Cerebellar Afferents (Nick L, Steve, Andrew) - 34
advertisement
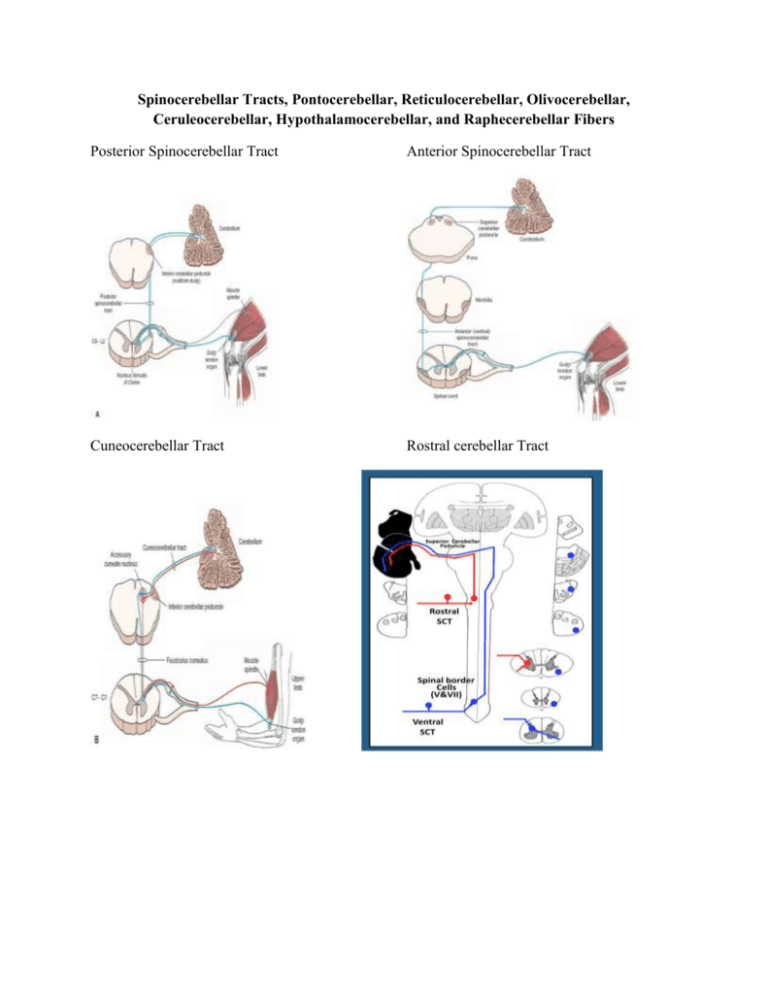
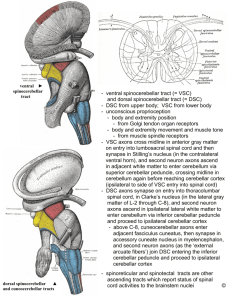
Spinocerebellar Tracts, Pontocerebellar, Reticulocerebellar, Olivocerebellar, Ceruleocerebellar, Hypothalamocerebellar, and Raphecerebellar Fibers Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract Cuneocerebellar Tract Rostral cerebellar Tract Posterior Spinocerebellar • From muscle spindles and GTO’s in the lower limb • Lamina VI and VII (Dorsal Nucleus of Clarke) at level of C8-L3 • Ascends Ipsilaterally • Enter cerebellum via ICP Anterior Spinocerebellar • From GTO’s in the lower limb muscles • Transmit info to lamina VI • Decussate and ascend Contralaterally • Most fibers recross the midline before reaching the cerebellum so the stimulus will go to both hemispheres • The fibers enter both hemispheres via the SCP Cuneocerebellar • Upper limb equivalent of the PSCT • Starts where PSCT left off (C8) • Axons ascend ipsilaterally via the cuneate fasciculus until reaching the accessory cuneate nucleus • Enters through the ICP Rostral cerebellar • Receives info from GTO’s in upper limb muscles • Begins at lamina VII at C4-C8 spinal segments • Transmits info from the cervical spinal cord to the ipsilateral cerebellum • Enters cerebellum via ICP and SCP Neurotransmitters All of these pathways use Glutamate Cerebellar Fibers Name Start Cerebellar Peduncle End Neurotransmitter Ips/Cont/Bi + = Excitatory Type - = Inhibitory Pontocerebellar Pontine Nuclei Reticulocerebellar Reticular formation MCP Fiber Glutamate (+) Contralateral Enkephalin Bilateral Raphecerebellar Raphe nuclei (in pons and medulla) MCP and ICP Hypothalamocerebellar Hypothalamus SCP Ceruleocerebellar Nucleus (locus) Ceruleus Olivocerebellar Inf. Olivary Nucleus ICP Cerebella r Nuclei and Cortex Serotonin Ipsilateral Histamine Bilateral Noradrenaline Ipsilateral Aspartate (+) Corticotropin Contralateral Releasing factor (+) mossy Climbing