Organelle = an internal, membrane- bound sac or - Biology
advertisement

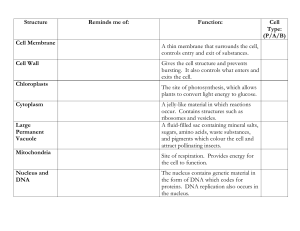
4.3 Defining Features of Eukaryotic Cells! Organelle = an internal, membranebound sac or compartment that serves one or more specialized functions.! A. Major Cellular Components! !" Include: nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), golgi body, vesicles, mitochondria, ribosomes, cytoskeleton.! Advantages of compartmentalization! 1." 2." Allows a large number of activities to occur simultaneously in a very limited space (i.e.: Organelle membranes physically separate incompatible reactions)! Allow compatible and interconnected reactions to proceed at different times.! B. Plant Cells vs.. Animal Cells! Plants! Large central vacuole! Chloroplasts! Cell wall! cuboidal ! Other plant organelles! Animals! !" A few small vacuoles! !" Cytoskeleton! !" Spherical shape! !" Centrioles (2)! !" Lysosomes! 4.4 The Nucleus! !" A cell#s structure and function begin with proteins.! !" Instructions for building proteins are contained in DNA.! Functions of the Nucleus! 1." 2." Localizes DNA - makes it easier for parent cells to copy their genetic instructions.! Outer membranes form a boundary where cells can control the passage of substances and signals to and from the cytoplasm! Parts of the Nucleus! 1." 2." 3." 4." Nuclear envelope = double membrane! Nucleoplasm = semisolid gel w/i nucleus.! Pores = openings in envelope! Nucleolus = dark body or bodies w/i nucleus that synthesize proteins and RNA that will be used to assemble ribosomes.! 5. DNA = genetic material! !" Chromatin = unorganized DNA and proteins (long & stringy)! !" Chromosomes = organized, coiled DNA and proteins (X#s)! 4.5 Cytomembrane System! !" Cytomembrane system = the series of organelles in which lipids are assembled and new polypeptide chains are modified into final proteins.! !" Includes the ER (rough & smooth, Golgi bodies, vesicles)! A. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)! !" Rough ER = covered with ribosomes, abundant in cells that make and secrete enzymes (ex: pancreas)! !" Smooth ER = lack ribosomes; abundant in cells that assemble lipids (ex: seeds, liver, muscle)! B. Golgi bodies! !" Process, package & secrete cellular substances! C. Vesicles! !" Tiny membranous sacs that transport substances throughout the cytoplasm.! !" Examples: ! ! !lysosomes = intercellular digestion! ! !peroxisomes = break down fatty acids and amino acids!