Biology 102 Chapter 29
advertisement

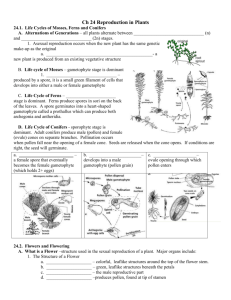
Biology 102 Chapter 30 The Evolution of Seed Plants 1. Define seed and list those groups of plants that produce seed. ---seed is fertilized, ripened ovule of gymnosperm or angiosperm ---seed consists of embryo, food supply, and seed coat 2. Explain how each of the following is significant in the progression from nonseed to the seed plants which are the dominant plants on Earth today. TERRESTRIAL HABITAT ---support ---water supply (access/conservation) and nutrients ---solving the “hanky-panky” problem SIZE AND DEPENDENCY OF GAMETOPHYTE/SPOROPHYTE ---let’s review the proposed evolutionary scheme once more ---Bryophytes have dominant gametophyte and reduced sporophyte --sporophyte dependent on gametophyte ---ferns have dominant sporophyte and reduced gametophyte --are nutritionally independent of each other ---gymnosperms have dominant sporophyte and further reduced gametophyte ---angiosperms have even further reduced gametophyte ---in seed plants, gametophyte nutritionally dependent on sporophyte HOMOSPOROUS VS. HETEROSPOROUS ---homosporous plant produces single type spore that develop into single type gametophyte that bears both male and female reproductive organs ---heterosporous plant produces two distinct types of spore --megaspore develops into larger female gametophyte (mega) --microspore develops into smaller male gametophyte (micro) ---Bryophyta is homosporous ---most ferns are homosporous (always exceptions) ---seed plants (gymno/angio) are heterosporous SPORES AS MEANS OF DISPERSAL ---spore (haploid reproductive structure) shed for dispersal by mosses and ferns ---seed plants retain the megaspore and female gametophyte develops within megasporangia and depend on sporophyte for food and water ---microsporangium produces male gametophyte (pollen), which is distributed by wind, insect, bird, plant breeder, etc. --pollen grain that reaches appropriate surface, develops further MECHANISM BY WHICH SPERM REACHES THE EGG ---mosses and ferns still dependent on moisture for sperm to swim to egg ---seed plants depend on pollen (male gametophyte) dispersal --appropriate location, pollen grain grows pollen tube --when tip of tube reaches megagametophyte, two sperm are released 3. Explain the difference between: POLLINATION AND FERTILIZATION ---pollination is transfer of pollen to appropriate structure --ovule/carpel/pistil ---fertilization is union of sperm and egg to produce single cell called zygote ---time for an Estesism CONES, FLOWERS, AND FRUITS ---cone is axis bearing tight cluster of scales or leaves specialized for reproduction ---flower is total reproductive structure of angiosperms --Dr. Richard’s favorite was “modified leaf with carpels” ---fruit is a ripened and mature ovary (or groups of ovaries) --sometimes applied to reproductive structures of other groups of plants NAKED SEED AND COVERED SEED ---gymnosperms are said to have “naked seeds” ---ovules and seeds are NOT protected by flower or fruit tissue ---angiosperms are said to have covered seeds ---ovary of flowering plant (with seeds it contains) develops into fruit after fertilization --hence, the term “covered seeds” 4. Describe the life cycle of a pine tree. ---pollen falls onto ovulate cone and enters ovule through micropyle ---germinates in ovule, forms pollen tube that digests its way through nucellus ---megaspore mother cells undergoes meiosis = 4 haploid megaspores (one survives) --it grows and divides repeatedly by mitosis = immature female gametophyte ---2 or 3 archegonia, each with egg, develop within multicellular gametophyte ---after 1 year = eggs ready for fertilization, 2 sperm cells have developed & pollen tube has grown through nucellus to female gametophyte ---fertilization occurs when one sperm nuclei unites with the egg nucleus --all eggs in ovule may be fertilized, but only one zygote develops into an embryo (usually) ---pine embryo (new sporophyte) has rudimentary root and several embryonic leaves --embedded in female gametophyte --nourishes the embryo until capable of photosynthesis ---ovule has developed into pine seed --embryo (2n), food source (n), surrounding seed coat (2n) ---scales of ovulate cone separate (about 1 more year), and winged seeds are carried by wind (usually) to new locations 5. Describe the structure of pollen and seed cones and distinguish between the two. ---multicellular gametophyte generation is reduced & develops from haploid spores that are retained within sporangia ---male gametophyte is the pollen grain (no antheridium) ---female gametophyte consists of multicellular nutritive tissue and an archegonium that develops within an ovule ---conifer life cycles are heterosporous --male and female gametes develop from different types of spores produced by separate cones ---pollen cones have microsporangia --cells undergo meiosis = haploid microspores --these small spores develop into pollen grains --pollen grains = male gametophyte ---ovulate cones have megasporangia --cells here undergo meiosis = large megaspores that develop into the female gametophyte ---each ovule initially includes a megasporangium (nucellus) enclosed in protective integuments --has single opening called micropyle 6. Identify the parts of a flower and describe a function for each. ---chalk talk time on flowers 7. Distinguish between perfect and imperfect flowers. ---flower containing both male and female reproductive parts is called “perfect” --has both megasporangia and microsporangia ---flower with only megasporangia OR microsporangia called “imperfect” --either stamens or carpels nonfunctional or absent in given flower 8. Distinguish between monoecious and dioecious flowering plants. ---monoecious means “one-housed” --megasporangiate and microsporangiate flowers occur on same plant (corn/birch) ---dioecious means “two-housed” --given plants produces either flowers with stamens or flowers with pistils but NEVER both --willows, date palms, and wacky-backy