Ionic Bonding
advertisement

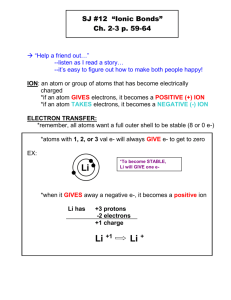
Types of Chemical Bonds • Covalent Bonds – Single – Double – Triple -- Polar -- Non-Polar Once again… AN OVERVIEW of the 3 main types of bond: while keeping in mind: • Ionic Bonds • Metallic Bonds • Other “Bonds” – Inter-Molecular Forces Ionic Bonds An ionic bond is the attraction between a metal cation and a non-metal anion Metallic Bonding Atoms are unhappy if their outer energy level is not full!! Atoms only bond with other atoms in order to fill their outer energy level. Covalent Bonds A covalent bond exists when two electrons are shared by non-metallic atoms. Ionic bonds Metal + Non-metal • Difference in electronegativity is high; so high that non-metal atoms will strip away valence electrons from the metal atoms, forming ions. Takes place in a “SEA” OF MOBILE VALENCE ELECTRONS These bonds are formed due to an attraction between opposite charges (+,-); there is no sharing of electrons. 1 Ionic Bonds Ionic Bonds 17+ 11+ Sodium Chlorine 17+ 11+ Sodium Ion (+1) Na now has 11p+ and 10e-. It now carries a charge of +1. Ionic Bonding: How it Works Chloride Ion (-1) Cl now has 17p+ and 18e-. It now carries a charge of -1 Rules for Naming Ionic Compounds: i) Metal + Non Metal ii) Ions Form (via electron transfer) • • iii) Opposites attract Name the cation Name the anion 2 Questions: Why don’t we need any prefixes? How do you name a cation or an anion? Naming Cations • Cation- if the charge is always the same (i.e. Groups 1, 2 or 13) just write the name of the metal. Examples: Sodium Aluminum Magnesium • Transition metals can have more than one type of charge, so we need Roman Numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Examples: Copper (II) Titanium (IV) Iron (III) +1 Some element always form the same old ions… +2 +3 -3 -2 -1 2 • • • • Na +1 Al +3 Fe +2 Pb +2 Name these Write Formulas for these • • • • Potassium ion Magnesium ion Chromium (IV) ion Mercury (II) ion Name these • • • • Cl-1 N-3 Br-1 S-2 Write Formulas for these • • • • Sulfide ion Iodide ion Phosphide ion Sulfide ion And practice with predicting formulae: SrBr2 ______ Strontium Bromide TiO2 ______ Titanium (IV) Oxide CoS ______ Cobalt (II) Sulfide Li3N ______ Lithium Nitride AlCl3 ______ Aluminum Chloride Naming Anions • Non-metals are predictable; each nonmetal element can only form one anion. • Change the element ending to – ide • Fluorine (F) becomes Fluoride (F1-) • Oxygen (O) becomes Oxide (O2-) Now for practice naming the compounds: KI Potassium Iodide __________________________ TiCl Titanium (I) Chloride __________________________ MnBr2 Manganese (II) Bromide __________________________ Al2O3 Aluminum Oxide __________________________ Ions are charged atoms… …or charged groups of atoms. Polyatomic ion: A covalently bonded group of atoms with a net charge. 1- Anions: Acetate C2H3O2 -1 Hydroxide Nitrate NO3-1 Permanganate MnO4-1 Nitrite NO2-1 Cyanide OH-1 CN-1 3 More polyatomic ions 2- Anions: SO4-2 Sulfite SO3-2 Carbonate CO3-2 Chromate CrO4-2 Dichromate Cr2O7-2 Sulfate 3- Anions: Phosphate PO4-3 Phosphite PO3-3 Ammonium NH4+1 Magnesium Hydroxide __________________________ Sodium Acetate NaC2H3O2 __________________________ CuSO4 KOH 1+ Cations: Now for practice naming these compounds: Mg(OH)2 Ionic Compounds containing polyatomic ions have ionic and covalent bonds: Copper (II) Sulfate __________________________ Calcium Phosphate Ca3(PO4)2 __________________________ K+ Ionic bond (:O H)- And practice with predicting these formulae: CaCO3 ______ Calcium Carbonate NaOH ______ Sodium Hydroxide KMnO4 ______ Potassium Permanganate Pb(NO3)2 ______ Lead (II) Nitrate MgSO3 ______ Magnesium Sulfite 4