Epithelial tissue Characteristic of epithelium Basal lamina Basement
advertisement

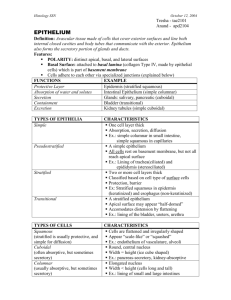
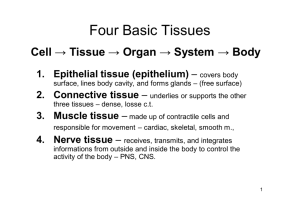
Characteristic of epithelium • cells Epithelial tissue Textus epithelialis – foundation is basal lamina – minimum of extra cellular matrix – plenty of intercellular junctions – various shapes – important for classification – variability of functions Štěpán Jelínek Basal lamina • thin layer of extracellular matrix – collagen IV. type, laminin, proteoglycans • two layers – lamina rara, lamina densa • lamina reticularis – part of connective tissue • foundation for epithelial cells • produced by epithelial, muscular, Schwann‘s cells and adipocytes Function of basal lamina • barier – selection in transport - proteoglycans – selection of cells – laminin • regeneration Basement membrane • two connected basal laminae – on the border of two epitheliums – lung, kidney – two laminae rarea, one lamina densa • basal lamina and lamina reticularis • visible in light microscope – PAS positive Polarity • apical part of cell – lumen of organ, surface of organ • basal (basolateral) part of cell – basal lamina in contact with lamina propria – wound healing, NM junction • polarisation and migration of epithelial cells 1 Lamina propria • contains vessels and nerves • mechanical support of epithelium • connects epithelium to another layers – usually undulated surface - papillae Specialisations of cellular surface • free surface – microvilli, stereocilia, cilia • lateral surface – intercellular junctions, interdigitations • basal surface – connection with BL, basolateral labyrinth Microvilli, stereocilia, cilia • microvilli – non-branching projections of cell – enlargement of cell surface • stereocilia – branched non – motile projections • cilia – non-branching motile projections – transport of extracellular mass Intercellular junctions (belt) • Zonula occludens – cell. membranes without intercell. space – five layers of membrane • Zonula adherens – intercell. space about 20 nm – thicker membrane – connected with cytoskeleton Intercellular junctions • adhesive – zonula adherens (belt desmosome) – desmosome (macula adherens) – hemidesmosome • occluding – zonula occludens (tight junction) • communicating – gap junction (nexus) Intercellular junction (spot) • Desmosome – intercell. space about 30nm • sometimes dark plate – connected with cytoskeleton – hemidesmosome • connection between cell and BL • Nexus (gap junction) – intercell. space about 2 nm – connexons – forms pores for ion transport 2 Regeneration of epithelium • fast and complete – faster with complete BL • continual regeneration of cells • stem cells • small intestine – 3 days • skin - 27 days Transporting cells • cells transporting ions (active) – microvilli, basolateral labyrinth – prox. a dist. tubule of kidney, striated ducts of sal. gl. • cells transporting using pinocytosis – transport of larger molecules – pinocytic sacs – endothelium Synthesising and trasporting cells • proteins – synthesis, modification, storage – serous cells of sal. gl., serous cells of pancreas • glycoproteins of mucus Types of epithelial cells • • • • • transporting cells signalising cells synthesizing and exporting cells myoepithelial cells stem cells Signalising cells • release signal molecules • neurocrine cells (neurons) – distribution across synapse • paracrine cells (DNES) – distribution – diffusely to ECM – secretory granules in basal part of cell • endocrine cells (suprarenal) – distribution - transport by blood stream – ultrastructure depends on type of substance Myoepihelial cells • cytokeratins, contractile microfilaments • acins and tubules of sweat, salivary, lacrimal gl. – mucus (lighter than cells prod. proteins) – mucous cells of sal. gl., goblet cells • steroids – lipid droplets, sER, tubular MIT 3 Stem cells • maternal • undiferetiated • regeneration of epithelium Classification of epitheliums • acording to spatial arrangement – flat – trabecular – reticular • according to function Flat epithelium • according to count of layers – simple – stratified – pseudostratified, transitional • according to shape of cells – squamous – cuboidal – columnar Trabecular epithelium • • • • cells in cords cords form web between cords are capillaries, nerves liver, adrenal, pituitary • keratinised and non-keratinised Classification according to function Reticular epithelium • cells are in contact only with their processes • cells form web • in „holes“ of web are other cells • thymus, bone marrow • • • • • • • epithelium covering - skin epithelium resorbtional - intestine epithelium respiratory - lung epithelium sensory – olfactory ep. epithelium muscular – myoepithelial c. epithelium germinal – testes epithelium secretory - glands 4 Glandular epithelium Types of gland • cells producing and releasing substrate • this substrate is used by organism • exocrine • type of secretion • endocrine – merocrine (pancreas) – apocrine (mammary gland) – holocrine (sebaceous gland) – excretion to lumen of organ – have ducts – do not have ducts – excretion to blood capillaries Types of exocrine glands • according to shape of secretory and excretory parts The end • simple glands • compound glands • tubular • alveolar (acinar) • tubulo-acinar next week • written test: Tissues • slide test 5