Discipline, Number, Title: Music 101, Music Appreciation Units and
advertisement

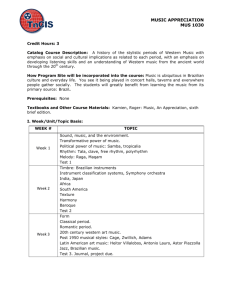
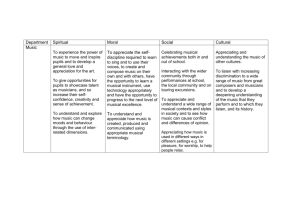
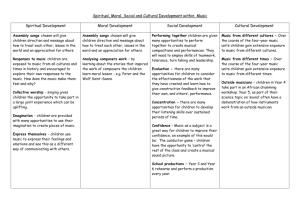
Music 101 Page 1 of 5 Course Outline of Record Curriculum Council Approval Date: 11/04/2013 Discipline, Number, Title: Music 101, Music Appreciation Units and Hours: 3.00 Units 48.00 Hours Lecture Catalog Entry: Designed to increase awareness and appreciation of music from the European classical tradition in relation to general culture and history. Develops basic understanding of musical elements and deepens students' experience of music. Recommended for non music majors. Requisites: Prerequisite: None Corequisite: None Recommended Preparation: None Repeatability: Non-Repeatable Pass/No Pass Only: No Open Entry/Open Exit: No Credit by Exam: No Course Purpose: z z z z z z z To acquaint the student with the great masterpieces of music through media and live concerts. To give an historical background of each period of music and of the composers' lives, stressing the influence of political, religious, social, and philosophical institutions on these composers and their music. To give the student a rudimentary knowledge about the technical aspects of music, thereby increasing appreciation of the talent and genius of composers and performers. To create an awareness that music is a body of literature which represents the thoughts and feelings of some of the greatest minds and spirits throughout history. To relate the history of music to other fields and to our contemporary life to make it relevant. To help the student develop powers of observation and reasoning and the ability to think for oneself. To instill in students the habit of attending concerts. http://www.curricunet.com/sccc/reports/course_outline_report.cfm?courses_id=2974 9/26/2014 Music 101 z z z Page 2 of 5 To develop critical listening and critical thinking. To develop the ability to express in language reactions to the music. To show how music from other world cultures has contributed to European classical music. Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to Students will demonstrate an understanding of basic significant western musical styles. Students will aurally identify the most important composers' representative compositions from each major music era. Course Identification Number(s) (C-ID): MUS 100 (approved 2013) Music Appreciation General Education & Transfer: CSU GE (Plan B): Area C1: Arts (Art, Dance, Music, Theatre) IGETC (Plan C): Area 3A: Arts SCC GE (Plan A): Area C: Humanities Transfer Status: A. Transfers to UC & CSU Applies to the Following Programs: Elementary Teacher Education - A.A. Degree for Transfer -Required Liberal Arts: Arts, Humanities, and Communication - A.A. Degree -Elective Philosophy - A.A. Degree -Elective Course Content and Objectives: Lecture Approx. Hours 3.00 Content Introduction to course. z z 6.00 The function of music in Western culture. Elements of musical art: melody, rhythm, harmony, tempo, vocal and instrumental music, instruments and their timbre. Objective Students will be able to identify the many functions of music and gain an understanding of the general parameters of music. The music of the Students will be able to place music of the Middle following time periods: Ages, Ars Nova and Renaissance into an historical time frame with antecedents from Jewish chant and other http://www.curricunet.com/sccc/reports/course_outline_report.cfm?courses_id=2974 9/26/2014 Music 101 Page 3 of 5 z z z 6.00 Baroque Period z 6.00 z z 9.00 Discussion of musical forms, style, symbolism, and notation. The music of Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven. Romantic Era introduction: Piano pieces and songs- Schubert Late Romantic, Impressionistic, and Early 20th Century music. z Students be able to associate various composers with the musical styles of these periods through visual observations of scores and listening to various compositions. Students will be able to identify the important elements of these musical styles and associate them with specific composers. Includes Far Eastern sources for Impressionistic music as well as black minstrel sounds and Romantic Periods. The music of Mahler, Debussy, Ravel, Stravinsky, Schoenberg, and Berg. Romantic Era. z Students be able to identify separate vocal, choral and instrumental styles and idioms. Purcell, Vivaldi, Bach Classical Period: z 6.00 The Middle Ages Middle Eastern sources. - Leonin and Perotin. Ars Nova Machaut, secular music. Renaissance French Chansons-Dufay, Josquin; Italian vocal music Palestrina, Lassus Gabrieli, Monteverdi, English Madrigal. Musical forms, program music, symphony, Students be able to: z z distinguish from among these various musical forms. associate with the music of these composers with http://www.curricunet.com/sccc/reports/course_outline_report.cfm?courses_id=2974 9/26/2014 Music 101 Page 4 of 5 z z 3.00 Romantic Opera. z 6.00 The following operas: Bizet: Carmen, Wagner: Walkure, Verdi: La Traviata, Puccini: LaBoheme. Contemporary Music. z 3.00 concerto, and opera. The music of Brahms, Mendelssohn, Schumann, Liszt. The concertos of Tchaikovsky and Schumann. The music of Bartok, Prokofiev, Ives, Crawford, Bernstein, Adams, Copland, Cage, Lutoslawski, Review and Synthesis. z the appropriate musical styles. identify differences between the Classical and Romantic Periods. Students be able to: z z identify basic components of opera: Aria, recitative, overture, dramatic and aesthetic elements identify themes which represent cultural ideas from European and non-European sources Students will be able to identify important trends in contemporary music including sources in Far Eastern and African music. Students will be able to distill basic concepts of classical music from European tradition. Course Materials: Forney, K. & J. Machlis, THE ENJOYMENT OF MUSIC: An Introduction to Perceptive Listening, 11th Ed. W. W. Norton & Company. 2011 (Required) ISBN:0393934152 $61.99 Forney, Kristine, Study Guide THE ENJOYMENT OF MUSIC: An Introduction to Perceptive Listening, 11th Ed. W. W. Norton & Company. 2011 (Recommended) ISBN:0393912396 $22.84 Instructional Methods: These measures are typical of the instructional methods of this course; however, instructors may employ other related methods and not all methods listed are necessarily performed by each instructor: Activity Critique Discussion Distance Education http://www.curricunet.com/sccc/reports/course_outline_report.cfm?courses_id=2974 9/26/2014 Music 101 Page 5 of 5 Guest Lecturers Lecture Mediated Learning Observation and Demonstration Projects Methods of Evaluation: These evaluation methods are typical of this course; however, instructors may employ other related methods and not all methods listed are necessarily performed by each instructor: Exams/Tests Papers Class Participation Class Work Homework Observation and evaluation of attitudes and actions Departmental Final Exam Outside of Class Assignments: Reading daily assignments in the text on the composers' lives, historical background of each period, and musical selections studied Writing synopses of the composer's lives, formulating study questions, fulfilling research assignments, and answering questions about the films and videos shown in class Listening to assigned selections from the standard classical music repertoire (contained on five listening tapes purchased by each student) Attendance at three or more live concerts and recitals Writing reviews of the concerts and recitals attended, relating the performance and compositions heard to compositions and composers studied in class. Critical listening, thinking, and writing should be stressed and utilized Outside Class Hours: 96 Hours Grading Criteria: z z z Exams, written and listening - 500 points Class participation and writing assignments - 100 points Attendance at live performances and written reviews - 100 points Total: 700 points GRADING SCALE z z z z z 630-700 points = A 560-629 points = B 490-559 points = C 420-489 points = D Below 420 points = F http://www.curricunet.com/sccc/reports/course_outline_report.cfm?courses_id=2974 9/26/2014