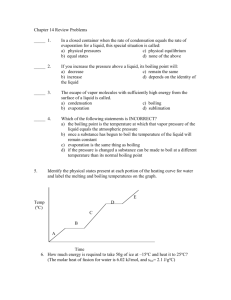
Evaporation and Condensation
advertisement

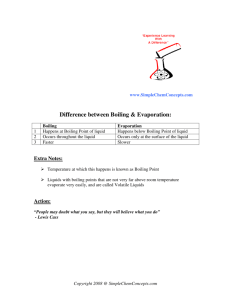
Evaporation and Condensation Directions: Read, highlight, and once you are finished reading, go to schoology.com and answer the questions. Remember to go to schoology.com by first going to wcsoh.org and selecting schoology at the top of the page! Evaporation When liquids turn into a gas, we call this evaporation. The temperature where a liquid turns into a gas is called the boiling point. Every substance on earth has a different boiling point. This should sound very similar to what you read for melting points. Water, for example, has a boiling point of 212oF (100oC) a temperature special to water only. As a liquid approaches its boiling point, the particles absorb more and more energy making them vibrate faster. Here’s the weird part though. When liquids reach their boiling point, the particles don’t continue to vibrate faster. You saw this when we boiled water (and when we melted ice). The heat instead goes into break the attraction the particles have to each other. When the liquid particles gain enough energy to overcome the attraction holding them together, they become a gas. Once they become a gas, the molecules are free to move faster and faster. Instead of just sliding over each other like they do in a liquid, they now have the ability to fly around attracted to nothing but themselves. Because molecules that are evaporating are absorbing heat, we refer to evaporation as an endothermic process. Remember, endo means “to enter” while thermic means “heat.” Liquid can also turn into a gas at temperatures lower than the boiling point. Evaporation occurs because some particles have enough energy to escape as a gas from the surface of the liquid even though the whole liquid hasn’t heated up yet. This is why even though it is cold outside and far below water’s boiling point that the pavement can be wet with snow melt in the morning, but by early afternoon the pavement has dried. If you stick your hand in the water, it will be really cold. The surface molecules though get enough energy to evaporate. Boiling vs. Evaporation Boiling Evaporation Occurs only at the boiling point Occurs all the time Occurs throughout the liquid Occurs only at the surface of the liquid Occurs rapidly Occurs slowly Condensation The opposite of evaporation is condensation. In this case a substance changes from a gas back to a liquid. It does this by losing heat energy. For water, condensation happens at 212oF (100oC). That same weird thing happens during condensation. The temperature stops until all of the gas has condensed turning into a liquid and then it is free to drop more. If that temperature seems familiar, it should because condensation and evaporation happen at the same temperature. The difference is that evaporation is endothermic, but condensation is exothermic. Remember that because the molecules are giving up their heat (getting colder), we refer to condensation as an exothermic process (exo means “to exit” while thermic means “heat”). Complete the following chart for Water in degrees Celsius Evaporation/Boiling Condensation Temperature where it occurs? Endothermic or Exothermic change? Temperature climbing or staying the same? Give an example where you have seen each change of state occur.