Lab 01: NaBH4 Reduction of Camphor 4 4
advertisement
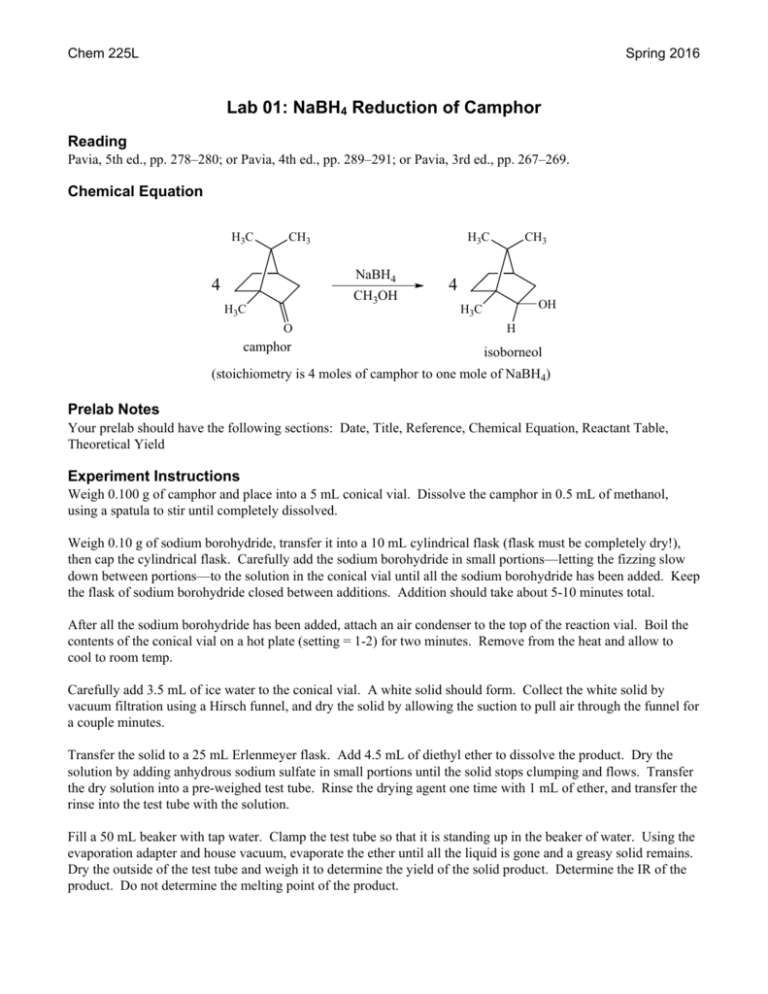
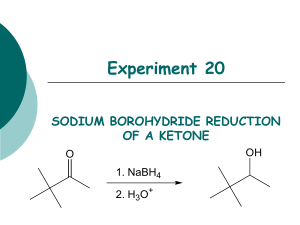
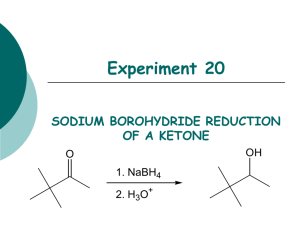
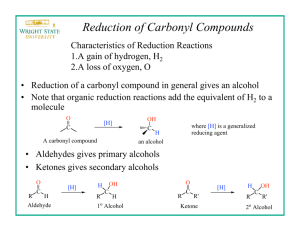
Chem 225L Spring 2016 Lab 01: NaBH4 Reduction of Camphor Reading Pavia, 5th ed., pp. 278–280; or Pavia, 4th ed., pp. 289–291; or Pavia, 3rd ed., pp. 267–269. Chemical Equation H3 C CH3 H3 C NaBH4 4 CH3OH H3 C O camphor CH3 4 OH H3 C H isoborneol (stoichiometry is 4 moles of camphor to one mole of NaBH4) Prelab Notes Your prelab should have the following sections: Date, Title, Reference, Chemical Equation, Reactant Table, Theoretical Yield Experiment Instructions Weigh 0.100 g of camphor and place into a 5 mL conical vial. Dissolve the camphor in 0.5 mL of methanol, using a spatula to stir until completely dissolved. Weigh 0.10 g of sodium borohydride, transfer it into a 10 mL cylindrical flask (flask must be completely dry!), then cap the cylindrical flask. Carefully add the sodium borohydride in small portions—letting the fizzing slow down between portions—to the solution in the conical vial until all the sodium borohydride has been added. Keep the flask of sodium borohydride closed between additions. Addition should take about 5-10 minutes total. After all the sodium borohydride has been added, attach an air condenser to the top of the reaction vial. Boil the contents of the conical vial on a hot plate (setting = 1-2) for two minutes. Remove from the heat and allow to cool to room temp. Carefully add 3.5 mL of ice water to the conical vial. A white solid should form. Collect the white solid by vacuum filtration using a Hirsch funnel, and dry the solid by allowing the suction to pull air through the funnel for a couple minutes. Transfer the solid to a 25 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add 4.5 mL of diethyl ether to dissolve the product. Dry the solution by adding anhydrous sodium sulfate in small portions until the solid stops clumping and flows. Transfer the dry solution into a pre-weighed test tube. Rinse the drying agent one time with 1 mL of ether, and transfer the rinse into the test tube with the solution. Fill a 50 mL beaker with tap water. Clamp the test tube so that it is standing up in the beaker of water. Using the evaporation adapter and house vacuum, evaporate the ether until all the liquid is gone and a greasy solid remains. Dry the outside of the test tube and weigh it to determine the yield of the solid product. Determine the IR of the product. Do not determine the melting point of the product. Chem 225L Lab 01: NaBH4 Reduction of Camphor Page 2 After determining the weight and IR of the product, add a small amount of wash acetone to dissolve the solid and dump the solution into the non-halogenated organic waste. Prelab Questions 1. Write the formal mechanism for the reaction of camphor with NaBH4. 2. Briefly explain why one mole of NaBH4 can react with four moles of camphor. 3. Briefly explain using complete sentences and a picture why only the only stereoisomer product formed is isoborneol (little to no borneol is formed in the reaction). Postlab Questions 1. Compare the IR spectrum of your product to the authentic IR spectrum of isoborneol and borneol in the lab textbook. Which does it most resemble? Which peaks (list the approximate frequencies) could you use to distinguish between the two possible products? 2. Calculate the percent yield of the reaction using the following formula: 100% 3. When the NaBH4 is added to the methanol solution, the mixture slowly gives off small gas bubbles. What is the gas that is formed? Based on this observation, briefly explain why an excess of NaBH4 is used in the reaction.