Clues
advertisement

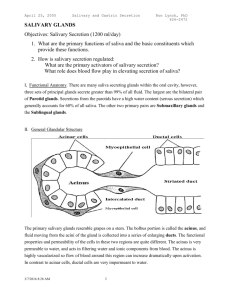
Word for Digestion ACROSS 3. A chronic, inflammatory disease of the colon characterized by ulceration and episodes of bloody diarrhea. 4. The phase of gastric secretion that begins before any food reaches the stomach, by parasympathetic reflexes caused by the smell, taste or thought of food. 8. Salivary glands on the floor of the mouth under the tongue, primarily mucous in type. 11. Salivary gland on the floor of the mouth on the inside surface of the jaw, primarily serous in type. 12. Circular muscles in the pharynx that pull the walls inward during swallowing. 13. The enzyme found in serous salivary secretion that splits starch and glycogen into disaccharides. 14. Distention of the rectal wall by feces acts as a stimulus that initiates the ___ reflex. 17. The enzyme produced by the gastric glands in the stomach that catalyzes the cleavage of large proteins into smaller protein chains. 18. The alternate contractions and relaxation of the longitudinal and circular layers of smooth muscle in the GI tract. 20. Glands that secrete digestive enzymes and mucus into the oral cavity. 24. The process by which food substances are changed into forms that can be absorbed through cell membranes. 26. A complex organ located in the curvature of the duodenum composed of both endocrine and exocrine tissue. 27. The acid that produces a low pH in the stomach between 1 & 3. 29. The tunic that consists of the peritoneum and a connective tissue layer. 31. A fancy word for heartburn. 32. A thin layer of bonelike material that encloses the root of a tooth, 35. Another term for “chew”. 37. The innermost tunic of the alimentary canal 38. A type of enzyme that catalyzes the digestion of lipids. 40. A hormone secreted by the duodenum in response to the presence of lipids which inhibits gastric secretion and mobility of the stomach. 41. An enlarged segment of the digestive tract in the left superior portion of the abdomen. 45. An inactive enzyme precursor which is activated in the stomach by HCl. 49. A thick connective tissue layer containing nerves, blood vessels and small glands below the mucosa. 50.The largest internal organ of the body and major blood chemical factory. 52. Flask shaped cells located in the epithelial layer of the duodenum that produce protective mucus. 54. A straight muscular tube that begins at the termination of the sigmoid colon and ends at the anal canal. 55. The muscularis layer of the GI tract has one smooth muscle layer that is arranged with the cell’s longitudinal to the long axis and the other layer has the cells arranged in a ___ pattern. 58. The canal that extends from the end of the rectum to the anus. 59. A reflex that empties the stomach which is triggered by an irritation or distention in some part of the alimentary canal. 60. A junction between the ileum and the large intestine. 62.Outer most covering of an organ, which is not within serous membranes, consisting of connective tissue from the area around the organ. 63. The tissue that is living, cellular and calcified surrounding the pulp cavity of a tooth. 64. A muscular tube about 9 meters long that passes through the body’s ventral cavity. 65. ___ factor is a glycoprotein that binds with vitamin B-12 and makes it more readily absorbed in the ileum. Word for Digestion DOWN 1. Semifluid material of ingested food mixed with secretions of the stomach. 2. A membranous fold that connects the midline of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. 3. Another name for the large intestine. 5. Bile salts ____ fats, by reducing surface tension of fat globules, into smaller bits that are more easily digested and absorbed. 6. The proximal end of the large intestine. 7. Large folds produced in the stomach when it is empty. 9. A peptic ___ is a condition in which stomach acid and/or bacteria digest the mucosal lining of the GI tract. 10. The region of the stomach nearest the esophageal opening. 13. External GI tract opening at end of the anal canal. 15. The cells located in the gastric glands that produce pepsinogen. 16. Name given to mass of food mixed with saliva that enters the pharynx. 17. The oral cavity is connected to the esophagus via the ___. 19. Part of the GI tract that leads from the pharynx to the stomach. 20. Acidity in the duodenum stimulates the hormone ___ to be released into the circulatory system to inhibit the gastric secretions of the chief and parietal cells. 21. The right & left hepatic ducts unit to form a single ___ hepatic duct. 22. The ___ duct from the gall bladder joins the hepatic duct from the liver to form the common bile duct. 23. 3 or 4 times a day, large portions of the transverse and descending colon undergo several strong peristaltic contractions called ___ ___. 24. The region of the small intestine where the majority of digestion and absorption take place. 25. The longest section of the small intestines, also the middle section. 26. The ___ cells of the gastric glands, produce hydrochloric acid. 28. A major function of the liver, that renders harmful chemicals to less toxic or harmless. 30. The phase of gastric secretion which starts when the food enters the stomach, caused by parasympathetic impulses due to distention of the stomach wall and presence of secretagognes. 33. Minute projections of the cell membrane that greatly increases the surface area of the villi. 34. A drug that stimulates the vomiting center of the medulla oblongata. 36. Following a meal an elevated amount of bicarbonate ions are excreted in the urine due to H+ removed from the blood to produce HCl in the stomach. This is called an ___ tide. 39. The opening between the stomach & small intestine is the ___ opening. 42. The gall bladder stores a secretion from the liver called ___. 43. The alveolar ridges around the tooth are covered by dense fibrous connective tissue & stratified squamous epithelium referred to as ___. 44. When the duodenum becomes filled with chyme it stretches the intestine causing an ___ reflex which sends parasympathetic impulses to the stomach which inhibit peristaltic waves. 46. A saclike structure on the inferior side of the liver that stores and concentrates bile. 47. The tunic that consists of two layers of smooth muscle. 48. A disease called mumps is an infection of these salivary glands. 50. A lymph capillary located in the villus. 51. A small blind tube, containing lymph nodules, attached to the cecum is called the ___ appendix. 53. A proteolytic enzyme in pancreatic juice that starts with the letter “t”. 56. The multitude of fingerlike projections found in the small intestine folds that contain cells of secretion and absorption. 57. A hormone produced by the stomach and duodenum that increases gastric secretion. 61. Extremely hard nonliving acellular substance covering teeth.