Toyota Way - Chapters 19
advertisement

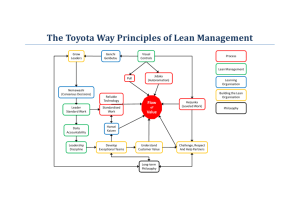
10/2/2014 The Toyota Way Chapters 19 & 20 October 2, 2014 1 Principle 13: Make Decision Slowly by Consensus, Thoroughly Considering All Options; Implement Rapidly Chapter 19 2 How you arrive at the decision is just as important as the quality of the decision Fundamental Statement 3 1 10/2/2014 • Finding out what is really going on, including genchi genbutsu • Understand underlying causes that explain surface appearances – asking “Why” five times • Considering alternative solutions and developing a detailed rationale for the preferred solution Decision Making Elements 4 • Building consensus within the team, including Toyota employees and outside partners • Use every efficient communication vehicle to do 1-4, preferably on one sheet of A3 paper Decision Making Elements cont. 5 • Satisficing • Optimizing Decision Making Goal 6 2 10/2/2014 • Engineers and managers trained to think in terms of sets of alternative solutions • What does this mean? • What does it mean in terms of the number o9f potential alternatives identified? Mind Set 7 • Delay decisions until you have considered a broad range of alternatives Lean’s Counter-intuitive Thoughts 8 • What is “nemawashi”? Nemawashi 9 3 10/2/2014 Alternative Decision Making Methods 10 “What value are we adding from the customer's perspective? The only thing that adds value in any type of process is the physical or information transformation of that product, service, or activity into something the customer wants TPS - asks 11 Use of authority by manager Manager ‘sells’ decision Manager presents decision and invites questions Manager Manager Manager presents presents defines tentative problem, limits, asks group to decision gets subject suggestions, make decisions to change makes decision with leader as equal member Managerial Authority vs. Subordinate Freedom delegates joins consults suggests sells Manager makes decision Area of freedom for subordinates Manager permits subordinat es to function within limits defined by superior 12 4 10/2/2014 Plan-Do-Check-Act in Proposal Process 13 • • • • • Clear objectives prior to the meeting The right people at the meeting Prepared participants Effective Use of Visual Aids Separate information sharing from problem solving • The meeting starts and ends on time4 Efficient Meeting Requisites 14 Principle 14: Become a Learning Organization Through Relentless Reflection and Continuous Improvement Chapter 20 15 5 10/2/2014 …where people continue to expand their capacity to create the results they truly desire , where new and expanded patterns of thinking are nurtured, where collective aspiration is set free , and where people are continually learning to learn together Learning Organization – Peter Senge 16 How do you learn new skills? Critical Issue 17 Knowledge Motivation Opportunity Requirements 18 6 10/2/2014 Standardization Innovation Learning & Improvement 19 • Learn from your mistakes • Determine the root cause of your problems • Provide effective countermeasures • Empower people to implement those measures • Transfer new knowledge Learning Organization 20 Ask “Why” 5 times Identifying Root Cause 21 7 10/2/2014 Level of problem Level of problem Why? Why? Level of problem Why? Level of problem Why? Level of problem Why? Level of problem Why 5 times 22 UK Men’s Bball team has problems shooting free throws Important Issue 23 Hansei – reflection Kaizen – continuous improvement Organizational Learning 24 8 10/2/2014 • Global performance measures – how is the company doing? • Operational performance measures – how is the plant or department doing? • Stretch improvement metrics – how is the business unit or work group doing? Role of Metrics 25 Cascade Policy Deployment Process 26 PDCA & Obtaining Flow 27 9 10/2/2014 28 10