon, and steel that has been combined and formed into a mixture that fits the size required on my vehicle. They offer the product in the town that I live in and therefore they provide place utility. The store has inventory in stock that meets my needs when I want to buy and they allow the transaction to occur more easily by accepting credit cards as a form of payment for the tires. Teaching Note: It is important to expand upon the notion of form utility to take into account both goods and services. Whether the production process results in a tangible product or an intangible service, it always converts inputs into outputs. In this conversion process, it may make major changes in raw materials or combine a set of finished components. A meat cutter performs a production function by reducing a side of beef to steaks, roasts, and ground beef. A railroad combines trains, rails, and employees to create its output: the service of carrying passengers where they want to go. Both of these processes create form utility. (See slide 1-3) 3. Discuss the activities involved in implementing the marketing concept. How do they pertain to customers, competitors, and the marketing organization? Implementing the marketing concept means accomplishing three things. First, understanding the needs and wants of the customer. Next, creating customer value through satisfaction and quality. Finally, operating more effectively and efficiently than the firm’s competitors. Clearly, this means that a firm that practices the marketing concept understands the customer, the competitive environment, and the goals that are appropriate for the organization. Teaching Note: General Electric’s 1952 annual report included a comment that is often considered the original description of the marketing concept. It is as follows: 6 “. . . introduces marketing at the beginning, rather than at the end of the production cycle, and integrates marketing into each phase of the business. Thus, marketing, through its studies and research, will establish for the engineer, the design and manufacturing departments, what the consumer wants in a given product, what price he is willing to pay, and where and when it will be wanted. Marketing will have authority in product planning, production, scheduling, and inventory control, as well as in sales, distribution, and servicing of the product.” (See slide 1-4) 4. Describe the steps in developing a marketing strategy. Why is it important to target prior to positioning? Why is positioning important prior to marketing mix decisions? The steps in developing a marketing strategy are: Situation analysis – understanding the marketing environment, the customers needs, and the competition Targeting – selecting groups of potential customers that the firm hopes to satisfy Positioning – creating a unique image for the firm’s products in the mind of the target market Developing the marketing mix – creating a product, price, place, and promotion strategy to meet the needs of the target market. Targeting is done first so that the customers are identified and understood. Positioning is done next so that the marketing mix strategies can be developed to support the product’s unique image. Teaching Note: The term “positioning” is most commonly applied to decisions concerning brands, but it is also used to describe the same decisions for stores, companies, and whole product categories. Product positioning decisions are strategic decisions. Consider Saturn’s positioning strategy. Saturn stresses value, made in America by caring workers, and dealers who respect customers. Saturn wants to be viewed as superior to its competitors on each of these attributes. If the target market does not value this image or values the image portrayed by competitors more, Saturn will surely fail. (See slide 1-5) 5. Compare and contrast the various eras of marketing, assessing the role each era played in reaching the current relationship era. During this century, the economy has moved through three basic eras in terms of the focus of business. Those eras are: The production era – emphasis is upon new products and production efficiency The sales era – emphasis is upon selling products more effectively The customer marketing era – emphasis is upon customer satisfaction and value Teaching Note: Another way that marketers distinguish between modern and historical approaches to the marketplace is to make a distinction between transactional and relational marketing. In the past, marketers focused on individual isolated exchanges to satisfy customer needs. Marketers practicing a more transactional approach were more concerned with attracting new customers than working hard to retain existing customers. A fundamental part of the modern era of marketing is seeking to establish and maintain mutually beneficial long-term 7 relationships with customers. One reason that relationship marketing appeals to firms is that it is much more profitable over the long-run. (See slide 1-6) 6. Discuss the five forces shaping marketing by showing how they help implement the marketing concept. The five forces are: Connecting through relationships – marketers learn that by perfectly meeting the customers needs, that customer will become loyal Connecting through technology – innovation is an important role of marketing Connecting with diversity – in an increasingly diverse society, marketers cannot assume that all people are the same and must also learn to understand others’ points of view Connecting globally – opportunities for marketers are worldwide Connecting ethically – social responsibility and ethical behavior are important to a company’s marketplace performance. Teaching Note: Marketing is obviously changing very fast. Vast and rapid technological changes are making an increasing number of products and services obsolete. Intense international competition and growth of truly global markets have forced firms to look well beyond their national boundaries. But marketing is not just important within the industrial sector. Social institutions of all kinds, which had thought themselves exempt from the pressures of the marketplace, are also beginning to recognize the need for marketing in the management of their affairs. Charities, colleges, museums, and even doctors are beginning to give attention to the marketing concept. (See slide 1-7) CASES: Case1: Starbucks 1. The definition of marketing describes four types of decisions made by made by marketers: product, price, promotion, and place. Identify a place and promotion decision Starbucks has made. A place strategy that Starbucks has made has been to locate stores primarily in large urban areas and college towns. Starbucks key promotion decision has been to communicate to customers that frequent visits to their stores is a lifestyle. 2. Based on the types of retail locations selected by Starbucks, what customer characteristics form its target markets? The typical Starbucks customer is active and on-the-go and would like to be able to enjoy premium coffee products anywhere they are at, in urban environments or while traveling at airports or even convenience stores. 8 3. The marketing concept holds that the purpose of marketing is to understand the needs and wants of customers and create customer value through satisfaction and quality more effectively and efficiently than competitors. Given the information provided in this case, summarize how Starbucks implements the marketing concept. Starbucks implements the marketing concept through its product quality. Despite its rapid growth, Starbucks refuses to compromise quality and it will not franchise its operations and is very selective about business alliances. This is all done in an effort to maintain the quality and image of the product that their customers desire. 4. In 1997, Starbucks opened a new store every business day. This includes global expansion into new markets. What factors must Starbucks consider as it continues to pursue global opportunities? Obviously, Starbucks must be careful to understand specific cultural tastes and preferences as it expands into global markets. People from different cultures or backgrounds do not necessarily have the same perceptions, needs, or wants. It is imperative that they understand and respect the diversity of the world’s customers. No two are alike. 9