BIO101 plant biology homework Name Label the parts of the flower
advertisement

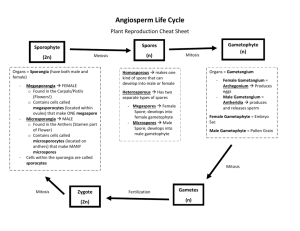
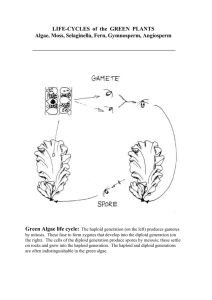
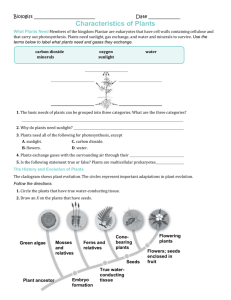
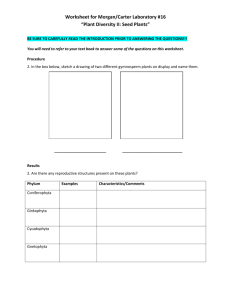
BIO101 plant biology homework Name ___________________________________ 1. Label the parts of the flower: petal, stigma, filament, ovary, sepal, pistil, stamen a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. ________________________ contains plant ovum ________________________ contains pollen sacs ________________________ traps pollen, female part ________________________ structure that pollen tube travels through ________________________ advertisement for pollinator, brightly colored ________________________ protects the floral bud ________________________, ________________________ compose the carpal ________________________ ,________________________ compose the anther ________________________ one structure missing in an incomplete flower ________________________ site of male gametophyte development Is this plant a monocot or a eudicot? ________________________ (half of the flower is shown) Is this plant an angiosperm? ________________________ 2. Sporophyte or gametophyte (S or G) a. ___Forms via meiosis b. ___Adult plant c. ___Polar nuclei d. ___Plant embryo e. ___Stem f. ___Pollen grain g. ___ Megaspore h. ___Microsporocyte mother cell i. ___ Diploid j. ___ Haploid k. ___ Egg nucleus 1 BIO101 plant biology homework 3. Which of the structures in the previous question are associated with female structures? 4. Match the tissue type. _____ ground tissue external to vascular tissue ____ may be triploid (3n), stores nutrients for developing seed _____ protects against water loss and disease _____ , ____2 dermal tissues _____ transports water from roots to plant _____ may exhibit trichomes _____ transports nutrients throughout plant _____, _______ 2 vascular tissues _____ ground tissue internal to vascular tissue _____ perpetual embryonic tissue A. Endosperm B. Epidermis C. Xylem D. Phloem E. Cortex F. Periderm G. Meristem H. Pith 5. Parenchyma, Collenchyma, or Sclerenchyma? (P, C, S) a. b. c. d. e. f. _____ fleshy tissue of fruits _____ resilient cells provide flexible support as in celery stem _____ least specialized plant cells, alive at maturity _____ rigid support for plants _____dead cells at functional maturity _____ thick secondary plant cell walls with lignin 6. Xylem or Phloem or Both (X or P or B) a. ____ tracheid cells b. ____ transports nutrients such as sugar c. ____ sieve tube element cells d. ____ forms vascular bundles e. ____ forms wood in secondary growth f. ____ present in a eudicot stem g. ____ transports water from roots to rest of plant 7. Groups of 3 a. 3 types of life cycles of flowering plants b. 3 particle types in soil c. 3 components of topsoil d. 3 live organisms in topsoil e. 3 factors that affect soil quality f. 3 plant macronutrients g. 3 functions of rhizobacteria h. 3 features of a monocot plant i. 3 features of a eudicot plant j. 3 groups of vascular plants k. 3 cells found in the male gametophyte l. 3 modes of pollination used by angiosperms 2 BIO101 plant biology homework 8. Fill in. You may use answers more than once or not at all embryo sac haploid diploid meiosis mitosis angiosperm gymnosperm sperm pollen grain microsporangium megaspores pollen tube polar nuclei cotyledon a. A diploid megasporocyte mother cell is undergoes a type of cell division called ________ to produce 4 haploid ______________, 1 of which survives. b. In the female reproductive organ of the plant, the ____________, a multinucleate structure with 8 haploid nuclei, (one of which is the ovum) forms. c. Also known as a pollen sac, contains cells that produce the male gametophyte ________ d. The male gametophyte is also known as a ____________ e. After double fertilization occurs in the angiosperm, the zygote is _______________ and the cell that will develop into the endosperm is _________________ f. The structure that extends through the style to deliver sperm to the female gametophyte is the ________________ g. The endosperm is formed by the union of a sperm and 2 _______ h. Double fertilization is a characteristic unique to the group of plants known as _________ i. The first plant leaves to form are __________________s 9. Place in correct order for angiosperm double fertilization 2 sperm cells are released from male gametophyte into embryo sac Diploid sporophyte develops Microsporangium bursts open Microsporocyte cells in microsporangium produce microspores Pollen grains land on stigma Pollen tube grows from tube cell in male gametophyte into ovary Zygote and embryo formation 10. 1n, 2n, or 3n a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. Haploid cell Sperm cell Polar nuclei Zygote Megasporocyte cell Megaspore Endosperm Diploid cell Sporophyte Cell with 3 sets of chromosomes Leaf cell Ovum/egg 3