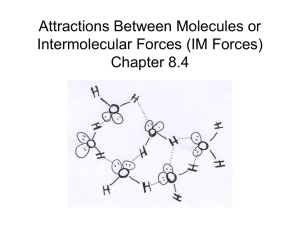
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
advertisement

Exam Name___________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The phase diagram of a substance is given above. This substance is a __________ at 25 °C and 1.0 atm. A) gas B) solid C) liquid D) supercritical fluid E) crystal 1) 2) Which one of the following cannot form a solid with a lattice based on the sodium chloride structure? A) CuO B) CuCl2 C) RbI D) LiF E) NaBr 2) 3) A substance that expands to fill its container yet has a density approaching that of a liquid, and that can behave as a solvent is called a(n) __________. A) plasma B) supercritical fluid and gas C) amorphous solid D) gas E) liquid 3) 4) In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are __________. A) strong enough to hold molecules relatively close together but not strong enough to keep molecules from moving past each other B) strong enough to hold molecules relatively close together C) not strong enough to keep molecules from moving past each other D) very weak compared with kinetic energies of the molecules E) strong enough to keep the molecules confined to vibrating about their fixed lattice points 4) 5) Some things take longer to cook at high altitudes than at low altitudes because __________. A) natural gas flames donʹt burn as hot at high altitudes B) water boils at a lower temperature at high altitude than at low altitude C) there is a higher moisture content in the air at high altitude D) water boils at a higher temperature at high altitude than at low altitude E) heat isnʹt conducted as well in low density air 5) 1 6) The substance with the largest heat of vaporization is __________. A) Cl2 B) I2 C) O2 D) Br2 6) E) F2 7) Elemental iodine (I2 ) is a solid at room temperature. What is the major attractive force that exists among different I2 molecules in the solid? 7) A) covalent-ionic interactions B) London dispersion forces C) dipole-dipole attractions D) dipole-dipole rejections E) ionic-dipole interactions 8) Which statement is true about liquids but not true about solids? A) They assume both the volume and the shape of their containers. B) They are highly ordered and not compressible. C) They flow and are not compressible. D) They flow and are highly ordered. E) They flow and are compressible. 8) 9) Based on the following information, which compound has the strongest intermolecular forces? 9) A) Ethanol Substance ΔHvap (kJ/mol) Argon (Ar) Benzene (C6 H6 ) 6.3 31.0 Ethanol (C 2 H5 OH) 39.3 Water (H 2 O) 40.8 Methane (CH 4 ) 9.2 B) Methane C) Benzene D) Argon 10) Of the following substances, __________ has the highest boiling point. A) CO2 B) Kr C) NH3 D) H2 O E) Water 10) E) CH4 11) Which statements about viscosity are true? (i) Viscosity increases as temperature decreases. (ii) Viscosity increases as molecular weight increases. (iii) Viscosity increases as intermolecular forces increase. A) (i) only B) (ii) and (iii) C) (i) and (iii) D) none E) all 11) 12) What types of intermolecular forces exist between HI and H 2 S? 12) A) dispersion forces, dipole-dipole, and ion-dipole B) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole C) dispersion forces, dipole-dipole, and ion-dipole D) dispersion forces, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole, and ion-dipole E) dipole-dipole and ion-dipole 2 13) A solid has a very high melting point, great hardness, and poor electrical conduction. This is a(n) __________ solid. A) molecular B) ionic C) metallic D) covalent network E) metallic and covalent network 13) 14) When NaCl dissolves in water, aqueous Na+ and Cl- ions result. The force of attraction that exists between Na+ and H2 O is called a(n) __________ interaction. 14) A) ion-ion B) dipole-dipole C) London dispersion force D) ion-dipole E) hydrogen bonding 15) Metallic solids do not exhibit __________. A) excellent thermal conductivity B) variable hardness C) excellent electrical conductivity D) variable melting point E) extreme brittleness 15) 16) The predominant intermolecular force in CaBr2 is __________. 16) A) London-dispersion forces B) dipole-dipole forces C) ion-dipole forces D) hydrogen bonding E) ionic bonding 17) Large intermolecular forces in a substance are manifested by __________. A) high heats of fusion and vaporization B) high critical temperatures and pressures C) low vapor pressure D) high boiling point E) all of the above 17) 18) How high a liquid will rise up a narrow tube as a result of capillary action depends on __________. A) only the magnitude of cohesive forces in the liquid B) the magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube, and gravity C) only the magnitude of adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube D) the viscosity of the liquid E) gravity alone 18) 3 19) Crystalline solids differ from amorphous solids in that crystalline solids have __________. A) a long-range repeating pattern of atoms, molecules, or ions B) appreciable intermolecular attractive forces C) atoms, molecules, or ions that are close together D) much larger atoms, molecules, or ions E) no orderly structure 19) 20) CsCl crystallizes in a unit cell that contains the Cs+ ion at the center of a cube that has a Cl- at each corner. Each unit cell contains __________ Cs+ ions and __________ Cl- , ions, respectively. 20) A) 2 and 4 B) 2 and 1 C) 1 and 1 D) 2 and 2 E) 1 and 8 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 21) The direct conversion of a solid to a gas is called __________. 21) 22) Chromium crystallizes in a body-centered cubic unit cell. There are __________ chromium atoms per unit cell. 22) 23) London Dispersion Forces tend to __________ in strength with increasing molecular weight. 23) 24) When lattice points occur only at the corners of a unit cell, the cell is called _________. 24) 25) In general, intramolecular forces determine the __________ properties of a substance and intermolecular forces determine its __________ properties. 25) 26) How many atoms are contained in a face-centered cubic unit cell? 26) 27) When lattice points occur at the center of each face, as well as each corner of a unit cell, the cell is called __________. 27) 28) When lattice points occur at the corners and at the center of a unit cell, the cell is called __________. 28) 4 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 29) According to the phase diagram shown above, the normal boiling point of this substance is __________°C. A) 0 B) -3 C) 38 D) 29 E) 10 29) 30) The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and temperature for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the __________ segment corresponds to the heat capacity of the solid. A) AB B) BC C) CD D) DE E) EF 30) 31) The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and temperature of a solid as it was heated. The heat flow into the sample in the segment __________ will yield the value of the △Hfusion of this substance. 31) A) AB B) BC C) CD D) DE 5 E) EF 32) The normal boiling point of the substance with the phase diagram shown above is __________ °C. A) 10 B) 20 C) 30 D) 40 E) 50 32) 33) On the phase diagram shown above, segment __________ corresponds to the conditions of temperature and pressure under which the solid and the gas of the substance are in equilibrium. A) AD B) AC C) AB D) BC E) CD 33) 6 34) The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and temperature of a solid as it was heated. The heat flow into the sample in the segment __________ will yield the value of the △Hvap of this substance. A) AB B) BC C) CD D) DE 34) E) EF 35) The heat of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ/mol. The heat capacity of liquid water is 75.3 J/mol · K. The conversion of 50.0 g of ice at 0.00°C to liquid water at 22.0°C requires __________ kJ of heat. A) 0.469 B) 3.8 × 102 35) C) 21.3 D) 17.2 E) Insufficient data are given. 36) __________ solids consist of atoms or molecules held together by dipole -dipole forces, London disperson forces, and/or hydrogen bonds. A) Molecular B) Metallic and covalent-network C) Covalent-network D) Ionic E) Metallic 7 36) 37) Based on molecular mass and dipole moment of the five compounds in the table below, which should have the highest boiling point? Substance Propane, CH3 CH2 CH3 37) Molecular Dipole Mass (amu) Moment (D) 44 0.1 Dimethylether, CH3 OCH3 46 1.3 Methylchloride, CH3 Cl 50 1.9 Acetaldehyde, CH3 CHO 44 2.7 Acetonitrile, CH3 CN 41 3.9 A) CH3 CH2 CH3 B) CH3 OCH3 C) CH3 CN D) CH3 CHO E) CH3 Cl 38) Potassium metal crystallizes in a body-centered cubic structure with a unit cell edge length of 5.31 Å. The radius of a potassium atom is __________ Å. A) 5.31 B) 1.33 C) 2.30 D) 1.88 E) 2.66 38) TRUE/FALSE. Write ʹTʹ if the statement is true and ʹFʹ if the statement is false. 39) The boiling points of normal hydrocarbons are higher than those of branched hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight because the London-dispersion forces between normal hydrocarbons are greater than those between branched hydrocarbons. 39) 40) Under ordinary conditions, a substance will sublime rather than melt if its triple point occurs at a pressure above atmospheric pressure. 40) 8 Answer Key Testname: CH11PRAC 1) C 2) B 3) B 4) A 5) B 6) B 7) B 8) C 9) E 10) D 11) E 12) B 13) D 14) D 15) E 16) E 17) E 18) B 19) A 20) C 21) sublimation 22) 2 23) increase 24) primitive cubic 25) chemical, physical 26) 4 27) face-centered cubic 28) body-centered cubic 29) D 30) A 31) B 32) D 33) B 34) D 35) C 36) A 37) C 38) C 39) TRUE 40) TRUE 9