Hypnosis
advertisement

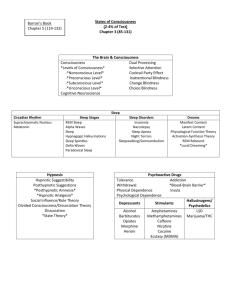
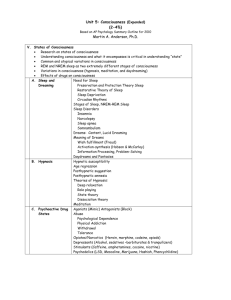
AP Psychology Unit 5: Consciousness Waking, Sleeping, Dreaming, & Hypnosis Key Topics and Terms: Consciousness Selective Attention Daydreams Circadian Rhythms Sleep Brain waves Sleep Disorders insomnia, narcolepsy Dreams Purpose: Theoretical Perspectives Content Hypnosis Social-cognitive view Neodissociation view Posthypnotic suggestion Hypnosis and pain Hidden observer States of Consciousness: Varying degrees of awareness of ourselves and outside world What are the different states of consciousness? Why do we need sleep? What are the purpose of dreams? States of Consciousness Selective Attention Waking States of Consciousness Level of Processing automatic controlled Content of Daydreams internal (imagination) and external (TV) sources success or failure aggression or hostility problem solving erotic fantasies gender differences Daydreams and Fantasies Fantasy Prone Personality Daydreams can help prepare for future events enhance creativity substitute for impulsive behavior Circadian Rhythms (“internal clock”) Circadian Rhythm: Cyclic changes in bodily processes over 24 hour period Sleep Major Stages (shifts in EEG patterns) Stage 1- alpha waves Stage 2- sleep spindles Stage 3 and 4- delta waves REM sleep- beta-like waves, dreams Function of Sleep restores bodily resources parallels circadian rhythms (survival?) Effects of Sleep Deprivation Sleep Across the Lifespan Sleep Deprivation Effects of Sleep Loss fatigue impaired concentration immune suppression irritability slowed performance accidents planes autos and trucks Sleep Deprivation Sleep Disorders Insomnia- difficulty falling asleep Somnambulism- sleepwalking Night Terrors high arousal-appearance of being terrified usually in Stage 4, within 2-3 hours of falling asleep, no memory Apnea- intermittently stop breathing Narcolepsy- unexpected bouts of sleep while awake Dreams Purpose of Dreams Psychodynamic view- repressed wishes Physiological view- brain’s interpretation of random bursts of activity Cognitive view- cerebral cortex is highly active Linking Dreams and Waking Behavior Hypnosis Hypnosis: A trance-like state leading to increased suggestibility a social interaction in which one person (the hypnotist) suggests to another (the subject) that certain perceptions, feelings, thoughts or behaviors will spontaneously occur Views of Hypnosis Social-cognitive view- expectations of social role as “hypnotized subject” Neodissociation view- a split between different levels of consciousness Evidence supports both views Hypnosis Divided Consciousness or Social Phenomenon? Hypnosis Orne & Evans (1965) Posthypnotic Suggestion Hypnosis and Pain Dissociation a split in consciousness Hidden Observer Hilgard’s term describing a hypnotized subject’s awareness of experiences, such as pain, that go unreported during hypnosis