first hourly examination
advertisement

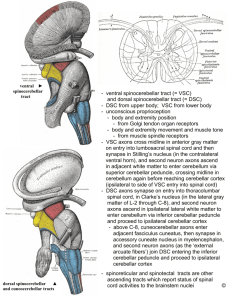
Name: _____________________________________________ FIRST HOURLY EXAMINATION NEUR1650 - STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Total pages: 9 September 30, 2010 Total Points: 101 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the letter(s) corresponding to ALL correct answers to each question. There will always be one and there may be more than one correct answer. (35 points). 1. Cerebrospinal fluid a. b. c. d. e. passes from the fourth ventricle into the subarachnoid space at the lateral apertures passes through the arachnoid granulations (arachnoid villi) into the jugular vein is produced by the ependymal cells lining the ventricles flows into the cerebral aqueduct from the fourth ventricle is typically sampled for medical tests at the lumbar cistern 2. Blood vessels included within the anterior (carotid) blood supply of the brain include the a. b. c. d. e. middle cerebral artery anterior inferior cerebellar artery superior cerebellar artery basilar artery posterior cerebral artery 3. Methods that have been used for tracing axonal projections in the anterograde direction include a. b. c. d. e. Nauta fiber degeneration method expression of reporter proteins under genetic control autoradiographic axon-transport technique the Marchi myelin-degeneration method in situ hybridization 4. A middle-aged financial consultant suffers a stroke that damages her midbrain ventrolaterally on the right, mainly damaging her right cerebral peduncle. Several weeks later, she has a massive heart attack and dies. A neuropathologist who is asked to analyze her nervous system at autopsy can be expected to find (among other things) a. neurons with swollen cell bodies and unusually pale Nissl substance in the left precentral gyrus b. axonal degeneration in the lateral funiculus on the right side of the thoracic spinal cord c. demyelination in the right side of the basilar pons (pontine protuberance) d. axonal degeneration in the pyramids of the medulla on the left side e. axonal degeneration in spinal nerves on the left side 2 5. Derivatives of the neural crest include a. b. c. d. e. the notochord Schwann cells the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord ganglia of the sympathetic chain first order sensory neurons providing tactile innervation of the fingertips 6. The ventral roots of the third thoracic segment (T3) include axons a. b. c. d. e. arising from the intermediolateral nucleus (or intermediolateral cell column) synapsing on vascular smooth muscle arising from alpha motor neurons in spinal segment C3 of neurons in the precentral gyrus innervating the intrafusal fibers of muscle spindles 7. The arachnoid a. b. c. d. e. is bathed on its inner surface (the side facing the brain) by cerebrospinal fluid sends protrusions through the dural wall of the superior sagittal sinus is continuous with the perineurium of the spinal nerves closely follows every contour of the brain surface, including cortical sulci lies between the dura mater and the brain surface II. TRUE or FALSE. Circle the correct letter. (30 points). T F 1. Axon terminals are the only neuronal structures capable of releasing synaptic vesicles. T F 2. Gap junctions permit direct passage of electrical current from one neuron to another. T F 3. A Nissl stain would stain the inferior cerebellar peduncle more than the inferior olive. T F 4. The myelin in the corpus callosum is produced by oligodendrocytes. T F 5. Tracers such as dextrans or horseradish peroxidase are transported in axons by an active process that depends critically on microtubules. T F 6. Carbanocyanine dyes (such as DiI) are fluorescent lipophilic molecules that permit tracing of axonal pathways in fixed, postmortem tissue. T F 7. In situ hybridization is a method that reveals the distribution of brain enzymes by harnessing their ability to catalyze histochemical reactions. T F 8. The inferior olive is a derivative of the embryonic rhombencephalon. T F 9. The putamen is a derivative of the embryonic telencephalon. 3 T F 10. The marginal layer of the neural tube contains the outgrowing axons of differentiating neurons. T F 11. Preganglionic sympathetic motorneurons are found mainly in the brainstem. T F 12. A dermatome is a cluster of embryonic mesodermal cells that are precursors of bone, muscle and connective tissue in a part of the body. T F 13. Axons arising from neurons in the dorsal column nuclei decussate in the midbrain. T F 14. The abducens nerve exits the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction. T F 15. The oculomotor nerve is the only cranial nerve exiting the dorsal surface of the brainstem. T F 16. The tail of the caudate nucleus lies in the temporal lobe. T F 17. The Circle of Willis lies rostral to the basilar artery. T F 18. During maturation of the embryonic spinal cord, the lumen of the neural tube becomes the central canal. T F 19. The lateral apertures of the ventricular system lie just caudal to the cerebellar peduncles. T F 20. All spinal nerves contain both motor and sensory axons. T F 21. Synapses with pre- and postsynaptic densities of comparable size (“symmetrical”) are generally excitatory rather than inhibitory. T F 22. The main blood supply for the cingulate gyrus comes from the middle cerebral artery. T F 23. The posterior cerebral artery supplies blood to the medial part of the temporal lobe. T F 24. The posterior communicating artery directly links the basilar and vertebral arteries. T F 25. Sensory axons carrying information from the vestibular apparatus enter the brainstem at the spinomedullary junction. T F 26. The blood supply of the cerebellum comes primarily from the carotid artery. T F 27. The funiculi of the spinal cord are derived from the marginal layer of the neural tube. T F 28. The motor cortex is derived from the basal plate. T F 29. Dysraphias such as anencephaly and spina bifida result from errors in neurulation in which the neuropores fail to close. T F 30. The site of action-potential initiation in neurons always lies within a few millimeters of the soma. 4 IV. SHORT ANSWER. The figure below is a transverse section of the CNS from patient who suffered single, well localized site of brain damage some months earlier. The section is mounted so that the right side of the CNS appears on the right side of the image. Answer the following questions as succinctly as possible. (9 points) 1. What level of the CNS is this section drawn from? Be as specific as possible. 2. What tract or pathway is found in the region of demyelination labeled A? 3. What tract or pathway is found in the region of demyelination labeled B? 4. Name a structure rostral to the midbrain that might have been damaged to produce this pattern of demyelination 5. Name a structure within the brainstem that might have been damaged to produce this pattern of demyelination. 6. Which side of the CNS would this lesion have been on? 7. What poorly myelinated tract is found in the position indicated by C? 5 8. The region indicated by D contains primary sensory axons. Where are the cell bodies of the neurons from which these axons arose? 9. In what nuclei do the primary sensory axons in D terminate in the brainstem? V. FILL IN THE BLANK. Identify each structure labeled. The same structure may be named more than once. The second figure (with structures k – o) is a transverse section of sheep brain. The other figures are from human CNS. (27 points). a. _______________________________________________________________ b. _______________________________________________________________ c. _______________________________________________________________ d. _______________________________________________________________ e. _______________________________________________________________ f. _______________________________________________________________ g. _______________________________________________________________ h. _______________________________________________________________ i. _______________________________________________________________ j. _______________________________________________________________ k. _______________________________________________________________ l. _______________________________________________________________ m. _______________________________________________________________ n. _______________________________________________________________ o. _______________________________________________________________ p. _______________________________________________________________ q. _______________________________________________________________ r. _______________________________________________________________ s. _______________________________________________________________ 6 t. _______________________________________________________________ u. _______________________________________________________________ v. _______________________________________________________________ w. _______________________________________________________________ x. _______________________________________________________________ y. _______________________________________________________________ z. _______________________________________________________________ aa. _______________________________________________________________ 7 8 sheep brain 9