cell organelles
advertisement

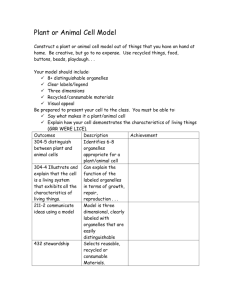
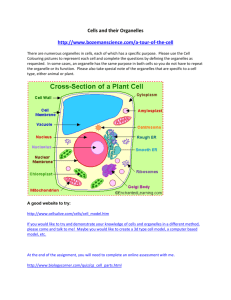
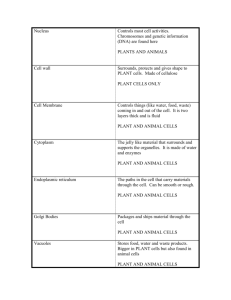
Topic: Cell Organelles Essential Question: How do the parts of a cell work together to function as a “system”? All those who believe in psychokinesis raise my hand. -Steven Wright 9/16/14 INB page 12-13 So what is LIFE? 1. 2. 3. 4. Made of cells -cell theory Uses energy for processes - metabolism Reacts to its environment- homeostasis Reproduction -genetic passing of traits Cell Organelles We are going to start our look at life by zooming in to study the basic unit of life – the cell - and its parts – organelles. Many of these organelles have complicated names that can be confusing. How can you make sense of these complicated names? One structure found in cells is called a lysosome. If you know that the “-some” comes from the root “soma” which means “body” and “lyso-” from “lysis”, meaning “loosen" or “split", what do you think a lysosome is? What could a lysosome do? On page 13, start by recording the following… Cell Theory • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic units of life. • Cells come from existing cells. In your notebook: • Make two columns on the top of page 12. • Label 1st column: “Give One” • Label 2nd column: “Get One” • In the “Give One”, list as many cell organelles as you can. • Go around the room, find a student who does not have one of your “Give One” organelles and share with them, then get one of that person’s that you do not have. • Pick up piece of Scratch Paper. Return to your seat. Number 1 to 20 on the paper. Cell Structure Knowledge Base Evaluation Write down the appropriate name or function for the structure identified. •1. The diagram below represents what general type of cell? 2. What is the name of the structure labeled “G”? 3. What is the name of the structure labeled “E”? 4. What is the name of cell organelle labeled “B”? 5. Identify the part of the cell labeled C. 6. Identify the cell organelle labeled D. 7. What structure takes up the majority of space in each of the cells below?. 8. What structure is between each of the cells below? 9. What cell structure is labeled A? 10. What large, round structure is labeled B? 11. What cell structure is labeled D? 12. Is this a plant or animal cell? How can you tell? 13. What cell structure is labeled D? 14. What cell structure is labeled B? 15. What organic molecule is produced in the cell structure labeled B? 16. What cell structure is labeled C? 17. What cell structure is labeled E? 18. What cell structure is labeled A? 19. What cell structure is labeled C? 20. What organic molecule is stored in the cell structure labeled C? Thank you- Hold on to your papers!!! Back to page 13… • Cells function as “systems”. • What IS a system? Cell Organelles Day 2 Essential Question: How do the parts of a cell work together to function as a “system”? When everything is coming your way, you're in the wrong lane. -Steven Wright 9/18/14 INB page 14-15 Today you will be forming groups to ultimately create a poster representing a metaphor of a CELL. 1. Pick a system metaphor from pitcher. 2. Get together as group. 3. Research organelles and record on page 15 using “jigsaw” technique. ▫ organelle name/ function/ sketch 4. Everyone should have list of all organelles and function. 5. Within group, assign 4 organelles per person. ▫ By the end of today. 6. Each creates metaphors for each organelle and brings back to group to “vet”. Cell Organelles Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Ribosome Cell Wall Nucleus Nucleolus Centrosome Lysosome Endoplasmic Reticulum Vesicle Golgi apparatus Mitochondrion Chloroplast Central Vacuole / Vacuole Nuclear envelope Plastid (ex. leucoplast) Create a Cell Metaphor Poster Reflects 16 Organelles Each connected within a system Cellular Structure/Function – connection to analogy explained accurately Graded: Individually for 4 organelle metaphors Group for poster aesthetics & neatness Cell Structures you should have on your poster. Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Ribosome Cell Wall Nucleus Nucleolus Centrosome Lysosome Endoplasmic Reticulum Vesicle Golgi apparatus Mitochondrion Chloroplast Central Vacuole / Vacuoule Nuclear Membrane Plastid (ex. leucoplast)