Arrhythmia Vipul Brahmbhatt, MD Cardiac Electrophysiologist Cardiology Consultant of Johnson City
advertisement
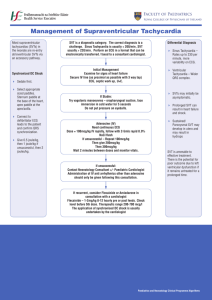
Arrhythmia Vipul Brahmbhatt, MD Cardiac Electrophysiologist Cardiology Consultant of Johnson City Outline • We will discuss Tachyarrhythmia • Understand SVT mechanism • Analyse EKG with Tachycardia • Differential Diagnosis of Wide complex Tachycardia INTRINSIC RATE SA NODE- 60-100 JUNCTION- 40-60 VENTRICULAR- 20-40 Insert Normal EKG. DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO TACHYCARDIA Wide Complex QRS>140msec Narrow Complex QRS<120msec Irregular Regular AVNRT AVRT A-Tach VT SVT with Aberrancy Preexited tachycardia Paced Rhythm Atrial fibrillation A- Flutter with Variable Conduction MAT AVNRT PSVT is a result of DUAL AV NODAL PATHWAYS AVNRT ABLATION SITE Accessory Pathway Mediated Tachycardia ACCESSORY PATHWAY LOCATION Short PR interval Initial Slurring of QRS (delta wave) Change in appearance of QRS complex. A. VT B. SVT with aberrancy C. Antidromic tachycardia Risk of SCD in Patient with WPW • • • • Shortest Preexited R-R Interval of <250msec either during Spontaneous A FIB or during Induced A FIB. History of Tachycardia Multiple Accessory Pathway Ebstein Anomaly. Management of Asymptomatic Patient with Preexitation Diagnosis <40 Year- 1/3 patient will have Symptoms Diagnosis after 40 Year unlikely to have symptoms Pt should be advised to seek attention if symptoms occur or any syncope Family H/O SCD or Prior Syncope Catheter Ablation is a choice if pt desires and in High Risk Public Job Catheter Ablation has Success rate of 95% with Complication rate 1-2% 35 YF with Asymptomatic Preexitation and LVEF of 10-15% LVEF Improved to 70% Post RFA Which of the following is true? A. Mechanism of tachycardia is VT B. Intravenous verapamil should help C. Immediate DCCV is needed D. Catheter ablation could be performed Atrial Fibrillation • • • • Paroxysmal Persistent Long standing Persistent Permanent CAUSE Pulmonary disease Infection, IHD Rheumatic Heart disease Alcohol intoxication (Holiday heart) Thyrotoxicosis, Toxins Electrolyte Imbalance Surgery, Structural heart disease Hypertension Pulmonary Vain Isolation About 70% Success Free of Arrhythmia Success Rate varies based on many Pt related factor and Duration of Atrial Fibrillation Dissociated PV potential • Wide complex Tachycardia Ventricular Paced Rhythm SVT with aberrancy Tachycardia Usually has Concordant Positive Precordial Lead Complexes Check Medication list class IA and IC Hyperkalemia Usually has LBBB morphology • SVT with AV nodal or HP system disease • SVT with Slow Ventricular conduction • AVART (Bypass tract tachycardia) • SVT with Drug and electrolyte effect • History and Physical Examination * Age >35 year * Prior MI or Structural Heart disease * Previous Palpitation favors SVT while first time palpitation after MI favors VT. * Do not let Symptoms Fool you * AV dissociation-- Cannon A wave Variable S1 Change in BP. * Termination with AV nodal Blocking agent favors SVT (remember rare case of VT) • EKG • QRS morphology SVT with aberrancy will have Typical RBBB or LBBB pattern Concordance R wave in precordial Leads either + or –(High specificity but low sensitivity about 20%) ## Remember AVART (1-6% of WCT) • QRS duration RBBB >140msec and LBBB >160msec. (be aware of Drug effect) occasionally VT can have relatively narrow (120-140mse) • QRS axis Northwest Axis favors VT. Axis change >40 degree compared to sinus Rhythm favors VT. LBBB with RAD Suggest VT and RBBB with normal Axis Suggests SVT Brugada Criteria for Differential Diagnosis of WCT • LBBB morphology during WCT V1R >40msec, R-S duration >60msec, notch on down stroke of S wave and R wave taller than that in Sinus Rhythm. V6any q wave in V6. • RBBB morphology During WCT V1 or V2 Monophagic R wave, R>r’, qR pattern V6 QR, QS, Monophagic R wave, rS. 55 YF with Recurrent palpitation and ICD Shock 21 YM presents with Palpitation and Presyncope 70 YM with Palpitation and persistent tachycardia • You only see what you look for and you only look for what you know! • Systematic approach • Understanding of common (and not-so-common) arrhythmias • Not all rhythm disorders produce symptoms • View the rhythm in the context of the patient’s overall condition: treat the patient, not the tracing