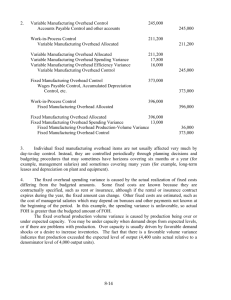
1. The purpose of a flexible budget is to
A. allow management some latitude in meeting goals.
B. eliminate cyclical fluctuations in production reports by ignoring variable costs.
C. compare actual and budgeted results at virtually every level of
production.
D. reduce the total time in preparing the annual budget.
2. Woodside Company manufactures tables with vinyl tops. The standard material
cost for the vinyl used per Style R table is $7.20 based on 8 square feet of vinyl at
a cost of $.90 per square foot. A production run of 1,000 tables in January resulted
in usage of 8,300 square feet of vinyl at a cost of $.85 per square foot, a total cost
of $7,055. The quantity variance resulting from this production run was
A. $255 favorable. B. $255 unfavorable. C. $270 favorable. D. $270
unfavorable.
= (8,300 × $0.90) – (8,000 × $0.9)
= $270 U
3. RHO Company, which began its operations on January 1, produces a single
product that sells for $10.25 per unit. Standard capacity is 80,000 units per year. This
year, 80,000 units were produced and 70,000 units were sold. Manufacturing costs
and selling and administrative expenses follow:
Fixed costs Variable costs
Raw materials — $2.00 per unit produced
Direct labor — $1.50 per unit produced
Factory overhead $120,000 1.00 per unit produced
Selling and administrative 80,000 0.50 per unit sold
What is the standard cost of manufacturing a unit of product?
A. $4.50 B. $5.00 C. $5.50 D. $6.00
Raw materials
Direct labor
Factory overhead - variable
Factory overhead - fixed
Standard unit manufacturing cost
$2.00
1.50
1.00
1.50 ($120,000 / 80,000 units)
$6.00
4. Which one of the following items is ignored when establishing an ideal standard?
A. Cost of materials B. Cost of electricity C. Vacation time D. Sick time
Not 100% sure about 4
5. Belo, Inc. uses a standard cost system. Overhead cost information for Product CO for
the month of October follows:
Total actual overhead incurred $14,750
Fixed overhead budgeted $1,800
Total standard overhead rate per direct labor hour $4.25
Variable overhead rate per direct labor hour $3.75
Standard hours allowed for actual production 3,400
What is the overall (net) overhead variance?
A. $100 favorable B. $100 unfavorable C. $300 favorable D. $300 unfavorable
= $14,750 – (3,400 × $4.25) = $300 Unfavorable
6. What type of direct material variances for price and quantity will arise if the actual
number of pounds of materials used exceeds standard pounds allowed but actual cost is
less than standard cost?
Quantity Price
A. Favorable Favorable
B. Unfavorable Unfavorable
C. Favorable Unfavorable
D. Unfavorable Favorable
The use of material in excess of standard will create an unfavorable usage (quantity)
variance. If the actual cost of the material is less than standard cost, this gives rise to a
favorable price variance.
95
7. Beres Corporation has developed the following flexible budget formula for annual
indirect
labor cost:
Total costs = $9,600 + $0.75 per machine hour
Operating budgets for the current month are based on 30,000 hours of planned machine
time. The amount of indirect labor costs included in this planned budget is
A. $2,425. B. $22,500. C. $23,300. D. $32,100.
Annual fixed costs of $9,600 / 12 = monthly fixed cost
30,000 machine hours × $.75 per machine hour
Indirect labor cost budgeted for the month
$ 800
22,500
$23,300
8. Carlson Co. has a standard material price of $2.80 per unit. During the month of
August, the cost of direct materials was $2.50 per unit for the 500 units produced. The
formula ($2.50 – $2.80) _ 500 yields the _______ variance for Carlson Co.
A. combined price-quantity B. materials price C. volume D. mix
9. Donellan Company has a standard and flexible budgeting system and uses a two
variance method of analysis of overhead variances. Selected data for the February
production activity follows:
Budgeted fixed factory overhead costs $70,000
Actual factory overhead incurred $250,000
Variable overhead rate per direct labor hour $7
Standard direct labor hours 25,000
Actual direct labor hours 26,006
The controllable variance for February is
A. $5,000 favorable. B. $5,000 unfavorable. C. $7,000 favorable. D. $7,000
unfavorable.
Actual factory overhead - standard overhead budgeted for actual level of production =
controllable variance
Budgeted fixed overhead
Standard direct labor hours
Variable overhead rate per hour
Variable overhead budgeted
Total overhead budgeted
Actual overhead incurred
Budget variance--unfavorable
$ 70,000
$25,000
x
7
175,000
$245,000
250,000
$ 5,000
10. If the total materials variance (actual cost of materials used compared with the
standard cost of the standard amount of materials required) for a given operation is
favorable, why must this variance be further evaluated as to price and usage?
A. There’s no need to further evaluate the total materials variance if it’s favorable.
B. Generally accepted accounting principles require that all variances be analyzed in
three stages.
C. All variances must appear in the annual report to equity owners for proper disclosure.
D. Evaluating a favorable variance helps management determine why the variance
occurred.
11. The Johns Company budgeted overhead at $125,000 for the period for Department A
based on a budgeted volume of 50,000 direct labor hours. At the end of the period, the
factory overhead control account for Department A had a balance of $126,000. The
actual (and allowed) direct labor hours were 52,000. What was the overapplied
(underapplied) overhead for the period?
A. $(4,000) B. $4,000 C. $(6,500) D. $6,500
Actual factory overhead incurred - factory overhead applied = over- or underapplied
factory overhead
Budgeted overhead / budgeted direct labor hours =
$125,000 / 50,000 = factory overhead application rate per direct labor
hour
Actual and allowed direct labor hours
Factory overhead applied
$
2.50
x 52,000
$130,000
Actual factory overhead incurred
Overapplied factory overhead for the period
$
126,000
4,000
12. Ben’s Climbing Gear, Inc. has direct material costs as follows:
Actual units of direct materials used 20,000
Standard price per unit of direct materials $2.50
Direct material quantity variance—favorable $5,000
What was Ben’s standard quantity of material?
A. $18,000 B. $20,000 C. $22,000 D. $24,000
$5,000 F = ($20,000 - standard quantity of materials allowed) x $2.50
$2,000 F* = $20,000 - standard quantity of materials allowed
$22,000** = standard quantity of materials allowed
* 5,000 F/ 2.50
** 20,000 + 2,000 (note that the favorable variance is added to the actual quantity to arrive
at the standard quantity because by definition, a favorable variance occurs when standard
quantities exceed actual quantities.)
13. Overapplied factory overhead would result if
A. the plant was operated at greater than normal capacity.
B. the plant was operated at less than normal capacity.
C. factory overhead costs incurred were greater than overhead costs charged to
production.
D. factory overhead costs incurred were less than overhead costs charged to
production.
14. The direct labor costs for Boundary Company follow:
Standard direct labor hours 34,000
Actual direct labor hours 33,500
Direct labor efficiency variance—favorable $12,000
Direct labor rate variance—favorable $15,075
Total payroll $252,925
What was Boundary’s standard direct labor rate?
A. $3.87 B. $8.00 C. $10.50 D. $12.00
Labor efficiency variance = (actual number of labor hours worked - standard number of
labor hours allowed) x standard labor rate per hour
$12,000 F = (33,000 -34,000) x standard labor rate per hour
Actual hours
Standard hours
Standard hours allowed in excess of actual hours
Efficiency variance:
33,500
34,000
500
hours
$12,000 / 500 hours = $24.00 standard rate
15. Elgin Company’s budgeted fixed factory overhead costs are $50,000 per month, plus
a variable factory overhead rate of $4.00 per direct labor hour. The standard direct labor
hours allowed for October production were 20,000. An analysis of the factory overhead
indicates that in October, Elgin had an unfavorable budget (controllable) variance of
$1,500 and a favorable volume variance of $500. Elgin uses a two-variance
analysis of overhead variances.
The actual factory overhead that Elgin incurred in October is
A. $126,500. B. $128,000. C. $128,500. D. $131,500.
Controllable variance = Actual factory overhead - Standard overhead budgeted for actual
activity level*
$1,500 U = Actual factory overhead - $130,000
Actual factory overhead = $131,500 (Unfavorable variance indicates that actual factory
overhead exceeds budgeted amounts.)
* Standard direct labor hours
Variable overhead rate per hour
Variable overhead budgeted
Fixed overhead budgeted
Total overhead budgeted
20,000
x $4.00
$ 80,000
50,000
$130,000
97
16. Thomas Company uses a standard cost system. Information for raw materials for
product RBI for the month of October follows:
Standard unit price $1.75
Actual purchase price per unit $1.60
Actual quantity purchased 4,000 units
Actual quantity used 3,900 units
Standard quantity allowed for actual production 3,800 units
What is the materials purchase price variance for Thomas Company?
A. $15 favorable B. $15 unfavorable C. $600 favorable D. $600 unfavorable
Materials purchase price variance = (actual unit price of materials - standard unit price of
materials) x actual quantity of materials purchased
Materials purchase price variance = ($1.60 - $1.75) x 4,000
Actual unit price
Standard unit price
Excess of standard price over actual
Quantity purchased
$1.60
1.75
$ .15
4,000
units
Purchase price variance (favorable - standard price exceeds actual)
$ 600
17. What type of standard cost is the absolute minimum cost possible under the best
conceivable operating conditions?
A. Practical B. Ideal C. Attainable D. Normal
18. The fixed overhead application rate is a function of a predetermined normal activity
level. If standard hours allowed for good output equal this normal activity level for a
given period, the volume variance will be
A. zero.
B. favorable.
C. unfavorable.
D. either favorable or unfavorable depending on the budgeted overhead.
19. Alyisa Corporation uses a standard cost system. Direct labor information for product
CER for the month of May is as follows:
Standard rate $8.00 per hour
Actual rate paid $8.20 per hour
Standard hours allowed for actual production 1,200 hours
Labor efficiency variance $800 unfavorable
What are actual hours worked?
A. 1,100 B. 1,300 C. 1,330 D. 1,400
Labor efficiency variance = (actual number of labor hours worked - standard number of
labor hours allowed) x standard labor rate per hour
$ 800 U = (actual number of labor hours worked - 1,200) x $8.00
Standard hours standard rate:
1,200 hours $8
Efficiency variance (unfavorable)
Actual hours (X) $8
X=
$10,400
$8
$9,600
800
$10,400
= 1,300 hours
20. A company experienced $21,000 in actual factory overhead incurred. During the
same period, budgeted factory overhead based on actual hours worked was $19,300. The
difference between these two amounts, $1,700, is called the _______ variance.
A. volume B. budget C. efficiency D. quantity
 0
0