Accounting Concepts & Conventions Explained
advertisement

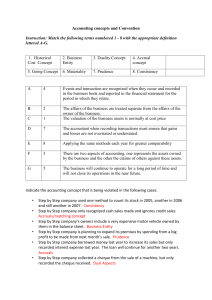
Accounting Concepts and Conventions Introduction Accounting concepts and conventions as used in accountancy are the rules and guidelines by that the accountant lives. All formal accounting statements should be created, and presented according to the concepts and conventions that follow. In the United Kingdom, four of the following accounting concepts are laid down in Statement of Standard Accounting Practice number 2 (SSAP 2: Disclosure of Accounting Policies), they are: Going concern concept Accruals or matching concept Consistency concept Prudence concept Going concern concept It is assumed that the business under consideration will remain in existence for the foreseeable future. Without this concept, accounts would have to be drawn up on the 'winding up' basis. That is, on what the business is likely to be worth if it is sold piecemeal at the date of the accounts. Accruals (Matching) concept. The purpose of this concept is to make sure that all revenues and costs are recorded in the appropriate statement at the appropriate time. Costs concerning a future period must be carried forward as a prepayment for that period and not charged in the current profit statement. For example, payments made in advance such as the prepayment of rent would not be treated as an expense in the current accounting period. Consistency concept This concept states that accounting policies and treatments should be applied consistently from one period to the next. Any variation in accounting policy or treatment may be permitted if the new policy or accounting treatment provides a fairer view of the business’s activities. Prudence concept Basically the concept says that whenever there are alternative procedures or values, the accountant will choose the one that results in a lower profit, a lower asset value and a higher liability value. The concept is summarised by the well known phrase 'anticipate no profit and provide for all possible losses'. Monetary measurement concept It simply and clearly states that only those transactions that are true financial transactions may be accounted for. That is, only those transactions that may be expressed in money values (whatever the currency) are of interest to the accountant. Materiality concept We are concerned here with the idea that accountants should concern themselves only with matters that are significant because of their size and should not consider trivial matters. The problem, of course, is in deciding what is and what is not material: we are concerned here with RELATIVE IMPORTANCE. Realisation concept The realisation concept helps the accountant to determine the point at that he feels that a transaction is certain enough for the profit to be made on it to be calculated and taken to the profit and loss account. Realisation occurs when a sale is made to a customer. The basic rule is that revenue is created at the moment a sale is made, and not when the account is later settled by cheque or by cash. Historical cost concept It basically means that accounting transactions are recorded and accounts are prepared using historical cost figures. That is the value at the date of transaction without adjusting for changing in prices or general inflation.