What is a Database?
advertisement
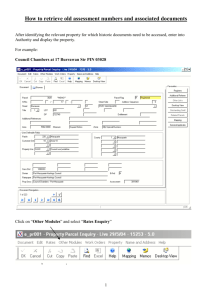
What is a Database? A relational database is a collection of related tables. A table is a kind of organised file where data about a certain type is organised into records (rows) and fields (columns). Each field in a table constitute a property of the data to be stored in the table. Example 1: The Sample Bookstore Database • Books Table (ISBN, TITLE, AUTHOR, YEAR, LISTPRICE, PUBLISHERID) • Publishers Table (PUBLISHERID, PUBLISHERNAME, ADDRESS, CITY, STATE, ZIPCODE, PHONE) • Orders Table (ORDERID, DATE, PUBLISHERID) • Order Details Table (ORDERID, ISBN, QUANTITY) KEY The key of a table is a combination of its fields that uniquely identify each record in that table. The underlined field(s) above are the keys of the corresponding tables. . Relationship Between Tables • The relation between the tables may be either one-to-many (1-M) or many-to-many (M-M). • For instance, a publisher will most probably publish more than one book. So, the relation between the Publishers and Books tables ‘s 1-M. On the other hand, there may be more than one book in a specific order and a specific book may be ordered several times, that is in several orders. So, the relation between the Order Details and Books tables is M-M. Microsoft Access is software that enables us to create and manage such databases. A Microsoft Access file has the extension mdb (Microsoft data base). • When you start Microsoft Access, it will ask you if you want to create a new database or open an existing database If you choose to open an existing database, the database window will be displayed on the screen. The database window has 7 objects: 1. 2. 7. Tables (open an existing table for editing, design a table, create a table) Queries (a query is a question about the database written in pre-defined forms) Forms (a form is a formatted window for managing data in a database) Reports (a report is a formatted print-out that outputs information about a database; a report may be based on a table or a query) Pages Macros (kind of computer program to be executed automatically one after another; is used to automate repetitive tasks) Modules (programming in Visual Basic for Applications) • Note that all objects are stored in a single Access file on disk. 3. 4. 5. 6. Create a New DB To open an existing database: Select the Open option from the File Tab Add a Table You can add a new table to an existing database by using the tools in the Tables group on the Create tab. A Table is displayed in one of two views: • Design View: to define the table initially, specify the fields it will contain or modify the table definition • Datasheet View: to add, edit or delete records Create a Table in Design View Database Fields For each field, you define: • • Field Name (up to 64 characters including letters, numbers, space) Data type – – – – – – – – – Number (digits, decimal point, plus or minus sign) Text (up to 255 characters) Memo (up to 64,000 characters) Date/time Currency Yes/No (Boolean/Logical) or True/False OLE (field created by another application) AutoNumber (1,2, ... assigns the next number when you add a record) Hyperlink (Web address-URL) Design View In the design view of a table the following information on each field is displayed: 1. 2. 3. Field Name Data Type Properties Plus the primary field(s)is indicated by a key before the field name. PROPERTY • A property is a characteristic or attribute of an object that determines how the object looks and behaves. Every access object (tables, forms, queries, reports) has a set of properties. Properties are displayed and/or changed in a property sheet. IMPORTANT NOTE: • First select the field in design view whose property you want to display. The field properties displayed in the design view are: • • • • • • • • • • Field Size (adjusts the size of a text field or limits the allowable value in a number field) Format (changes the way a field is displayed) Input Mask (data validation: the data entered by the user must match the input mask) Caption (label other than the field name to be used in reports and forms) Default Value Validation Rule (rejects data that does not conform to the validation rule) Validation Text (error message to be displayed when data does not conform to the validation rule) Required (must value) Allow Zero Length (null text or memo fields) Indexed (for efficient search purposes each table may be indexed on various fields, e.g. surname; the table is indexed on the primary key by default) MODIFICATIONS ON A FIELD • In order to add/delete a field in the design view select (point to) the corresponding field(s), right click and select add/delete rows as appropriate. • In order to change the primary key, point to the row where the new primary key field resides, right click and select the primary key command. • If the primary key is composed of more than one field, select all the components by pressing the Ctrl key upon selection and then issue the Primary Key command. Find and Replace Commands • Home Tab; Find/Replace Command . • If the Match Case check box is checked then ph is different than PH. • The search is performed over the specified field/table in the Look In list box. • In the Match list box, selecting Whole Field identifies that Davis is different than Davison. • The replacement may either be selective or automatic. Selective replacement is a loop of find next and replace/find next combination whereas automatic replacement means clicking the replace all button. FILTERING A filter displays a subset of records from the table according to a specified criteria. The easiest way to implement a filter is: • to click in any cell that contains the value of the desired criterion. • Then click the Filter by Selection button on the Database toolbar. Deleting a table from a database Select its icon in the Tables Group of the and press the Delete key. Exiting Access 1. 2. Close the table(s) File Menu; Close Exit Access File Menu; Exit