10.24 Short Run.handout.inclass LO1 Using Incremental Analysis
advertisement
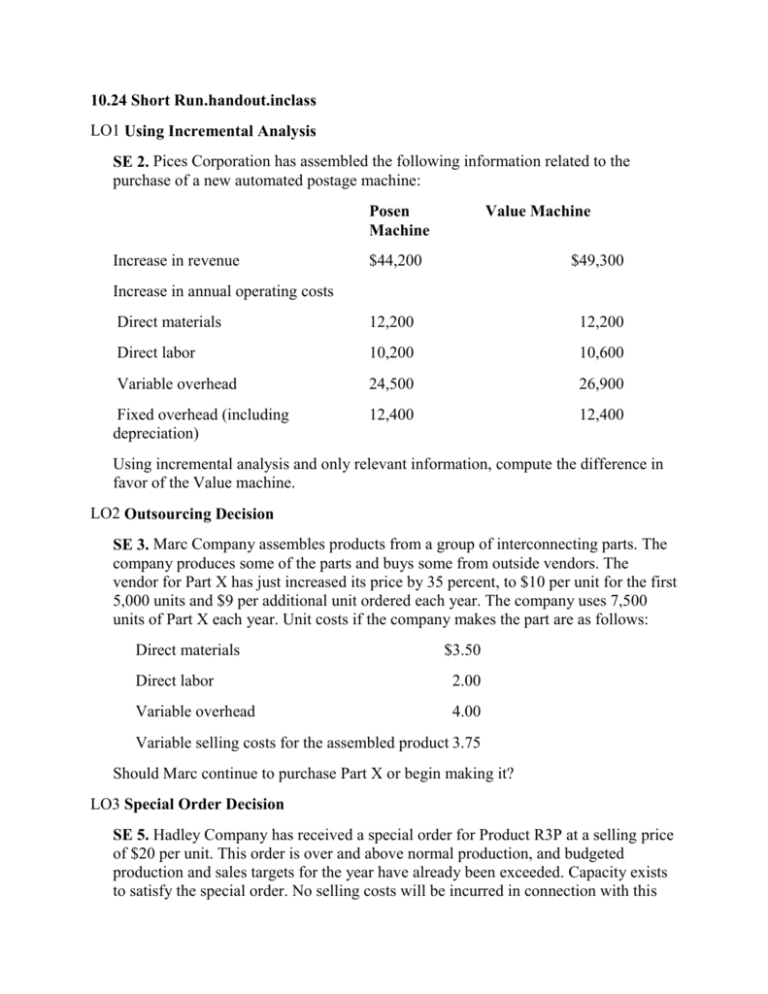
10.24 Short Run.handout.inclass LO1 Using Incremental Analysis SE 2. Pices Corporation has assembled the following information related to the purchase of a new automated postage machine: Posen Machine Increase in revenue Value Machine $44,200 $49,300 Direct materials 12,200 12,200 Direct labor 10,200 10,600 Variable overhead 24,500 26,900 Fixed overhead (including depreciation) 12,400 12,400 Increase in annual operating costs Using incremental analysis and only relevant information, compute the difference in favor of the Value machine. LO2 Outsourcing Decision SE 3. Marc Company assembles products from a group of interconnecting parts. The company produces some of the parts and buys some from outside vendors. The vendor for Part X has just increased its price by 35 percent, to $10 per unit for the first 5,000 units and $9 per additional unit ordered each year. The company uses 7,500 units of Part X each year. Unit costs if the company makes the part are as follows: Direct materials $3.50 Direct labor 2.00 Variable overhead 4.00 Variable selling costs for the assembled product 3.75 Should Marc continue to purchase Part X or begin making it? LO3 Special Order Decision SE 5. Hadley Company has received a special order for Product R3P at a selling price of $20 per unit. This order is over and above normal production, and budgeted production and sales targets for the year have already been exceeded. Capacity exists to satisfy the special order. No selling costs will be incurred in connection with this order. Unit costs to manufacture and sell Product R3P are as follows: direct materials, $7.60; direct labor, $3.75; variable overhead, $9.25; fixed overhead, $4.85; variable selling costs, $2.75; and fixed general and administrative costs, $6.75. Should Hadley Company accept the order? LO4 Segment Profitability Decision SE 7. Peruna Company is evaluating its two divisions, North Division and South Division. Data for North Division include sales of $530,000, variable costs of $290,000, and fixed costs of $260,000, 50 percent of which are traceable to the division. South Division’s efforts for the same period include sales of $610,000, variable costs of $340,000, and fixed costs of $290,000, 60 percent of which are traceable to the division. Should Peruna Company consider eliminating either division? Is there any other problem that needs attention? LO5 Sales Mix Decision SE 8. Snow, Inc., makes three kinds of snowboards, but it has a limited number of machine hours available to make them. Product line data are as follows: Wood Plastic Graphite Machine hours per unit 1.25 1.0 1.5 Selling price per unit $100 $120 $200 Variable manufacturing cost per unit $45 $50 $100 Variable selling costs per unit $15 $26 $36 In what order should the snowboard product lines be produced? LO6 Sell or Process-Further Decision SE 9. Gomez Industries produces three products from a single operation. Product A sells for $4 per unit, Product B for $6 per unit, and Product C for $10 per unit. When B is processed further, there are additional unit costs of $3, and its new selling price is $10 per unit. Each product is allocated $2 of joint costs from the initial production operation. Should Product B be processed further, or should it be sold at the end of the initial operation? LO6 Sell or Process-Further Decision SE 10. In an attempt to provide superb customer service, Richard V. Meats is considering the expansion of its product offerings from whole hams and turkeys to complete ham and turkey dinners. Each dinner would include a carved ham or turkey, two side dishes, and six rolls or cornbread. The accountant for Richard V. Meats has compiled the following relevant information: Product Sales Revenue if No Additional Service Ham Sales Revenue if Additional Processing Processed Further Costs $30 $50 $15 20 35 15 Turkey A cooked, uncarved ham costs Richard V. Meats $20 to produce. A cooked, uncarved turkey costs $15 to prepare. Use incremental analysis to determine which products Richard V. Meats should offer. LO1 Incremental Analysis E 2. The managers of Lennox Company must decide which of two mill blade grinders—Y or Z—to buy. The grinders have the same purchase price but different revenue and cost characteristics. The company currently owns Grinder X, which it bought three years ago for $15,000 and which has accumulated depreciation of $9,000 and a book value of $6,000. Grinder X is now obsolete as a result of advances in technology and cannot be sold or traded in. The accountant has collected the following annual revenue and operating cost estimates for the two new machines: Grinder Y Grinder Z Increase in revenue $16,000 $20,000 Direct materials 4,800 4,800 Direct labor 3,000 4,100 Variable overhead 2,100 3,000 Fixed overhead (depreciation included) 5,000 5,000 Increase in annual operating costs 1. Identify the relevant data in this problem. 2. Prepare an incremental analysis to aid the managers in their decision. 3. Should the company purchase Grinder Y or Grinder Z? LO2 Outsourcing Decision E 3. One component of a radio produced by Audio Systems, Inc., is currently being purchased for $225 per 100 parts. Management is studying the possibility of manufacturing that component. Annual production (usage) at Audio is 70,000 units; fixed costs (all of which remain unchanged whether the part is made or purchased) are $38,500; and variable costs are $0.95 per unit for direct materials, $0.55 per unit for direct labor, and $0.60 per unit for variable overhead. Using incremental analysis, decide whether Audio Systems, Inc., should manufacture the part or continue to purchase it from an outside vendor. LO3 Special Order Decision E 5. Antiquities, Ltd., produces antique-looking books. Management has just received a request for a special order for 2,000 books and must decide whether to accept it. Venus Company, the purchaser, is offering to pay $25.00 per book, which includes $3.00 per book for shipping costs. The variable production costs per book include $9.20 for direct materials, $4.00 for direct labor, and $3.80 for variable overhead. The current year’s production is 22,000 books, and maximum capacity is 25,000 books. Fixed costs, including overhead, advertising, and selling and administrative costs, total $80,000. The usual selling price is $25.00 per book. Shipping costs, which are additional, average $3.00 per book. Determine whether Antiquities should accept the special order. LO4 Elimination of Unprofitable Segment Decision E 8. Guld’s Glass, Inc., has three divisions: Commercial, Nonprofit, and Residential. The segmented income statement for last year revealed the following: Guld’s Glass, Inc. Divisional Profit Summary and Decision Analysis Commercial Division Nonprofit Division Residential Division Total Company Sales $290,000 $533,000 $837,000 $1,660,000 Less variable costs 147,000 435,000 472,000 1,054,000 Contribution margin $143,000 $ 98,000 $365,000 $ 606,000 Less direct fixed costs 124,000 106,000 139,000 369,000 Segment margin $ 19,000 ($ 8,000) $226,000 $ 237,000 Less common fixed costs Operating income 168,000 $ 69,000 1. How will Guld’s Glass, Inc., be affected if the Nonprofit Division is dropped? 2. Assume the elimination of the Nonprofit Division causes the sales of the Residential Division to decrease by 10 percent. How will Guld’s Glass, Inc., be affected if the Nonprofit Division is dropped? LO4 Elimination of Unprofitable Segment Decision E 9. URL Services has two divisions: Basic Web Pages and Custom Web Pages. Ricky Vega, manager of Custom Web Pages, wants to find out why Custom Web Pages is not profitable. He has prepared the reports that appear on the next page. 1. How will URL Services be affected if the Custom Web Pages Division is eliminated? 2. How will URL Services be affected if the Design segment of Custom Web Pages is eliminated? 3. What should Ricky Vega do? What additional information would be helpful to him in making the decision? URL Services Segmented Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31 Basic Web Pages (1,000 units) Service revenue Custom Web Pages (200 units) Total Company $200,000 $150,000 $350,000 Direct professional labor: design $ 32,000 $ 80,000 $112,000 Direct professional labor: install 30,000 4,000 34,000 Direct professional labor: maintain 15,000 36,000 51,000 Total variable costs $ 77,000 $120,000 $197,000 Contribution margin $123,000 $ 30,000 $153,000 Less variable costs Less direct fixed costs Depreciation on computer equipment $ 6,000 $ 12,000 $ 18,000 Depreciation on servers 10,000 20,000 30,000 Total direct fixed costs $ 16,000 $ 32,000 $ 48,000 Segment margin $107,000 ($ 2,000) $105,000 Less common fixed costs Building rent $ 24,000 Supplies 1,000 Insurance 3,000 Telephone 1,500 Website rental 500 Total common fixed costs $ 30,000 Operating income $ 75,000 Custom Web Pages Division URL Services Segment Profitability Decision Incremental Analysis Design Install Maintain Total Service revenue $60,000 $25,000 $65,000 $150,000 Less variable costs 80,000 4,000 36,000 120,000 Contribution margin ($20,000) $21,000 $29,000 $ 30,000 Less direct fixed costs 6,000 13,000 13,000 32,000 Segment margin ($26,000) $ 8,000 $16,000 ($ 2,000) LO5 Scarce Resource Usage E 10. EZ, Inc., manufactures two products that require both machine processing and labor operations. Although there is unlimited demand for both products, EZ could devote all its capacities to a single product. Unit prices, cost data, and processing requirements follow: Product E Product Z Unit selling price $70 $230 Unit variable costs $30 $90 Machine hours per unit 0.4 1.4 Labor hours per unit 2.0 6.0 Next year, the company will be limited to 160,000 machine hours and 120,000 labor hours. Fixed costs for the year are $1,500,000. 1. Compute the most profitable combination of products to be produced next year. 2. Prepare an income statement using the contribution margin format for the product volume computed in 1. LO5 Sales Mix Decision E 11. Grady Enterprises manufactures three computer games. They are called Rising Star, Ghost Master, and Road Warrior. The product line data are as follows: Rising Star Ghost Master Road Warrior Current unit sales demand 20,000 30,000 18,000 Machine hours per unit 2.0 1.0 2.5 Selling price per unit $24.00 $18.00 $32.00 Unit variable manufacturing costs $12.50 $10.00 $18.75 Unit variable selling costs $6.50 $5.00 $6.25 The current production capacity is 110,000 machine hours. 1. Which computer game should be manufactured first? Which should be manufactured second? Which last? 2. How many of each type of computer game should be manufactured and sold to maximize the company’s contribution margin based on the current production activity of 110,000 machine hours? What is the total contribution margin for that combination? LO6 Sell or Process-Further Decision E 13. H & L Beef Products, Inc., processes cattle. It can sell the meat as sides of beef or process it further into final cuts (steaks, roasts, and hamburger). As part of the company’s strategic plan, management is looking for new markets for meat or meat by-products. The production process currently separates hides and bones for sale to other manufacturers. However, management is considering whether it would be profitable to process the hides into leather and the bones into fertilizer. The costs of the cattle and of transporting, hanging, storing, and cutting sides of beef are $125,000. The company’s accountant provided these data: Product Sales Revenue if Sold at Sales Revenue if Sold Split-Off After Further Processing Additional Processing Costs Meat $100,000 $200,000 $80,000 Bones 20,000 40,000 15,000 Hides 50,000 55,000 10,000 Should the products be processed further? Explain your answer. LO6 Sell or Process-Further Decision E 14. Six Star Pizza manufactures frozen pizzas and calzones and sells them for $4 each. It is currently considering a proposal to manufacture and sell fully prepared products. The following relevant information has been gathered by management: Product Pizza Calzone Sales Revenue if No Additional Processing Sales Revenue if Processed Further Additional Processing Costs $4 $8 $5 4 10 5 Use incremental analysis to determine which products Six Star should offer.