AP Macroeconomics Unit 1 Part 1 Review Test
advertisement

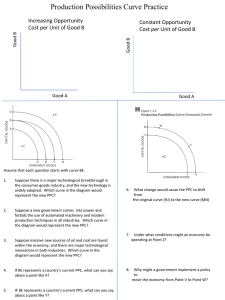
AP Macroeconomics Unit 1 Part 1 Review Test (Chapters 1-2) 1. The study of economics involves the fundamental problem of: a. Deriving a productions possibilities curve b. Defining opportunity costs c. Analyzing the impacts of political decision making d. The allocation of scarce resources to competing uses 2. “If I didn’t have a date tonight, I would save 420 and spend the evening playing bridge,” your friend comments. The opportunity cost of the date is: a. $20 b. $20 plus a night of bridge c. dependant on how pleasant the date turns out to be d. not playing bridge that evening 6. Pick the normative statement from the list below: a. New tax laws are needed to help the poor. b. Teenage unemployment reduces the potential output of our economy c. Old age pensions raise the standard of living for the elderly. d. Increased female unemployment is due in part to the increased number of women looking for a job. 7. Which one of the following is true? a. More spending on research and development will not have an impact on economic growth. b. Economic growth does not really alter the choices present for the economy c. No matter how much economic growth occurs, scarcity is still a problem d. Economic growth causes a production possibilities curve to be bowed out. 8. Macroeconomics approaches the study of economic from the viewpoint of: a. Individual firms b. Individual consumers c. The operations of specific product and resource markets d. The entire economy 9. All economic systems must answer certain fundamental questions. Which actions is NOT one of those questions? a. Which actions should government take to reduce inflation? b. How should resources be organized so that production takes place? c. Once production occurs, how is society’s output to be distributed? d. What types of goods and services are to be produced? Use the graph below to answer questions 3-5 A Military Goods E D C B Consumer Goods 3. Given the production possibilities curve above, at which point would there be unemployment or underemployment of resources? a. A d. D b. B e. E c. C 4. Given the above PPC, if society suddenly decided that military goods were no longer necessary and chose not to produce any, we could expect to operate at a point such as: a. A d. D b. B e. E c. C 10. As a consequence of the condition of scarcity: a. Individuals and communities have to make choices from among alternatives b. There is never enough of anything c. Things which are plentiful have relatively high prices d. Production has to be centrally planned 5. Suppose the president has stated that he believes the economy could produce additional military goods while also expanding the production of consumer goods. If the president believes this can be accomplished, in a short period of time, he must believe the economy is operating at a point such as: a. A d. D b. B e. E c. C 11. Which of the following would not shift an economy’s PPC? a. A doubling of the labor force b. A doubling of the number of machines c. A doubling of the money supply d. More advanced technology 12. Which one of the following is an illustration of a microeconomic question? a. Is the quantity of automobiles purchased in one year dependent upon the price of automobiles? b. Does government spending influence the total level of employment in the economy? c. Is the purchasing power opf the dollar higher or lower today than it was in 1980? d. Is a command economy superior to a market economy? 13. Which one of the following statements implies that PPCs are likely to be curved, rather than straight lines? a. Ultimately all resources are scarce. b. Most resources are more productive in certain uses than in others? c. Unemployment is a more serious problem for some social groups than others d. Economists are notoriously poor at drawing straight lines 14. the field on which a farmer grows wheat is an example of ___. The workers who harvest it are ___. The tractors they use are ___. The farmer, who rent the field, pays the workers, and buys the tractors, represents _____. The correct answers to the above are, respectively: a. land, entrepreneurship, capital, labor b. land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship c. land, entrepreneurship, land, labor d. none of the above 15. The PPC illustrates the basic principle that: a. An economy will automatically seek that level of output at which all of its resources are employed. b. An economy’s capacity to produce increase in proportion to its population size. c. If al the resources of an economy are in use, more of one good can be produced only if less of another good is produced d. All of the above 16. A number of agricultural sub-Saharan nations of Africa have over-farmed and overgrazed their land to the extent that significant portions of it have turned into desert. This suggest that: a. The concavity of the PPCs of such nations has increasec b. The PPCs of such nations have shifted inward c. The PPCs of such nations have shifted outward d. The nations are operating at some point outside of their PPCs. 17. Points C, D, E, and H on the adjacent PPC show: a. an inefficient allocation of society’s scarce resources b. a constant tradeoff between tanks and automobiles Tanks c. possible combinations of tanks and automobiles d. unattainable combinations of tanks and automobiles C D G E F H 18. A friend of your keeps regular schedule. Each day she spends Automobiles 7 hours in school, 5 hours watching TV and eating, and 8 hours sleeping and divides the other four hours between studying and a newspaper route. Your friend says, “I added a new block to my route last month and my grade point average in my classes dropped by .2. Last week I added another new block and my GPA dropped by .51. What the deal?” You explain that: a. delivering papers dims one’s senses b. this is a case of misplaced effort c. this is an example of the law of increasing costs d. economic models are not well suited to your friend’s situation 19. Assume an economy is characterized by unemployment and a failure to realize least-cost production. The immediate effect of resolving these problems will be to: a. Move the level of actual output closer to the economy’s PPC. b. Create a less equal distribution of income c. Shift its PPC to the left d. Shift its PPC to the right 20. Which one of the following is real capital? a. A pair of stockings d. A share of IBM stock b. A dump truck e. A T-Shirt c. A saving account 21. Which one of the following is a normative statement (see graph): a. Point C is superior to B because it is important to look to the future of society. B b. If society is initially at C, it must sacrifice R 6 units of bread to obtain one more unit E of tractors A c. If society produces 2 units of tractors D and 12 units of bread, it is not using its available resources with maximum efficiency d. Ceteris paribus, the combination of outputs represented by D will result in more rapid growth than will the combination represented by point C. 20 16 A B 12 C 8 D 4 E 1 2 Tractors 3 4