Spinocerebellar Tracts: Anatomy & Function
advertisement

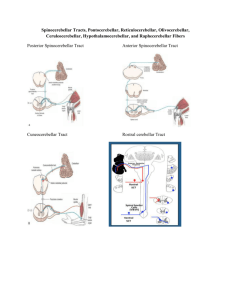
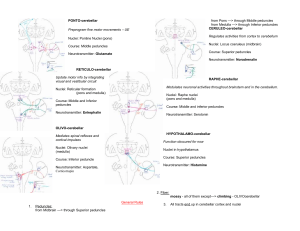
ventral ► spinocerebellar tract dorsal spinocerebellar ▲ and cuneocerebellar tracts - ventral spinocerebellar tract (= VSC) and dorsal spinocerebellar tract (= DSC) - DSC from upper body; VSC from lower body - unconscious proprioception - body and extremity position - from Golgi tendon organ receptors - body and extremity movement and muscle tone - from muscle spindle receptors - VSC axons cross midline in anterior gray matter on entry into lumbosacral spinal cord and then synapse in Stilling’s nucleus (in the contralateral ventral horn), and second neuron axons ascend in adjacent white matter to enter cerebellum via superior cerebellar peduncle, crossing midline in cerebellum again before reaching cerebellar cortex (ipsilateral to side of VSC entry into spinal cord) - DSC axons synapse on entry into thoracolumbar spinal cord, in Clarke’s nucleus (in the lateral gray matter of L-2 through C-8), and second neuron axons ascend in ipsilateral lateral white matter to enter cerebellum via inferior cerebellar peduncle and proceed to ipsilateral cerebellar cortex - above C-8, cuneocerebellar axons enter adjacent fasciculus cuneatus, then synapse in accessory cuneate nucleus in myelencephalon, and second neuron axons (as the ‘external arcuate fibers’) join DSC entering the inferior cerebellar peduncle and proceed to ipsilateral cerebellar cortex - spinoreticular and spinotectal tracts are other ascending tracts which report status of spinal cord activities to the brainstem nuclei ©