Four Basic Tissues
advertisement

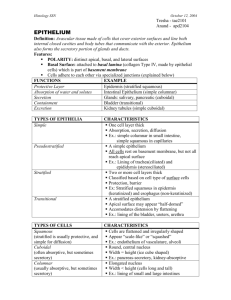
Four Basic Tissues Cell → Tissue → Organ → System → Body 1. Epithelial tissue (epithelium) – covers body surface, lines body cavity, and forms glands – (free surface) 2. Connective tissue – underlies or supports the other three tissues – dense, losse c.t. 3. Muscle tissue – made up of contractile cells and responsible for movement – cardiac, skeletal, smooth m., 4. Nerve tissue – receives, transmits, and integrates informations from outside and inside the body to control the activity of the body – PNS, CNS. 1 Epithelial tissue • Classification and characteristics of epithelial tissue • Polarity of epithelial cells • Surface modification of epithelial cells a. Apical : cilia, microvilli, stereocilia b. Lateral: intercellular junctions, interdigitations c. Basal: basement membrane, hemidesmosome, focal adhesion; basal striation (infolding). 2 Characteristics of epithelium • Avascular • Minimal intercellular material • Cells closely apposed with cell-to-cell adhesion molecules --- cell junctions – Creates a selective barrier between external enviornment and the underlying connective tissue • Functional and morphologic polarity – apical domain, lateral domain, and basal domain • Basement membrane – non-cellular, proteinpolysaccharide rich layer 3 Classification of epithelial tissue (I) Cell layers Shape simple squamous cuboid stratified pseudostratified columnar cuboid columnar transitional 4 Classification of epithelial tissue (II) Presence of apical surface modifications: cornified (keratinizied) or noncornified Cilia : ciliated or nonciliated Microvilli : Striated border - intestine Brush border - kidney (proximal tube) Stereocilia: long microvilli – epididymis (ductus defrence) 5 Simple epithelium • Simple squamous • Simple cuboidal • Simple columnar: apical surface with modifications, e.g. ciliated, striated border • Pseudostratified columnar: ciliated, stereocilia Simple squamous epithelium: endothelium Vascular system-endothelium Exchange Body cavities Barrier Bowman’s capsule (kidney) Respiratory spaces (lung) Silve stain of mesothelium spread preparation Intercellular substance is stained in black by silver Simple cuboidal epithelium Small ducts of exocrine gland Surface of ovary Kidney tubules Thyroid follicles Absorption Barrier secretion Simple columnar epithelium Small intestine Colon Stomach lining and gastric gland Gallbladder Absorption Secretion Colon (human) : Goblet cell GL: intestinal gland Exocrine Pancreas (Monkey) Simple columnar Simple squamous Simple cuboid Epi-2010 11 Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia Trachea and bronchial tree Efferent ductules of epididymis Secretion Absorption Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia Ductus deferens of epididymis Secretion Stratified epithelium Stratified squamous: Corninzed (keratinized) or Noncorninzed (nonkeratinized) Stratified cuboidal Stratified columnar transitional 14 Noncornified stratified squamous epithelium Epidermis Oral cavity and esophagus vagina Barrier protection Cornified (Keratinized) stratified squamous epithelium Stratified cuboidal epithelium Sweat gland duct Large duct of exocrine gland Anorectal junction Barrier conduit Stratified columnar epithelium Largest ducts of exocrine glands Anorectal juntion Barrier conduit 18 Transitional epithelium • Urinary tract • Between stratified cuboidal to stratified squamous • The surface cells are large and pale stained with a scalloped outline • The luminal cell membrane appeared thickened and densely stained Transitional epithelium Polarity Apical domain Lateral domain Basal domain 21 Apical domain • Microvilli - regular & irregular • Stereocilia - non-motile, long and (Stereovilli) irregular microvilli • Cilia – motile, (9+2) doublets primary (monocilia), (9+0) no active nodal, (9+0) rotation 22 Apical Domain and Its Modification Microvilli – regular & (1-3µm) irregular (short) Simple columnar epi. with striated border = microvilli Kidney Brush border Intestine Striated border Striated border stained red by periodic acid Schiff (PAS)– Glycocalyx of microvilli Uterine gland small projection Syncytiotrophoblast (placenta) irregular, branch intestine regular 23 Microvilli - actin filament +tropomyosin 24 Stereocilia – long microvilli, irregular (up to 120µm) Epididymis – pseudostratified columnar with stereocila 25 Epididymis – pseudostratified columnar with stereocila : (absorption) Stereocilia of the sensory epithelium of the ear : sensory mechanoreceptors (vibration) 26 Cilia – microtubule (axoneme) recovery stoke Trachea pseudostratified effective stoke ciliated epithelium MTOC: microtubule organizing center motor protein (MTOC) 27 Lateral surface: cell junctions terminal bar (LM) = junctonal complex (EM) = tight junction + intermediate junction + desmosomes anchor Terminal bar -tight junction (zonula occuldens) -intermediate (zonula adherens) -macula adherens (desmosomes): mechanical adhesion, composed of keratin filaments and dense plaque -gap junction (nexus): connexon Terminal bars in pseudostratified epithelium 29 Terminal Web & terminal Bar terminal bar (LM) = junctonal complex (EM) = tight junction (ZO) + intermediate junction (ZA) + desmosomes (MA) 30 Tight junction-occluding junction (zonula occuldens) P phase Zipper-like 31 Zonula occludens strands proteins – occludins, claudins (aqueous channels), JAM (Junctional adhesion molecule), ZO-1, ZO-2, ZO-3 32 Claudin molecules (aqueous paracellular channels) , and complexity and number of junctional strands, determine the permeability 33 Anchoring junctions Cell Adhsion Molecules (CAMs) Lateral surface 1. Zonula adherens – (intermediate junction), actin filaments 2. Macula adherens – (desmosomes), interact with intermediate filaments 3. Focal adhesions – (focal contact) 4. Hemidesmosomes Basal surface 34 Zonula adherens ( belt desmosomes, intermediate junction) 35 =intermediate junction = zonula adherens =intermediate filament + microfilament 36 Intercalated disk (閏盤) = fascia adherens + nexus (belt desmosome) (gap junction) Cardiac muscle 37 Macula adherens (desmosome, spot desmosom) Desmoplakin, plakoglobin “Cadherin zipper” 38 Desmosomes; Nucleus Intermediate filament 39 Luminal surface Occludin lateral Actin filaments E-cadherin Keratin filaments Desmocollin Desmoglein Basal surface Communicating junction: Gap Junction (Nexus) Gap junction (nexus): connexin, connexon, 41 Epi-2010 42 Lateral infoldings (interdigitations) Intestine Gallbladder -- Na+-K+ ATPase 43 Basal domain and its specializations in cell-to-extracellular matrix • Basement membrane • Cell to extracellular junction • Basal membrane infoldings 44 Basement membrane H&E PAS 45 Basement membrane 1. Basal lamina -- lamina lucida (rara) lamina densa (fibronectin ,collagen, laminin, entactin/nidogen, proteoglycan) 2. Lamina reticularis Lamina rara (lucida) Lamina densa Lamina reticularis Structure attachment, compartmentalization, filtration, tissue scaffolding, regulation and signaling 46 1 2 3 1 3 2 Basement membrane Epi-2010 47 Anchoring junction: Focal adhesion (contact) and hemidesmosome Focal adhesion: dynamic Focal contacts play an important role in sensing and transmitting signals from the extracellular environment into the interior of the cell. (mechanosensitivity) Actin Phosphotyrosine (a product of tyrosine kinase reaction) 48 Hemidesmosome: strong and stable adhesion 49 Basal infolding of plasma membrane Basal striation of proximal convoluted renal tubule 50 No duct hormone Pancreatic acinar cell lactating sebaceous gland (skin) Unicellular goblet cells Multicellular exocrine (intraepithelial, epithelial) merocrine, apocrine, holocrine, serous, mucous, mixed paracrine endocrine 51 duct secretary Epi-2010 52 53 Epithelial tissue • Classification and characteristics of epithelial tissue • Polarity of epithelial cells • Surface modification of epithelial cells Apical : cilia, microvilli, stereocilia Lateral: intercellular junctions, interdigitations • Termnal bar = junctioal complex • Junctional complex: zonula occludens (tight junction), zonula adherens (intermediate junction), macula adherens (desmosome), • Gap junction (nexus), lateral interdigitation • Terminal web • Basal: basement membrane, hemidesmosome, focal adhesion; basal striation (infolding). 54