AP Psychology
advertisement

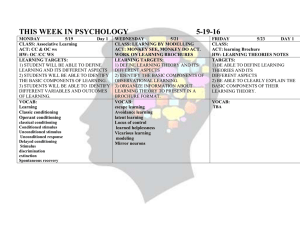
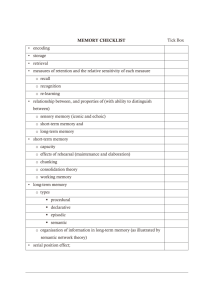
AP Psychology: Chapter 4 & 6 Test Review Ch. 4 Absolute threshold for the senses Just noticeable difference for temperature Study by Krosnick 1992 of attitudes and subliminal messaging (people exposed to subliminal negative emotion-arousing photos) Sensory adaptation Know anatomy of Eye. Lens, Iris, Pupil, Optic disk, Rods, Cones (dark adaptation) Red, green and blue light converging at one point leads to your brain to perceive what color light? Opponent processing theory Trichromatic theory Proffitt’s study of geographical slant (1995) What does the phenomenon of size constancy imply? Be familiar with the anatomy of the ear. What might happen if the basilar membrane was longer according to place theory? The perception of timber corresponds to a sound wave’s what? Frequency theory Know anatomy of taste organ (tongue) Nontasters vs. Supertasters What is the perception of smell referred to as? Which sensory system not project upward through the cerebral cortex? Be familiar with smell- sensory adaptation. Where in the brain are sensory receptors in the skin processed? Kinesthetic system Occipital, frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes Ch. 6 Given scenarios, you should be able to distinguish what is the conditioned response, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and unconditioned stimulus. Classical conditioning Operant conditioning Generalization Response renewal Higher order conditioning According to Skinner, a stimulus is a reinforcer if it does what? Skinner box- cumulative record (steep slope in the line indicates what?) Discriminative stimulus What happens when there is a long delay between a response and reinforcement? Which behavior is most difficult to extinguish? Fixed ratio, variable ratio, fixed interval, variable interval Aversive event Avoidance behavior Mowrer’s theory of avoiding feared stimulus Punishment Evolutionary perspective on learning suggests what? What highlights the importance of cognitions in observational learning? Conditioning: nature vs. nurture Behavior modification Discriminative stimulus Thorndike’s Law of Effect