Angiosperms
Angiosperms
Earth’s dominant plants
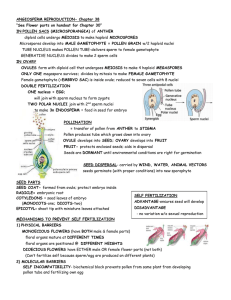
Angiosperm Characteristics
Vascular Dominant sporophyte generation
Flowering plants
Xylem – vessel elements
Double fertilization
Seeds are covered in a fruit
Phloem – sieve tube elements
2 Largest Classes
Monocots
Grasses, corn, palms
Mainly herbaceous
Parallel veins in leaves
Flower parts – multiples of
3
Seed – 1 cotyledon, endosperm
Eudicots
Roses, sunflowers, maples
Herbaceous or woody
Branched veins
Flowers – multiples of 4 or
5
Seed – 2 cotyledons
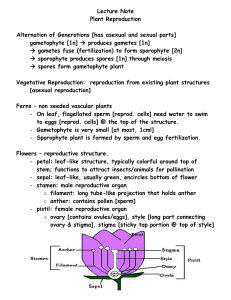
Flowers
Reproductive part of angiosperms
4 parts: sepals, petals, stamens, carpels
Complete vs. Incomplete flowers
Perfect vs. Imperfect flowers
Reproduction
Pollination
Wind
Water
Pollinators
Double Fertilization
Germination
What happens in the anther?
Pollen sac contains many microsporocytes
Meiosis 4 haploid microspores
Each microspore pollen grain (immature male gametophyte
Each pollen grain contains 2 cells:
Tube cell
Generative cell
Anther splits – sheds pollen
What happens in the pistil?
Each ovule in ovary contains megasporocyte
Meiosis 4 haploid megaspores
3 megaspores disintegrate
Remaining megaspore divides gametophyte
(aka embryo sac)
Gametophyte contains 7 cells w/ 8 nuclei
Egg cell contains 1 nucleus
Large center cell contains 2 polar nuclei
Double Fertilization
Pollen lands on sticky stigma
Tube cell forms pollen tube through style into ovary
Generative cell divides 2 sperm cells
Double Fertilization
1 sperm fertilizes egg zygote embryo
1 sperm fuses with both polar nuclei 3 n cell
endosperm
Seed and Fruit Formation
Ovule develops into seed
Ovary wall enlarges
Ripens into fruit
Flower parts fall off
Fruits:
Protect seeds from dessication
Aid in dispersal
Success of Flowering Plants
Seeds an advantage over spores
Cross-pollination – increases variation
Animals disperse pollen and fruit farther than wind
Efficient xylem
Vessel elements
Broad leaves
efficient photosynthesis
Abscission
Reduces water loss
Adaptability of sporophyte generation