Moys Classification Scheme: Legal Materials Guide
advertisement

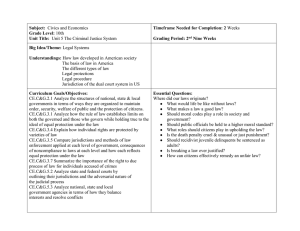
Examples of Call (or shelf mark) Numbers Using the Moys Classification Scheme (Example 1) KN } Subject classification [KN 10 Contract] 10 } .K1 Jurisdiction facet indicator [.K1 Australia] CHE Shelf locator [first 3 letters of author or title main entry] 1988 Publication date Commonly used Jurisdiction Facet Indicators .A1 England .B2 Scotland .F1 Canada .G1 United States .K1 Australia .K2W Western Australia .L1 New Zealand MOYS CLASSIFICATION SCHEME The full bibliographic details of the book are: Cheshire, G C, Cheshire and Fifoot’s law of th contract. (Butterworths, 6 Australian ed, 1988). (Example 2) KM } Subject classification [KM 526 Australian 526 } & Jurisdiction indicator Criminal Law] .Z2 Legal form [.Z2 casebook] EDW Shelf locator [first 3 letters of author or title main entry] 1976 Publication date The full bibliographic details of the book are: E J Edwards, R A Hayes and R S O’Regan, Cases on the Criminal Code: being cases and material on the criminal law in Queensland, Western Australia and Papua New Guinea. (Law nd Book Company Ltd., 2 ed, 1976). CRAVEN LAW LIBRARY The collection is classified according to the Moys classification scheme, 4th edition 1. The scheme was developed on the basis that legal materials may be divided most conveniently into: • primary materials (Statute and case law) • secondary materials (Treatises and periodicals). The central feature of the scheme is the treatment as a unit of those countries whose legal systems are based almost entirely on the English Common Law, i.e. England and Wales, Ireland, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, United States and the former British West Indian colonies. Territorial jurisdictions with Civil Law systems or legal systems not wholly based on the Common Law e.g. those in Africa, Latin America, Asia and Europe, are treated as separate units. 1 Elizabeth Moys, Moys Classification and Thesaurus for Legal Materials, (K G Saur, 4th ed, 2001). Within the Common Law Unit Primary Materials are subdivided first, by territorial jurisdiction and then by form (parliamentary publications [including Statutes] and law reports). Secondary Materials are subdivided first by subject and then territorial jurisdiction within each subject area. Periodicals are interfiled with other secondary materials. In other national systems, division by country comes first followed by form (for primary materials) and subject (for secondary materials). Reference books; jurisprudence; international law; religious legal systems and ancient and medieval law are treated separately from these national systems. A broad outline of the Moys Classification Scheme is given below. SUBJECT CLASSIFICATION Reference Works Jurisprudence Biography International Law Conflict of Laws Religious Legal Systems Ancient & Medieval Law K KA KB 10-22 KC 1-1425 KC 2000-2150 KD KE SUBJECT CLASSIFICATION Common Law Primary Materials British Isles KF Canada, USA KG Australia, N Z KH Common Law - Treatises/Periodicals General KL Legal Profession 50-101 Admin. of Justice 200-319 Legal History 400-480 Public Law KM Constitutional & Administrative Law 31 - 334 Taxation 335-337 Criminal Law & Procedure 500-690 Criminology 700-799 Private Law KN Contract and Tort 5-39 Property (Real & Personal) 50-110 Personal & Social Laws 150-169 Family Law 170-179 Industrial Law 190-198 Equity 200-203 Trusts & Trustees 210-221 Commercial Law 250-287 Companies 262-265 Sale of Goods 280-287 Insurance 290-295 Finance 300-315 Maritime Law 330-339 Practice & Procedure 350-400 Evidence 390-399 Comparative Law KP Other Modern Legal Systems Africa KR Latin America KS Asia and Pacific KT Europe KV European Communities KW