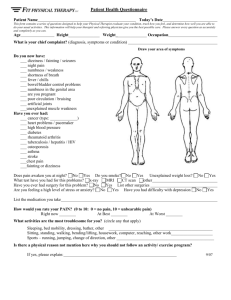
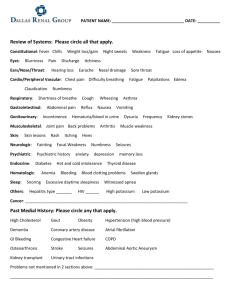
OMM in the ED - The American College of Osteopathic Emergency
advertisement

Treatment Suggestions for Common ED Complaints Chest Pain • Inhibition for ribs (highest yield will be superior rib in the group-pain decreases respiration, decreasing motion of rib) • Diaphragmatic release • Rib raising • Functional treatments to thoracic spine • • • • Pneumonia Gentle articulatory technique to the ribs and spine Rib raising (supine lateral traction and passive range of motion to inhalation and exhalation) Lumbocostal arch release (external arcuate liga- ment release by lateral traction to 12th ribs) Direct diaphragm release Direct sternal release Thoracic duct release Condylar decompression (possible vagal involve- ment), CV4 • Gentle fascial release to hip and sacroiliac Kidney Stones • Occipitoatlantal and cranial base decompression and release • Still technique for somatic dysfunction of thoracolumbar junction/thoracic diaphragm • Thoracolumbar (T10-L2) paraspinal inhibition • Rib raising • Counterstrain of anterior myofascial tender Psoas muscle spasm treatment • L umbar/sacral/pelvic soft tissue articulation and/or decompression and release Sources: American Osteopathic Association. Foundations for Osteopathic Medicine. 2nd ed. Lippincott William & Wilkins; 2002. Savarese, RG. OMT Review. 3rd Ed. OMT Review; 2003. Treatment Suggestions for Common ED Complaints SOB/Palpitations • Rib raising • Thoracic spine-muscle energy • Thoracic spine-myofascial release • Cervical spine-suboccipital release • Thoracic inlet-myofascial release • Thoracic outlet-myofascial release • Lymphatic pump techniques Back Pain • Proposed treatment sequence: Leg restrictors, pubes, superior innominate upslip (shear), lumbar spine, sacrum, innominate, iliopsoas • Direct- HVLA, muscle energy, articulatory • Indirect-Strain counterstrain, functional methods • *Look for back pain red flags before treating* [such as paresthesias, bowel/bladder incontinence, neurologic deficit, insidious onset, constitutional symptoms] • • • • • • • Pelvic Pain Cranial techniques OA condylar decompression HLVA to the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine Muscle energy to the sacrum and pelvis Articulatory techniques to the feet Pelvic diaphragm release Pedal pump OMM in the ED Sympathetic Innvervations T`1-T4: Head and neck T1-T4: Heart T1-T6: Lungs T5-L2: GI Tract and Pelvis T5-T9: Upper GI, Liver, Duodenum, Pancreas T10-T11: Small Intestine, Right Colon, Adrenals, Gonads, Kidney’s, Upper Ureter T12-L2: Left Colon, Pelvis, Lower Ureter, Bladder, Genetalia Parasympathetic Innervations CN III, VII, IX -> head CN X ->heart, lungs, trachea, liver, gallbladder, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, small intestine, ascending and transverse colons. S1-3 ->sex organs, external genitalia, bladder and its sphincters *No parasympathetic innervation of the extremities Cranial Nerve Lesions C5: Weakness of the deltoid. Numbness of the shoulder. Biceps reflex diminished or absent. C6: Weakness of the biceps brachii. Biceps brachii reflex diminished or absent. Numbness over the thumb. C7: Weakness of the triceps brachii. Triceps brachii reflex diminished or absent. Numbness of the index and middle fingers. C8: Weakness of the interossei (tested by having patientspreadfingersagainstresistance). Reflex Numbness of the ring and little finger. Lumbar Nerve Lesions L4: Pain over the low back, hip, posterolateral thigh, and anterior leg. Numbness of the anteromedial thigh and knee. Weakness and atrophy of the quadriceps. Knee jerk reflex diminished. L5: Pain over the sacroiliac joint, hip, lateral thigh, and leg. Numbness of the lateral leg and web of the great toe. Weakness with dorsiflexion of the great toe and foot with difficulty walking on heels, foot drop possible. Atrophy is minor. Uncom- mon to have changes in reflexes (if present, absent or diminished posterior tibial reflex) Compiled by Cara Norvell, DO Images: The Ohio Univeristy Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine S1: Pain over the sacroiliac joint, hip, posterolateral thigh, and leg to heel. Numbness in the back of the calf, lateral heel, lateral foot, and lateral toe. Weakness with plantar flexion of the foot and great toe with difficulty walking on the toes. Atro- phy of the gastrocnemius and soleus. Ankle jerk reflex diminished or absent.