molarHmCdT student ppt2012
advertisement

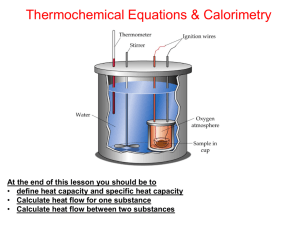
CALCULATION OF ENTHALPY CHANGES MOLAR ENTHALPY - the enthalpy change for 1 mole of a substance associated with a chemical, physical or nuclear change the units will J or kJ per mole EX. A common refrigerant , Freon-12, has a molar mass of 120.91 g/mol. The molar enthalpy to vaporize Freon is 34.99 kJ/mol. If 500 g of Freon is vaporized, what is the enthalpy change? SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY - the symbol is C - the units are J/g˚C or Jg-1˚C-1 Specific heat capacity is a measure of how ‘easily’ a substance changes temperature. A substance with a high heat capacity can absorb more energy without changing temperature than a substance with low specific heat. HEAT TRANSFER PROBLEMS - When Tf is greater than Ti : - When Tf is less than Ti: EX. A 150 g sample of Pb at 100.0 °C is plunged into a beaker containing 50 g of water at 22.0 °C. The final temperature of the mixture is 28.8 °C. a) What is the energy change (q) for the water? b) How much energy is lost by the Pb? c) Calculate the CPb. EX. While running an adult expends 5.0 x 105 J/mile. If this energy could be transferred as heat to a beaker of water, how many grams of water could be heated from 25.0 °C to 100.0 °C? CALORIMETRY Calorimeter – an insulated device used to determine temperature changes during a chemical or physical process. - the calorimeter is part of the surroundings Two Kinds: 1) 2) Simple Calorimetry -the process occurs at constant pressure ΔHobserved = mCΔT = - ΔH rxn RECALL that ΔH is + for an ENDOTHERMIC change and – for an EXOTHERMIC ASSUMPTIONS: - for a dilute aqueous solution, use Cwater = 4.18 J/g°C as the heat capacity for the solution - 1 mL of solution = 1 g of solution - no heat is transferred to the outside of the calorimeter( ie the calorimeter is perfectly insulated) See Diagram EX. 5.00 mL of 1.0 mol/L NaOH and 5.00 mL of 1.0 mol/L HCl are mixed in a simple calorimeter. The initial temperature of each substance is 23.0 °C. After mixing, the temperature rose to 27.5 °C. a) What is the enthalpy change for this rxn? b) Calculate the energy change per mole of HCl. EX. 1.50 g of NH4NO3 is added to 35.0 g of water in a simple calorimeter. The initial temperature of the water is 22.7°C and the final temperature of the mixture is 19.4 °C. Calculate the enthalpy change per mole of salt. Bomb Calorimetry - the process occurs at constant volume - used to measure the heat released in a combustion reaction See Diagram q observed = C’ΔT = - q combustion NOTE: EX. A food manufacturer wishes to know the number of calories per serving of a new dessert. They hire a chemist at the Dep’t of Consumer Affairs to help them out. a) The chemist places a 1.00 g sample of the dessert in a bomb calorimeter. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 8.151 kJK-1. The temperature increases by 4.937 °C. Calculate the number of food calories (kcal) in the sample of dessert. b) A single serving of the dessert weighs 30.00 g. How many food calories are in the dessert?