Mangement of Supraventricular Tachycardia
advertisement

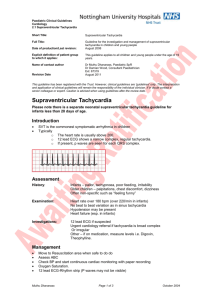
Management of Supraventricular Tachycardia Most supraventricular tachycardias (SVTs) in the neonate are re-entry atrioventricular SVTs via an accessory pathway. Synchronized DC Shock Sedate first. Select appropriate sized paddles. Sternum paddle at the base of the heart, apex paddle at the apex/axilla. Connect to defibrillator ECG leads to the patient and confirm QRS synchronization. Give 0.5 joule/kg, then 1 joule/kg if unsuccessful, then 2 joules/kg. SVT is a diagnostic category. The correct diagnosis is a challenge. Sinus Tachycardia is usually < 200/min, SVT usually > 220/min. Perform an ECG in a format that can be electronically transferred / faxed to a consultant cardiologist. Initial Management Examine for signs of heart failure Secure IV line (as proximal as possible with 3 way tap) ECG, septic work up, U+E. If Stable: Try vagotonic manoeuvres – oropharyngeal suction, face immersion in cold water for 5 seconds Do not put pressure on eyeballs. Adenosine (IV) Need continuous ECG Dose = 100mcg/kg IV rapidly, follow with 2-5mls rapid 0.9% NaCl flush If unsuccessful – Repeat 100mcg/kg Then give 200mcg/kg Then 300mcg/kg Wait 2 minutes between doses and monitor vitals. If unsuccessful: Contact Neonatology Consultant +/- Paediatric Cardiologist Administration of IV anti arrhythmics other than adenosine should only be given following this consultation. Differential Diagnosis Sinus Tachycardia – Rates up to 230 per minute, more variability on ECG. Ventricular Tachycardia – Wider QRS complex. SVTs may initially be asymptomatic. Prolonged SVT can result in heart failure and shock. Sustained/ Paroxysmal SVT may develop in utero and may result in hydrops SVT is amenable to effective treatment. There is the potential for poor outcome due to left ventricular dysfunction if it remains untreated for a prolonged time. If recurrent, consider Flecainide or Amiodarone in consultation with a cardiologist Flecainide – 1-2mg/kg 8-12 hourly pre or post feeds. Check level before 5th dose. Therapeutic range 200-700 mcg/l The application of synchronised DC shock is usually undertaken by the cardiologist Paediatrics and Neonatology Clinical Programme Algorithms References: 1. Kothari DS, Skinner JR. Neonatal tachycardias: an update. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2006;91: F 136-F144 2. Dixon J, Foster K, Wyllie J, Wren C. Guidelines and adenosine dosing in supraventricular tachycardia. Arch Dis Child 2005;90:1190-1191. 3. Sreeram N, Wren C. Supraventricular tachycardia in infants: response to initial treatment. Arch Dis Child 1990;65:127-129. 4. APLS SVT Protocol This care pathway has been produced by the National Paediatric and Neonatology Clinical Programme. It is aimed at medical, nursing and allied health professionals working in Irish neonatal units. Algorithm number: N13 Document drafted by: National Paediatric and Neonatology Clinical Programme Revision number: 1.0 Document Status: Approved Date of Last Update: 29/8/12 Document approved by: Paediatric and Neonatology Clinical Programme Working Group Neonatal Clinical Advisory Group Approval date: 13/12/12 Revision date: January 2015