a Copy
advertisement

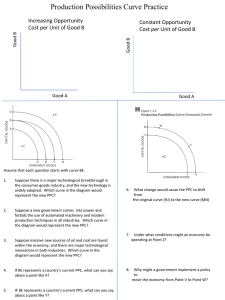
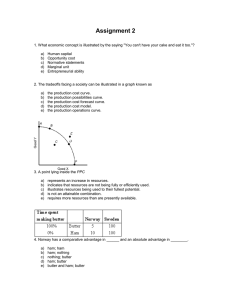
Homework: - Answer Chapter 1 Discussion Questions 9 & 10. - Answer AP Review Questions 6 & 7. - Do Problems #1, 2, 5, 6, & 7 on pages 22 & 23. Questions from last Thursday’s problem sets? Chapter 1 Review The Economizing Problem Society’s wants are unlimited. Economic resources are scarce. Resource Categories • Land (land and natural resources) • Capital: all manufactured goods used in producing consumer goods and services. – NOT money, that’s how it’s used in finance. • Labor • Entrepreneurial Ability Resources • Resources are also known as the FACTORS OF PRODUCTION. - Your book will refer to “resource markets” where these resources are bought and sold, and that’s fine, but AP generally uses the term “factor markets.” The Economizing Problem • Using scarce resources to satisfy the maximum amount of wants. To get there, an economy must attain: • Full Employment: full use of all available resources (not just labor). • Full Production: Most efficient use of our resources. – Productive efficiency: the production of goods and services in the least costly way. – Allocative efficiency (optimal allocation): producing the particular mix of goods and services that society most wants. Production Possibilities Tables, Curves, Frontiers. The Production Possibilities Curve • Is Downward Sloping. –Why? The Production Possibilities Curve • Is Bowed Out (or concave) to the axis. –Why? The Production Possibilities Curve Rice • It’s Bowed Out due to the law of increasing opportunity costs. Wheat A production possibilities curve for security and all other goods and services. What is the opportunity cost of increasing security from SA to SB ? Answer: OA - OB The Production Possibilities Curve • You will see some PPCs that are straight, rather than bowed out. –What does that tell us? –Why use a straight PPC? – Review: tell me about these points: X, W, A-E. Allocative Efficiency (optimal allocation) • What combination of goods and services is most wanted by society? • Requires that the production or consumption of a good be increased until its marginal benefit = marginal cost. Unemployment and Productive Inefficiency • Both will cause an economy to produce goods at some point inside of its PPC. Economic Growth • Will cause a PPC to shift outwards. 1. Assume that Patelland produces only socks and shoes, and that its available resources are not completely adaptable to both purposes. a. Sketch a correctly labeled PPC for Patelland. (2 pts.) b. Draw and label a point on the PPC that shows Patelland experiencing unemployment. (1 pt.) c. Draw a new curve on your PPC that shows the effect of an increase in land suitable for growing cotton and improvements in leather tanning technology. (2 pts.) 2. Assume that Bloomersburg produces only bats and balls, and that its available resources are completely adaptable to both purposes. a. Sketch a correctly labeled PPC for Bloomersburg. (2 pts.) b. Draw and label a point on the PPC that shows Bloomersburg operating at full employment and productive efficiency. (1 pt.) c. Draw a new curve on your PPC that shows the effect of an improvement in woodturning lathes in Bloomersburg. (2 pts.)