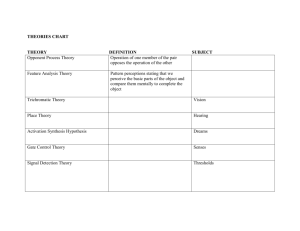
THEORIES OF EMOTION
advertisement
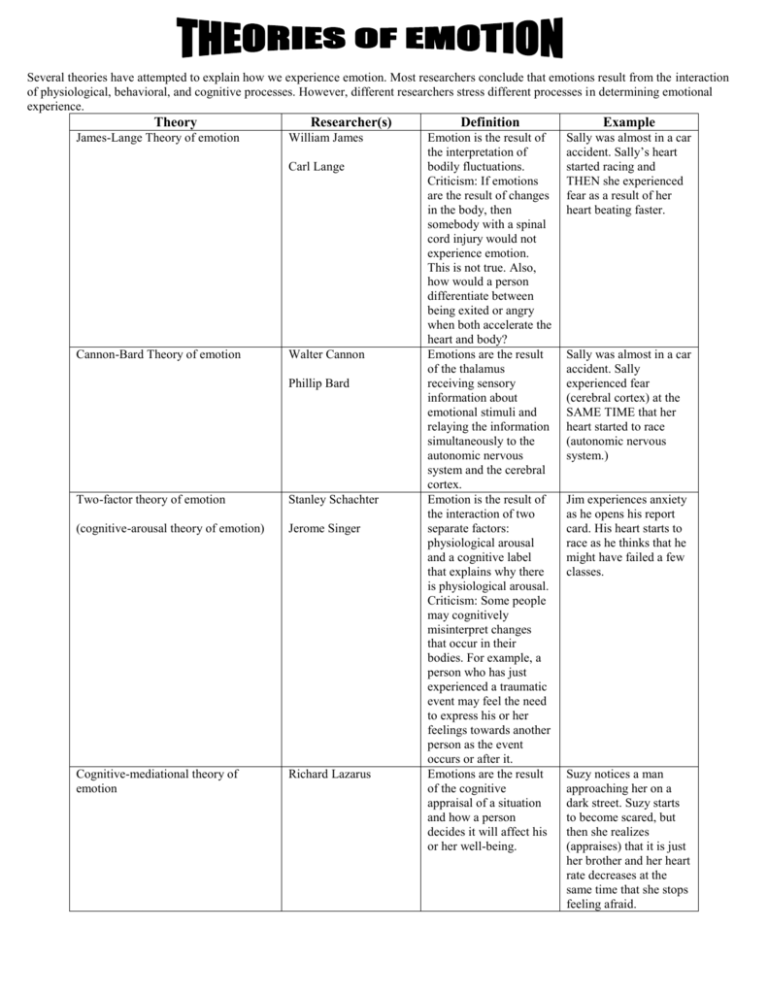
Several theories have attempted to explain how we experience emotion. Most researchers conclude that emotions result from the interaction of physiological, behavioral, and cognitive processes. However, different researchers stress different processes in determining emotional experience. Theory James-Lange Theory of emotion Researcher(s) William James Carl Lange Cannon-Bard Theory of emotion Walter Cannon Phillip Bard Two-factor theory of emotion Stanley Schachter (cognitive-arousal theory of emotion) Jerome Singer Cognitive-mediational theory of emotion Richard Lazarus Definition Example Emotion is the result of the interpretation of bodily fluctuations. Criticism: If emotions are the result of changes in the body, then somebody with a spinal cord injury would not experience emotion. This is not true. Also, how would a person differentiate between being exited or angry when both accelerate the heart and body? Emotions are the result of the thalamus receiving sensory information about emotional stimuli and relaying the information simultaneously to the autonomic nervous system and the cerebral cortex. Emotion is the result of the interaction of two separate factors: physiological arousal and a cognitive label that explains why there is physiological arousal. Criticism: Some people may cognitively misinterpret changes that occur in their bodies. For example, a person who has just experienced a traumatic event may feel the need to express his or her feelings towards another person as the event occurs or after it. Emotions are the result of the cognitive appraisal of a situation and how a person decides it will affect his or her well-being. Sally was almost in a car accident. Sally’s heart started racing and THEN she experienced fear as a result of her heart beating faster. Sally was almost in a car accident. Sally experienced fear (cerebral cortex) at the SAME TIME that her heart started to race (autonomic nervous system.) Jim experiences anxiety as he opens his report card. His heart starts to race as he thinks that he might have failed a few classes. Suzy notices a man approaching her on a dark street. Suzy starts to become scared, but then she realizes (appraises) that it is just her brother and her heart rate decreases at the same time that she stops feeling afraid.