Lewis Structures & VSEPR Theory: Molecular Geometry
advertisement

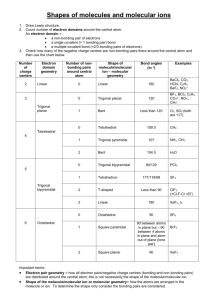
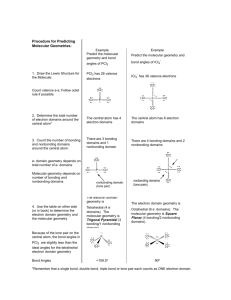
Journal Entry Draw Lewis structures for the following molecules: a) SCl2 b) CNF Molecular Geometry and VSEPR Theory • Whenever the atoms of a molecule bond together, the molecule takes on a particular shape. • Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of a molecule’s atoms in space. • VSEPR theory is the model used to explain the shapes of molecules. • VSEPR – Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. • The main idea of this theory is that electron pairs on the central atom of a molecule will position themselves in such a way as to minimize repulsion. • There are two types of electron pairs: – bonding pairs (shared) – nonbonding or lone pairs (unshared) • Example – CH4 – 4 electron pairs (tetrahedral electron geometry) – 4 bonding / 0 nonbonding pairs – molecular geometry = tetrahedral – bond angles are 109.5° • Example – NH3 – 4 electrons pairs (tetrahedral electron geometry) – 3 bonding / 1 nonbonding – molecular geometry = trigonal pyramidal – bond angles are 107° – Why are bond angles less? • Example – H2O – 4 electron pairs (tetrahedral electron geometry) – 2 bonding / 2 nonbonding – molecular geometry = bent – bond angle = 104.5° – Why are bond angles less? – Unshared pairs of electrons repel the adjacent bonding pairs more strongly than the bonding pairs repel each other. VSEPR and Multiple Covalent Bonds • For the VSEPR model, multiple bonds are counted as one bonding pair when determining the shape of the molecule. • Example – CH2O – 3 electron pairs (trigonal planar electron geometry) – 3 bonding / 0 nonbonding – molecular geometry = trigonal planar – bond angles = 120° • Example – NOCl – 3 electron pairs (trigonal planar electron geometry) – 2 bonding / 1 nonbonding – molecular geometry = bent – bond angles = approx. 120° • Example – CO2 – 2 electron pairs (linear electron geometry) – 2 bonding / 0 nonbonding – molecular geometry = linear – bond angles = 180° Bonding Pairs Nonbonding Pairs Shape Example 2 0 Linear CO2 3 0 Trigonal Planar CH2O 2 1 Bent NOCl 4 0 Tetrahedral CH4 3 1 Trigonal Pyramidal NH3 2 2 Bent H2O