Matter & Energy: Particle Nature Study Guide
advertisement

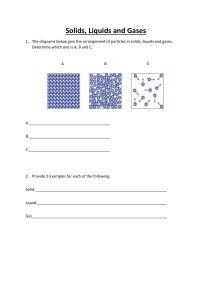
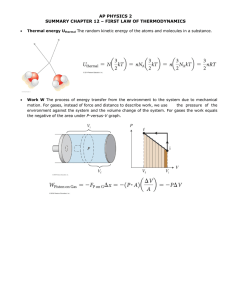
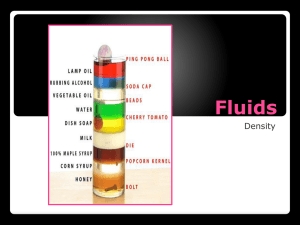
Matter and Energy: Understanding Particle Nature What should I study? Particles versus Empty Space o What do we find between particles? o How come we can walk through liquids and gases? o How come gases can be compressed? o How does the amount of empty space compare in the three states of matter? Qualities of air o Does air push? Does it take up space? Does it have mass? o How do you know? What experiments/ observations support you conclusion? o What is a vacuum? o o Matter and Reactions o What is conservation? o Is mass conserved? Is volume? How can you test this? o Describe the work of John Dalton o Balancing Equations o Physical Properties of Matter Physical versus Chemical changes o What changes and what stays the same? What does each of these terms mean? o Synthesis versus Decomposition reaction o Examples of physical and chemical changes. o Separating Mixtures based on physical properties Particles o What does density mean? What are the units of measure? o o the relationship between mass and volume? How does density relate to sinking and floating? Percent underwater. Rate the density of objects based on whether they are sinking/floating. change from one state of matter to another state of matter? How does temperature affect particle motion and diffusion? How does a thermometer work and what does it actually mean to measure temperature? 1st and 2nd Law of Thermodynamics (directions of energy flow – warm to cool) o Density o What is the formula for finding Density? What is o What ahs to happen for a substance to Particle Motion Model o What do we mean by particle? How does it relate to matter? o What is mass? What is the difference between mass and weight? o How do particles move in liquids and gases? How do they move in solids? (speed, directions, etc). o How can we represent particle motion using particle pictures (what are the key components)? o Parts of an atom - Proton, Neutron, and electron o Relationship between atoms, molecules, and elements Misc o Finding Mass, Volume (both ways), and Heating and Cooling as Processes o What does it mean to call heating a process? Why can’t heat be a physical thing? o What are the different types of heating and how do they work? (conduction, convection, and radiation) o What are the phase/states of matter? density o Using Energy Bar Charts do describe heating. o Reading the Periodic Table o Using Atomic Models to solve problems o Common Chemical symbols Where can I find materials to study? Notebook notes Website resources, blogs, & conference Old labs and Quizzes Worksheets / handouts How can I study? Answer questions on the study guide Make up problems /concept questions Email or IM - Mr. Finley Reread notes and blogs Group study on Class conference Note cards on key vocab. / concept