Acid-Base Lab - Bath County Schools
advertisement

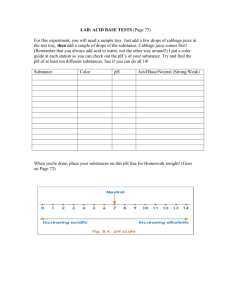
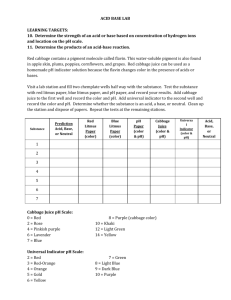
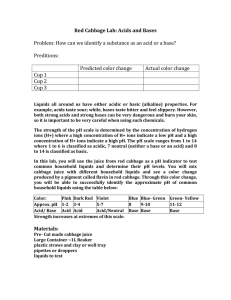
Acid-Base Lab Lab #4 Problem: What happens when acids and bases are mixed? Hypothesis: Procedure: 1) Form your hypothesis and write it down. 2) Make a data table that looks like the one below. 3) Pour ~1/4 of a test tube worth of cabbage juice into 5 different test tubes and place them back in the holder. 4) Using a dropper add a few drops of each of the 5 labeled substances into its’ own test tube. Only one chemical mixed with cabbage juice per test tube. 5) Record the changes in your data table. 6) Summarize under your data table: Cabbage juice is a universal indicator. It changes color in the presence of acids and bases. The strength of acids and bases are represented on the pH scale. A neutral substance has a pH of 7 and is neither an acid nor a base. An acid has a pH less than 7. The lower the number the stronger the acid. A base has a pH greater than 7. The higher the number the stronger the base. The cabbage juice is a great indicator because you can actually determine the strength of acids and bases from use of it. 7) In a 6th test tube add the cabbage juice and the strong acid. 8) Slowly use a dropper and add the strong base to the 6th test tube that contains the cabbage juice and strong acid until the color is similar to cabbage juice and water. 9) Summarize under your data table: When acids and bases are mixed a chemical reaction known as a neutralizing reaction takes place. If equal amounts of equal strength acids and bases are mixed they will neutralize each other and produce a pH neutral salt and water that is pH neutral. Data: Substance Weak Acid Strong Acid Water (Neutral) Weak Base Strong Base Conclusion: Color before adding Color after adding