Acid Base Lab - Waukee Community School District Blogs
advertisement
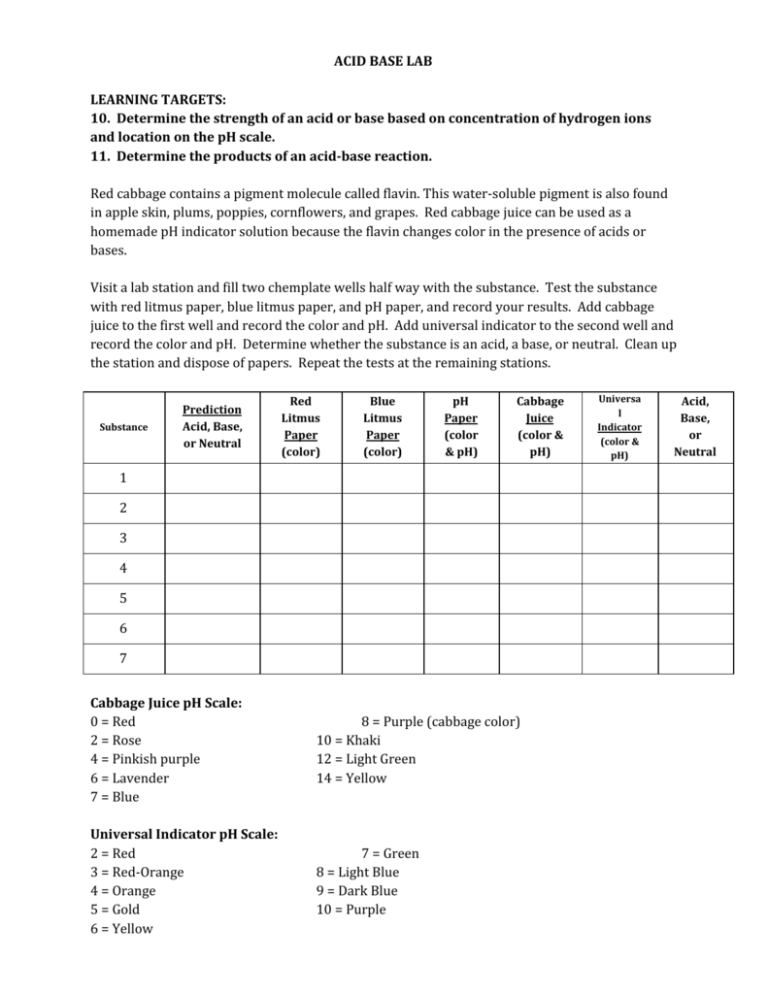
ACID BASE LAB LEARNING TARGETS: 10. Determine the strength of an acid or base based on concentration of hydrogen ions and location on the pH scale. 11. Determine the products of an acid-base reaction. Red cabbage contains a pigment molecule called flavin. This water-soluble pigment is also found in apple skin, plums, poppies, cornflowers, and grapes. Red cabbage juice can be used as a homemade pH indicator solution because the flavin changes color in the presence of acids or bases. Visit a lab station and fill two chemplate wells half way with the substance. Test the substance with red litmus paper, blue litmus paper, and pH paper, and record your results. Add cabbage juice to the first well and record the color and pH. Add universal indicator to the second well and record the color and pH. Determine whether the substance is an acid, a base, or neutral. Clean up the station and dispose of papers. Repeat the tests at the remaining stations. Substance Prediction Acid, Base, or Neutral Red Litmus Paper (color) Blue Litmus Paper (color) pH Paper (color & pH) Cabbage Juice (color & pH) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Cabbage Juice pH Scale: 0 = Red 2 = Rose 4 = Pinkish purple 6 = Lavender 7 = Blue 8 = Purple (cabbage color) 10 = Khaki 12 = Light Green 14 = Yellow Universal Indicator pH Scale: 2 = Red 3 = Red-Orange 4 = Orange 5 = Gold 6 = Yellow 7 = Green 8 = Light Blue 9 = Dark Blue 10 = Purple Universa l Indicator (color & pH) Acid, Base, or Neutral ACID BASE LAB Questions: 1. List your substances in order from lowest pH to highest pH. 2. Predict the identity of each substance. 3. Why is it important to use both blue and red litmus paper to determine whether a substance is an acid or a base? 4. How does the pH of a strong acid compare with a pH of a weak acid? 5. How does the pH of a strong base compare with the pH of a weak base? 6. Describe the pH scale. Which pH numbers indicate acids? Which pH numbers indicate bases? 7. What are characteristics of acids? 8. What are characteristics of bases? 9. Look at the acids on your list. What do these substances have in common? What other things probably also have acidic pHs? 10. Look at the bases on your list. What do these substances have in common? What other things probably also have basic pHs? 11. How is the pH scale related to hydrogen and hydroxide ions? 12. How does a neutralization reaction relate to acids and bases? 13. Why are Tums or Rolaids used to treat stomachaches? 14. Solve the following acid/base neutralizations: a. HNO 3+ KOH → KNO 3 + __________ b. H 2SO 4+ Ca(OH) 2→ __________ + H 2O c. HNO + H 3+ __________ → LiNO 3 2O d. _________ + Al(OH) 3→ AlF 3+ H 2O e. HCl + Be(OH) → __________ + H 2 2O