Earthquake Analysis: Seismogram Interpretation Worksheet
advertisement

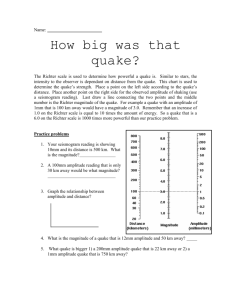
Earthquakes: Critical Thinking Directions: Interpret the seismograms below to evaluate this earthquake. Station A: Fresno, CA 1. Label the P and S waves in each seismogram. 2. Lag time is the difference in time between the P wave arrival and S wave arrival. a. Write down the lag time in seconds for each seismogram (write on the seismogram). Station B: Las Vegas, NV b. Which station has the shortest lag time? _________________ c. Which station has the longest lag time? __________________ 3. Station C: Phoenix, AZ Amplitude is the height of the tallest S peak in mm. a. Write the amplitude (in mm) next to the tallest S peak for EACH seismogram. b. Which station has the greatest amplitude? _________________ c. Which station has the smallest amplitude? __________________ 4. Based on seismic data, which city is closest to the EPICENTER of the quake. Defend your answer with a reason. (sentences) Figure 2: S-P Lag Time Figure 3: Nomogram (for Magnitudes) Directions: Use the lag time from your FRESNO seismogram to determine the distance to the epicenter (lag time graph). Mark this distance on the nomogram. Then mark the amplitude you measured from the FRESNO seismogram. Connect these two points with a line. 5. How far away from the epicenter is Fresno? 6. What is the magnitude of this quake on the Richter scale? 7. A few months after this quake, a _____ quake occurred in eastern Turkey. Fifty one people died, 100 people were injured, 5000 were displaced and over 1,000 buildings were heavily damaged or destroyed. How could this Turkish quake be so much more damaging than the southern California quake you measured? Think of factors OTHER THAN SIESMIC WAVE SIZE that can influence how devastating a quake can be.