painting/spraying operations
advertisement
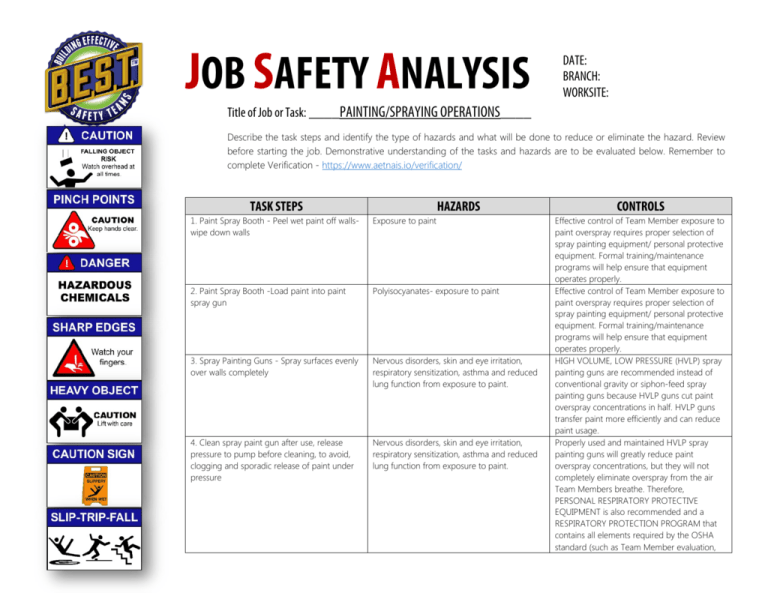
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS DATE: BRANCH: WORKSITE: Title of Job or Task: ____PAINTING/SPRAYING OPERATIONS____ Describe the task steps and identify the type of hazards and what will be done to reduce or eliminate the hazard. Review before starting the job. Demonstrative understanding of the tasks and hazards are to be evaluated below. Remember to complete Verification - https://www.aetnais.io/verification/ TASK STEPS HAZARDS 1. Paint Spray Booth - Peel wet paint off wallswipe down walls Exposure to paint 2. Paint Spray Booth -Load paint into paint spray gun Polyisocyanates- exposure to paint 3. Spray Painting Guns - Spray surfaces evenly over walls completely Nervous disorders, skin and eye irritation, respiratory sensitization, asthma and reduced lung function from exposure to paint. 4. Clean spray paint gun after use, release pressure to pump before cleaning, to avoid, clogging and sporadic release of paint under pressure Nervous disorders, skin and eye irritation, respiratory sensitization, asthma and reduced lung function from exposure to paint. CONTROLS Effective control of Team Member exposure to paint overspray requires proper selection of spray painting equipment/ personal protective equipment. Formal training/maintenance programs will help ensure that equipment operates properly. Effective control of Team Member exposure to paint overspray requires proper selection of spray painting equipment/ personal protective equipment. Formal training/maintenance programs will help ensure that equipment operates properly. HIGH VOLUME, LOW PRESSURE (HVLP) spray painting guns are recommended instead of conventional gravity or siphon-feed spray painting guns because HVLP guns cut paint overspray concentrations in half. HVLP guns transfer paint more efficiently and can reduce paint usage. Properly used and maintained HVLP spray painting guns will greatly reduce paint overspray concentrations, but they will not completely eliminate overspray from the air Team Members breathe. Therefore, PERSONAL RESPIRATORY PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT is also recommended and a RESPIRATORY PROTECTION PROGRAM that contains all elements required by the OSHA standard (such as Team Member evaluation, selection of appropriate air-purifying or supplied-air respirators, fit-testing, training, and maintenance) will be needed to fully protect Team Members from this hazard. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Do Not Mix Chemicals. Use assigned chemicals only. REQUIRED EDUCATION & TRAINING • • • • • • • • GHS – Hazard Communication Respiratory program Respiratory FIT testing 6S procedure Slips, trips, and falls Bloodborne pathogens Near miss reporting Fall protection REQUIRED PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (PPE) • • • • • • • • • • • • • Safety Glasses Chemical resistant gloves Fall protection Hearing protection Hard hat Safety steel toe shoes Safety goggles Harness lanyard Slip resistant shoes Leather gloves Face shield Respirator Tyvek suit JSA CLIENT CONTACT INFORMATION FIRE PULLS LOCATION ___________________________________ Training Observation Rating FIRE EXTINGUISHER LOCATION ___________________________________ Please mark “X” in the appropriate color to indicate a record of understanding and demonstrative ability to complete tasks: SAFETY SHOWER LOCATION ___________________________________ EYE WASH LOCATION ___________________________________ FIRST AID/ MED. STATION LOCATION ___________________________________ EMERGENCY PHONE NUMBER ___________________________________ Completed the tasks correctly without additional instruction Completed the tasks with limited instruction Difficulty completing tasks and process. Notes: Notes: If you are being asked to perform work that you believe is unsafe, talk to your supervisor. If the issue is not resolved, call EHS at X2615, X5747, X5174 or Security at X5227 OPERATIONS CONTACT EHS & RISK MGMT. [614]246.8166 [614]246.8305 [FAX] safetyrisk@aetnabuilding.com MEDCOR [800]775.5866 HOURS: 24/7 JOB STEPS POTENTIAL HAZARDS RECOMMENDED SAFE JOB PROCEDURES Break down the job into its basic steps, e.g., what is done first, what is done next, and so on. You can do this by: For each step, ask yourself what accidents could happen to the employee doing the job. You can get the answers by: 1. Observing the job 2. Discussing it with the operator 3. Drawing on your knowledge of job 4. A combination of the three. 1. Observing the job. 2. Discussing it with the operator 3. Recalling past accidents 4. A combination of the three Record the steps in their normal order of occurrence. Describe what is done, not the details of how it is done. Ask yourself; can he/she be struck by or contacted by anything; could they strike against or come in contact with anything; could the employee be caught in, on, or between anything; can they fall; be over exerted; or be exposed to anything injurious such as gas, radiation, welding rays, etc.? For example, acid burns, fumes. For each potential accident or hazard, ask yourself what safeguards should be provided for the employee and how should the employee do the job step to avoid the potential accident, or what should they do or not do to avoid the accident. You can get your answers by: 1. Observing the job for leads 2. Discussing precautions with experienced job operators 3. Drawing on your experience 4. A combination of the three Usually three or four words are sufficient to describe each basic job step. For example, the first basic job step in using a pressurized water fire extinguisher would be: 1. Remove the extinguisher from the wall bracket. Completed by: ____________________________________ Be sure to describe specifically the provided safeguards and precautions an employee must use. Don’t leave out important details. Number each separate recommended precautions with the same number you gave the potential accident (see center column) that the precaution seeks to avoid. Use simple do or don’t statements to explain recommended precautions as if you were talking to the employee. Signature: ____________________________________



![[Agency] recognizes the hazards of lead](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007301017_1-adfa0391c2b089b3fd379ee34c4ce940-300x300.png)




