Consciousness
advertisement

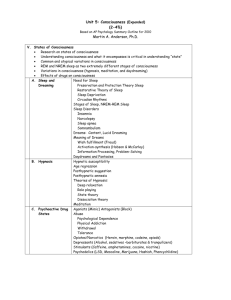
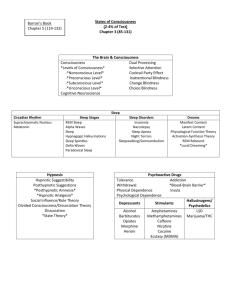
Consciousness Awareness Attention Selective Attention Divided Attention Dichotic Listening Consciousness Ways of Studying Consciousness •Structuralism – Introspection •Behaviorism •Psychophysiology •Subjective Report Consciousness Altered States of Consciousness •Dreaming •Drug States •Hypnosis •Meditation •Near Death Experiences Sleep & Dreaming Stages of Sleep REM Rebound How Much Sleep? Disorders The Purpose of Sleep Dreams Drug States: Types of Drugs Stimulants Depressants •Amphetamine •Alcohol •Cocaine •Barbiturates •Ecstasy (MDMA) •Nicotine •Caffeine Hallucinogens •Valium •LSD •Narcotics •Mescaline •PCP •Psilocybin •Marijuana Drug States: Addiction Tolerance Habituation Opponent Process Theory Opposite Aftereffects Return to Baseline Effects of Repeated Usage Dependence Withdrawal Drug States: Other Factors Dosage Mode of Ingestion Prior Experience Set (Expectancy) LO 4.4 Stages of sleep Stages of Sleep and Brain Waves • Electroencephalograph (EEG) - allows scientists to see the brain wave activity as a person passes through the various stages of sleep and to determine what type of sleep the person has entered. Stages of Sleep and Brain Waves • Alpha waves - brain waves that indicate a state of relaxation. • Relaxed but awake: Alpha waves • Theta waves - brain waves indicating early stages of sleep. • Stage 1: Theta waves appear • Light sleep; person may claim to still be awake • Hypnogogic sensations may occur (floating, falling) and can be incorporated into real memories • Hypnogogic = sensory experiences without sensory stimuli • Hypnic jerk – knees, legs, or whole body jerks • Stage 2: Sleep spindles (brief bursts of rapid brain activity) • Asleep but may respond to some events, such as ringing phone • Sleeptalking may occur Hypnosis • Hypnosis – altered state of consciousness in which the person is especially susceptible to suggestion • 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 Elements of Hypnosis: focus relax accept suggestions use imagination Clinical Hypnosis Posthypnotic amnesia – temporary explicit memory loss, but memories are still there, can affect behavior, and usually returns to conscious awareness Posthypnotic suggestion - suggestion to be carried out after the subject is no longer hypnotized used by some clinicians to help control undesired symptoms and behaviors Most effective for pain control, headaches, asthma, skin and weight conditions (psychologically-based) Less effective for addictions (physiologically-based) Power of believing is the key