Economics Worksheet: Scarcity, Systems, Growth
advertisement
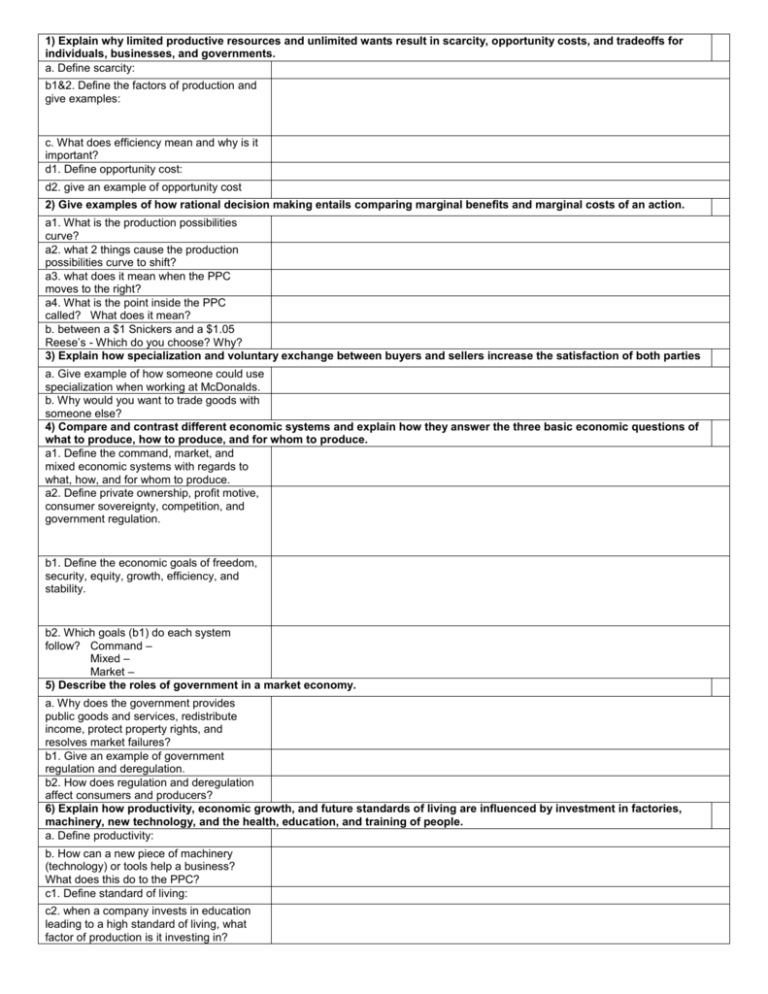
1) Explain why limited productive resources and unlimited wants result in scarcity, opportunity costs, and tradeoffs for individuals, businesses, and governments. a. Define scarcity: b1&2. Define the factors of production and give examples: c. What does efficiency mean and why is it important? d1. Define opportunity cost: d2. give an example of opportunity cost 2) Give examples of how rational decision making entails comparing marginal benefits and marginal costs of an action. a1. What is the production possibilities curve? a2. what 2 things cause the production possibilities curve to shift? a3. what does it mean when the PPC moves to the right? a4. What is the point inside the PPC called? What does it mean? b. between a $1 Snickers and a $1.05 Reese’s - Which do you choose? Why? 3) Explain how specialization and voluntary exchange between buyers and sellers increase the satisfaction of both parties a. Give example of how someone could use specialization when working at McDonalds. b. Why would you want to trade goods with someone else? 4) Compare and contrast different economic systems and explain how they answer the three basic economic questions of what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. a1. Define the command, market, and mixed economic systems with regards to what, how, and for whom to produce. a2. Define private ownership, profit motive, consumer sovereignty, competition, and government regulation. b1. Define the economic goals of freedom, security, equity, growth, efficiency, and stability. b2. Which goals (b1) do each system follow? Command – Mixed – Market – 5) Describe the roles of government in a market economy. a. Why does the government provides public goods and services, redistribute income, protect property rights, and resolves market failures? b1. Give an example of government regulation and deregulation. b2. How does regulation and deregulation affect consumers and producers? 6) Explain how productivity, economic growth, and future standards of living are influenced by investment in factories, machinery, new technology, and the health, education, and training of people. a. Define productivity: b. How can a new piece of machinery (technology) or tools help a business? What does this do to the PPC? c1. Define standard of living: c2. when a company invests in education leading to a high standard of living, what factor of production is it investing in?











