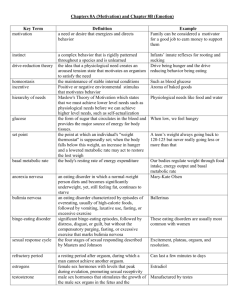
THEORIES CHART
advertisement
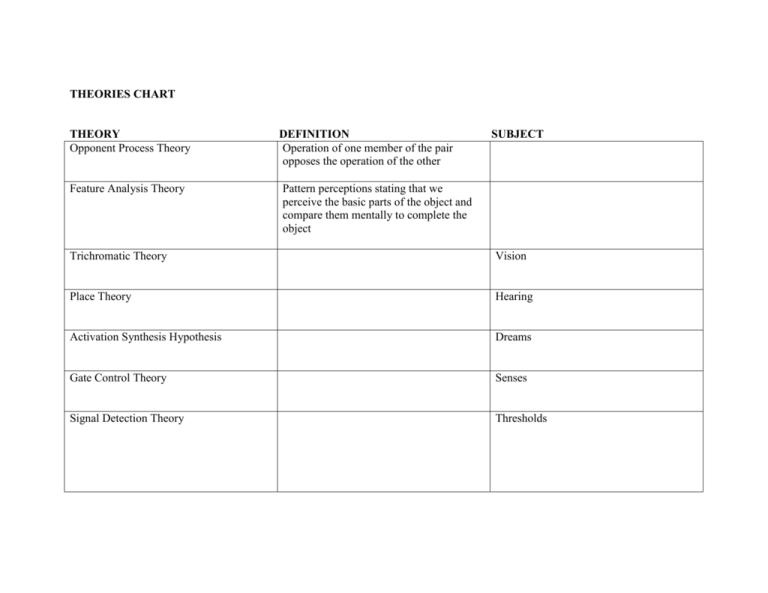
THEORIES CHART THEORY Opponent Process Theory Feature Analysis Theory DEFINITION Operation of one member of the pair opposes the operation of the other SUBJECT Pattern perceptions stating that we perceive the basic parts of the object and compare them mentally to complete the object Trichromatic Theory Vision Place Theory Hearing Activation Synthesis Hypothesis Dreams Gate Control Theory Senses Signal Detection Theory Thresholds James Lang Theory Stimulus ----- physiological change---emotion Cannon and Bard Theory Facial Feedback Hypothesis Emotion Making certain facial expressions produces corresponding emotion Schachter and Singer Appraisal Hypothesis Emotion Optimum Level Theory Each individual’s body functions best at some specific level of arousal Contingency Theory Strength of a CR depends on the ability of the CS to predict occurrence of a US State Dependent Learning Theory Retrieval will be facilitated if the individual’s physiological and emotional state during retrieval matches Encoding Specificity Theory Memory Frequency Theory Hearing - Effectiveness of memory retrieval is directly related to the similarity of ones that were present when the memory was originally encoded Classical conditioning Vision/emotion Information from emotional stimuli is simultaneously relayed by the thalamus to higher brain centers and the sympathetic nervous system Pain sensations are transmitted to the spinal cord stimulating the release of substance P which then stimulates an impulse to the brain Emotion Emotion Threshold measurement that takes the nature and background of stimulation into account Direct relationship between dream content and brain activity Memory Motivation Physiological arousal is an undifferentiated state Basilar membrane vibrates at different rates to create perception of different pitches Perception 3 types of cones, one for each primary color Basilar member vibrates at different places to create perception of different pitches