Production Possibilities Curve - Abernathy-ApEconomics
advertisement

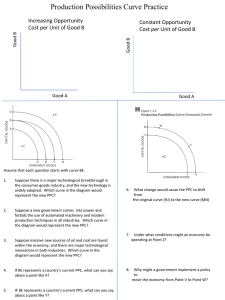
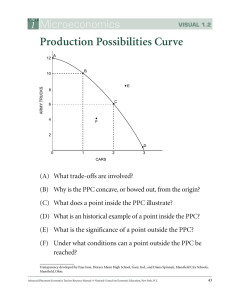
Production Possibilities Curve • *Remember what a trade-off is: it is when you give up something to have something else • Economist use the Production Possibilities Curve model to show the trade-offs necessary in any economy ▫ The purpose is to improve our understanding of tradeoffs by considering a simplified economy that produces only two goods • There is a crucial distinction between points inside or on the PPC and points outside the PPC. ▫ If a point is inside the curve it shows that something is feasible or possible ▫ If a point is outside of the curve it shows that something is not feasible or possible. • The PPC also shows both the extreme trade-offs as well as less extreme trade-offs • The PPC is also useful for illustrating the general economic concept of efficiency ▫ An economy is efficient if there are no missed opportunities or if there is a way to make some people better off without making other people worse off. • If an economy is producing at a point on its production possibilities curve- the economy is efficient in production *Remember: to be inefficient means you are missing the opportunity to produce more of both • Another example of inefficiency in production occurs when people in an economy are involuntarily unemployed. ▫ When this occurs an economy is not efficient in production because it could produce more output if those people were employed ▫ The PPC shows the amount that can possibly be produced if those people were employed Another way to say this is changes in unemployment move the economy closer to, or further away from the PPC The curve is determined by what would be possible if there was full employment in the economy. • It is important to remember that efficiency in production is only part of what’s required for an economy to be efficient. ▫ Efficiency also requires that an economy allocate its resources so that consumers are as well off as possible. If an economy does this we say that it is efficient in allocation • Efficiency for the economy as a whole requires both efficiency in production and efficiency in allocation. REMEMBER: What is opportunity costs? 3. Types of Opportunity Costs 1. As unchanging or zero opportunity cost ▫ If the opportunity cost does not change when a unit is added it is reflected in a vertical axis and horizontal axis. 2. As a constant opportunity cost ▫ If as you move down the slope and it has a constant slope it is implying a constant opportunity cost. (12 to 10= -2, 10 to 8 = -2, etc) 3. Increasing opportunity cost a. It is reflected in a bowed out slope