Incident Response Planning - (PwC)

www.pwc.com
How to effectively respond to an information security incident
Agenda
Analogy
Plan Preparation
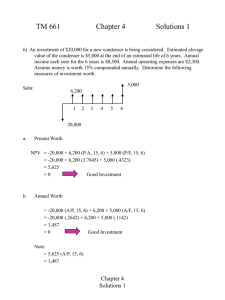
Incident Handling Overview
Collect & Triage
Investigation
Containment
Eradication
Recovery
PwC 2
Are you going in the water?
PwC 3
Initial incident response steps
• Gather documentation
- Contact lists, network diagrams, etc
• Designate incident leads
• Notify proper contacts
- Internal contact
◦ Legal, management, internal support leads
- External contacts
◦ Legal, Vendor support, trusted third parties, law enforcement
PwC 4
Incident handling overview
• Based on NIST 800-61 Incident Handling
- Detect and Analyze (Triage)
- Containment
- Collect, Preserve and Investigate
- Eradication
- Recovery (lessons learned)
Recovery
Detect and analyze
Contain
Eradicate
Collect &
Preserve
PwC 5
Detection and analysis
PwC 6
Do we have an incident? (Yes/No)
• How were we notified
- Internal vs. External
• Deploy experienced people to determine if you have a real incident
• Is this a regulatory, legal or contractual issue?
PwC 7
Practical example
• eCommerce Site:
- Client reported the server performance issue
- Tech Support found the load too high
- Developer examined the code
◦ Identified foreign code on the server, referred to security
- Security began collecting data
◦ Contacted External Incident Response team
PwC 8
Practical example
• Incident Response Team
- Examined the server
- Recommended blocking IP addresses
- Examined the server population
- Provided a written report of the incident
- Recommended Eradication
- Recommended policy and procedure changes
PwC 9
Exfiltration
PwC 10
What to do next
• Incident Classification (DDoS, Malware, Unauthorized Access)
• Triage the problem – follow the evidence
• What are my capabilities?
• What am I looking for?
• How will I accomplish what I need to do?
PwC 11
Collection and preservation
PwC 12
Evidence preservation
• Proper forensic collection and documentation
- Collect what you need to answer the questions
• Malware analysis
- What are we dealing with and what is it capable of?
◦ Data exfiltration
◦ Keylogger
◦ Sniffer
◦ Dumping memory
PwC 13
Data to collect
• Forensic images of the systems compromised
• Firewall Logs
• Web server logs
• Proxy server logs
• Netflow data
• Syslogs (Unix)
• Local Windows event logs
• Domain Controller event logs
PwC 14
Triage process flow
Incident Handler
Forensics
Yes
Compromised Host
No
Information Security
Malware present
Yes
Malware Analysts
No
Hardening Monitoring
PwC 15
Containment
PwC 16
Initial containment 1-3 days
• Apply M&M approach (hard & crunchy on outside, soft & chewy on inside)
• Data characterization (add rings of security)
• Grab low hanging fruit
- Update AV, Flag suspicious files, HIDS/HIPS, create IDS signatures, block traffic, change passwords, disable accounts
- Change to manual procedures if necessary
PwC 17
What don’t I know
• Where do I need increased visibility
- Review logs, increase auditing/logging
◦ System, database, network device, etc
- Process to secure, archive, collect ,review logs
- As the British say, Mind the gap!
SQL Query logging example:
PwC 18
SQL query logging example
• Sophisticated attack on database
- Cracked the PINS for banking cards
- Used SQL injection to inject malicious executable into the database
- Withdrawal limits on the cards are raised to maximize the amount that can be withdrawn
- No SQL logging performed on the databases
- Client using a SQL query recorder
PwC 19
Eradication & remediation 2-4 weeks
• Remove malware
• Re-image and/or rebuild systems
- Consider legacy applications
• Delete/disable accounts
• System and Network device hardening
• Increase log monitoring
PwC 20
Longer term issues
• Data Flows
• Application Characteristics
• Server Characteristics
• Risk Factors
• Regulatory and Compliance Issues
PwC 21
Recovery – Long term goals
• Implement a Information Security group with a CISO
• Integrate Information Security into all facets of the business
• Network Isolation and segmentation
• System hardening
• Annual security audits (include penetration testing)
- Include 3 rd party connections
• Implement a Sensitive Data Program
PwC 22
Recommendations
• Ensure there is an incident response plan in place
• Know where your crown jewels are located
• Regular security assessments conducted by outside firm
• Have an incident response support team on speed dial
PwC 23
Questions
Contact:
Dave Nardoni 213-356-6308
Jef Dye 213-217-3976
PwC 24
© 2012 PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the United States member firm, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network. Each member firm is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details. This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors.