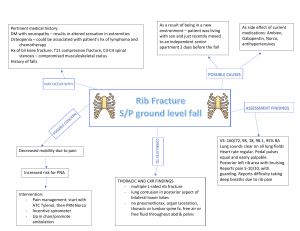
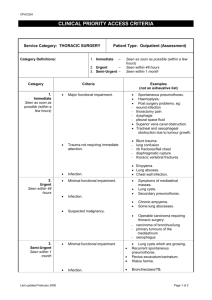
Lung segmentation method using the rib information The initial lung
advertisement

Lung segmentation method using the rib information The initial lung segmentation and 3d surface extraction followed Bae’s method [1]. Bae’s method calculated the thoracic cavity region by segmenting multi-organs, while the inner thoracic wall and diaphragm were modeled by using a threedimensional surface-fitting method. But on the contrary to Bae’s method which extracted the thoracic cavity, we applied the rib surface to lung segmentation (Fig. 1). To apply the extracted surface, we used the morphological operations (Fig. 2). This operation is the sequence of 4 pixel closing (house-made function), fill-hole, and opening operations (kernel size 2- ITK library function) [2]. Prasad et al. developed the probabilistic method to use the rib information for selecting the threshold [3]. As there is irregular gab between the lung boundary and the rib surface, it is so difficult to use the rib surface. A level set method can be applied for the movement of active contour under a highly weighted curvature term. This level set can preserve the convex shape. We used a library class in ITK Toolkit called as Shape Detection Level Set Image Filter [2]. For parameter setting in the class, the Propagation Scaling, the Curvature Scaling, the number of iterations and root mean square error were set to 1, 10, 150, and 0.3, respectively. In this class, generally, the values of the edge potential map approach zero as the corresponding region is close to the edges. The edge potential map value of the initial lung was set to zero, while the other area was set to one. The level set makes different result shape from different initial shape in the aspect of the optimization. Especially, in this case, the level set adapted the limited iteration to reduce the band gap between the lung and the thoracic cavity, and this limited iteration was selected empirically. So the combination of the morphological operation and the level set is the good way to use the thoracic cavity information to improve the diseased lung segmentation. REFERENCES 1. 2. 3. Lama VN, Flaherty KR, Toews GB et al (2003) Prognostic value of desaturation during a 6-minute walk test in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:1084-1090 National Library of Medicine Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit (ITK) Kim N, Seo JB, Lee Y, Lee JG, Kim SS, Kang SH (2009) Development of an automatic classification system for differentiation of obstructive lung disease using HRCT. J Digit Imaging 22:136-148